08.requestLayout和invalidate、postInvalidate
requestLayout 和 invalidate、postInvalidate
invalidate、postInvalidate
该方法递归调用父容器的 invalidateChildInParent 方法,直到调用 ViewRootImpl 的 invalidateChildInParent 方法,最终触发 ViewRootImpl 的 performTraversals,此时 mLayoutRequested 为 false,不会触发 onMeasure 和 onLayout 方法,会触发 onDraw 方法
postInvalidate 和 invalidate 功能一样,只是它能在非 UI 线程中调用
注意: 继承至 ViewGroup 的自定义控件中,invalidate 是默认不重新绘制子 view 的,有以下两种方法来触发重新绘制的过程:
- 在构造函数中调用
setWillNotDraw(false); - 给 ViewGroup 设置背景。调用
setBackground(drawable)。
ViewGroup 的 invalidate
一般的 ViewGroup 都是 SKIP_DRAW 的,所以都是走 dispatchDraw,dispatchDraw 的实现一般在 ViewGroup 里,就是调用子 view 的 draw,所以一般来说 ViewGroup 的 invalidate 就是对子 view 进行重绘(android.view.View#draw(android.graphics.Canvas, android.view.ViewGroup, long))
invalidate、postInvalidate 区别
- 对于 invalidate,就是从 view 开始一层层往上层调用,直到 ViewRootImpl,然后重新绘制一遍。
- 对于 postInvalidate,就是在 viewRootImpl 中给 handler 发送了一个请求重绘的消息,然后接着走 invalidate,只是这个起始是可以在非 UI 线程上进行。
需要注意的是,invalidate 和 postInvalidate 方法请求重绘 View,只会调用 draw 方法,如果 View 大小没有发生变化就不会再调用 layout,并且只绘制那些需要重绘的 View 的脏的 Rect,也就是谁调用,重绘谁。
子线程能不能 invalidate?
子线程能更新 ui 的情况
任何线程都可以更新 UI,也都有更新 UI 导致崩溃的可能;关键就是 view 被绘制到界面时候的线程(也就是最顶层 ViewRootImpl 被创建时候的线程)和进行 UI 更新时候的线程是不是同一个线程,如果不是就会报错
ViewRootImpl 未创建
Activity#onCreate/onResume 中可以直接在子线程更新 UI,此时 ViewRootImpl 还未创建,自然就不会 checkThread
在 ViewRootImpl 创建之前 invalidate 不受线程限制,Activity 的 onResume 后,ViewRootImpl 创建了
ViewRootImpl 创建
Android8.0 及以上 分情况
- 硬件加速可用,子线程可以更新 UI
- 硬件加速不可用,走软件绘制逻辑,子线程不能更新 UI
Android 8.0 及之后新增了 onDescendantInvalidated 方法,当开启硬件加速时,是可以在子线程调用 invalidate 方法而不报错的;Android 8.0 及之后关闭硬件加速之后不能在子线程调用 invalidate(),硬件加速效果默认开启,所以默认是可以在子线程调用的
Android8.0 一下 不能子线程更新 UI
Android8.0 之前不管是否开启了硬件加速,在子线程会报
Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.
其他情况
- skipInvalidate 了可以子线程更新 UI,view 不可见&&没有动画&&不是 ViewGroup
1
2
3
4
5
private boolean skipInvalidate() {
return (mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != VISIBLE && mCurrentAnimation == null &&
(!(mParent instanceof ViewGroup) ||
!((ViewGroup) mParent).isViewTransitioning(this));
}
- 走的软件绘制,invalidateChildInParent 返回 null,不会走到 ViewRootImpl 也可以;parent#invalidate 了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(final int[] location, final Rect dirty) {
if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID)) != 0) { // 当parent调用了invalidate时该条件为false
return mParent;
}
return null;
}
mBinding.btTtt.bt3.setOnClickListener {
(mBinding.tvTouchView.parent as View).invalidate()
thread {
BaseLog.d("thread id:${Thread.currentThread().id}")
mBinding.tvTouchView.invalidate()
}
}
子线程更新 UI 可能的问题
- UI 假死,UI 混乱
子线程能更新 UI 源码分析
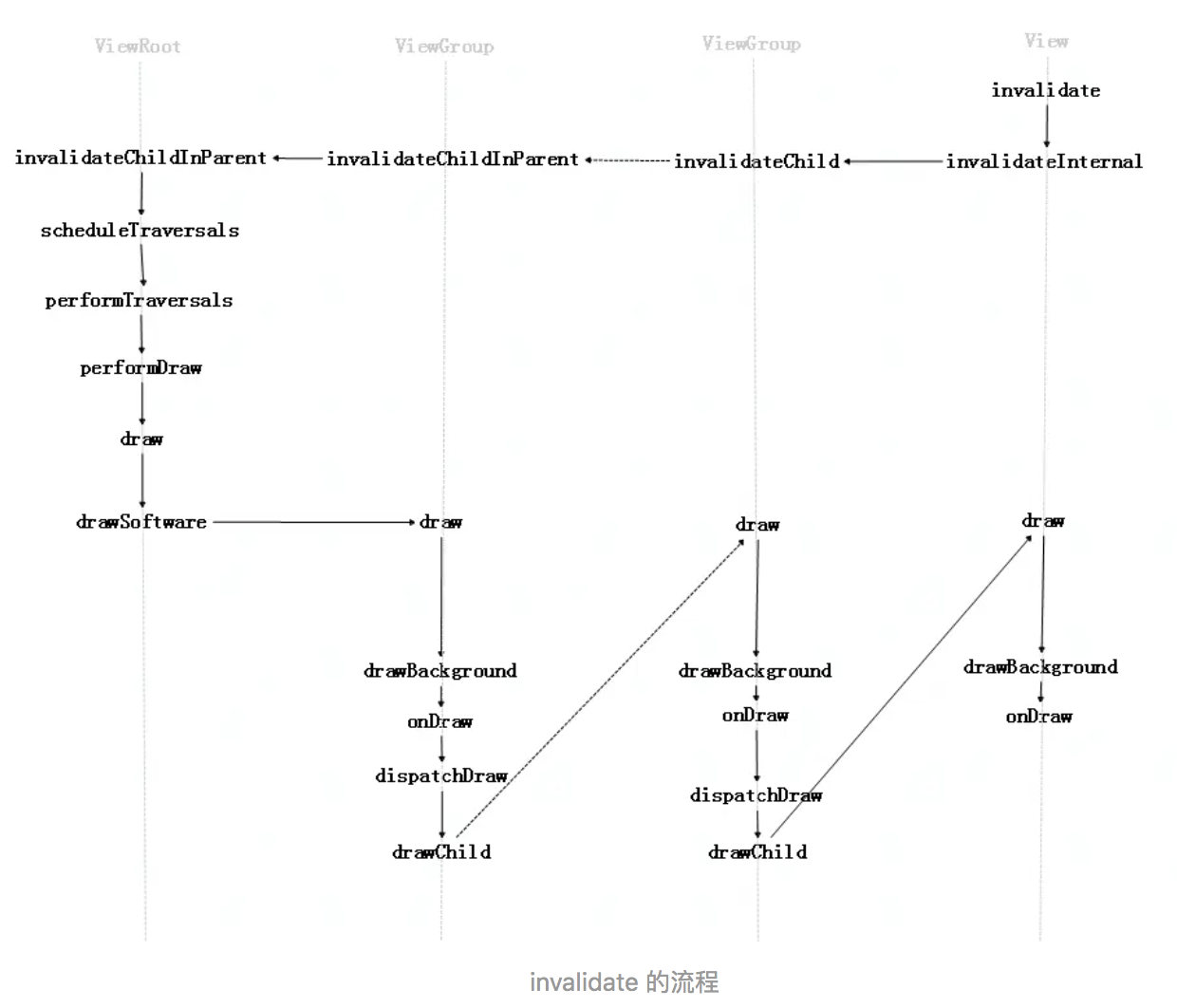
下面是源码分析,invalidate 流程:
1
2
3
4
android.view.View#invalidate() ->
android.view.View#invalidate(boolean) ->
android.view.View#invalidateInternal ->
android.view.ViewGroup#invalidateChild ->
看看 ViewGroup#ViewGroup
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
// View
public final void invalidateChild(View child, final Rect dirty) {
final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
if (attachInfo != null && attachInfo.mHardwareAccelerated) {
// HW accelerated fast path
onDescendantInvalidated(child, child); // 1
return;
}
do {
// ...
parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty); // 2
if (view != null) {
// Account for transform on current parent
Matrix m = view.getMatrix();
if (!m.isIdentity()) {
RectF boundingRect = attachInfo.mTmpTransformRect;
boundingRect.set(dirty);
m.mapRect(boundingRect);
dirty.set((int) Math.floor(boundingRect.left),
(int) Math.floor(boundingRect.top),
(int) Math.ceil(boundingRect.right),
(int) Math.ceil(boundingRect.bottom));
}
}
} while (parent != null);
}
#1 部分是开启了硬件加速,#2 步是没有开启硬件加速。
先看开启了硬件加速,调用了 ViewGroup#onDescendantInvalidated:
1
2
3
4
5
6
// ViewGroup
public void onDescendantInvalidated(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target) {
if (mParent != null) {
mParent.onDescendantInvalidated(this, target);
}
}
最终走到了 ViewRootImpl#onDescendantInvalidated:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public void onDescendantInvalidated(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View descendant) {
// TODO: Re-enable after camera is fixed or consider targetSdk checking this
// checkThread();
if ((descendant.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION) != 0) {
mIsAnimating = true;
}
invalidate();
}
void invalidate() {
mDirty.set(0, 0, mWidth, mHeight);
if (!mWillDrawSoon) {
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
而 ViewRootImpl.invalidate() 并没有调用 checkThread(),所以是可以在子线程调用 invalidate() 的。
而如果没有开启硬件加速,调用的是 ViewGroup#invalidateChildInParent:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// ViewGroup
public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(final int[] location, final Rect dirty) {
if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID)) != 0) { // 当parent调用了invalidate时该条件为false
return mParent;
}
return null;
}
ViewGroup#invalidateChildInParent 如果返回了 null 就不会走到 ViewRootImpl 了,也就可以在子线程更新 ui 了,那么什么时候会返回 null?
parent 调用了 invalidate
ViewGroup#invalidateChildInParent 如果返回了 mParent,最终走到了 ViewRootImpl#invalidateChildInParent:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// ViewRootImpl Android29
public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(int[] location, Rect dirty) {
checkThread();
if (dirty == null) {
invalidate();
return null;
} else if (dirty.isEmpty() && !mIsAnimating) {
return null;
}
// ...
invalidateRectOnScreen(dirty);
return null;
}
可以看到 ViewRootImpl#invalidateChildInParent 该方法会调用 checkTread(),子线程调用 invalidate 会报 Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.
- 非 UI 线程能调用 View.invalidate()?
https://www.jianshu.com/p/753441fcbad2
requestLayout
- 该方法会递归调用父容器的 requestLayout 方法,直到触发 ViewRootImpl 的 requestLayout→performTraversals() 方法,此时 mLayoutRequested 为 true,该 View 的所有 parent 都是触发 onMeasure 和 onLayout
- requestLayout 如果没有改变 l,t,r,b,那就不会触发 onDraw;但是如果这次刷新是在动画里,mDirty 非空,就会导致 onDraw
相关问题
invalidate 会不会导致 onMeasure 和 onLayout 被调用呢?
invalidate 中,在 performTraversals 方法中,mLayoutRequested 为 false,所有 onMeasure 和 onLayout 都不会被调用。
为什么 TextView 的 setText 改变大小时依次调用 requestLayout 和 invalidate,按说只需要 requestLayout 不就够了吗
TextView 的源码里也经常看到 invalidate 和 requestLayout 一起用的情况
invalidate 会导致 ViewRootImpl 的 peformDraw 被调用,那怎么保证不绘制所有的 view,而只绘制某个 view 呢?
requestLayout 如果没有改变 l,t,r,b,那就不会触发 onDraw,通过 Button 触发一个 view 的 requestLayout,发现居然触发了 onDraw
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior"
tools:showIn="@layout/activity_main"
tools:context="com.fish.a1.MainActivity">
<com.fish.a1.ATextView
android:id="@+id/b0"
android:text="Hello World!"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<Button
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/b0"
android:id="@+id/b1"
android:text="Hello World!"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</RelativeLayout>
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
findViewById(R.id.b1).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
View v1=findViewById(R.id.b0);
v1.requestLayout();
}
})
Button 按下首先是出现按下效果,然后触发 click 事件,click 事件是 post 出去的,不是立刻发生的。所以 Button 按下,首先出现 press 效果,然后触发 click 事件,会导致 2 轮 doTraversal。
- 第一轮 doTraversal
Button 按下会触发动画,导致 ViewRootImpl#invalidate,mDirty 会被设置为全屏,并且触发一次 scheduleTraversals
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//ViewRootImpl#invalidate
void invalidate() {
mDirty.set(0, 0, mWidth, mHeight);
if (!mWillDrawSoon) {
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
然后 performTraversals 被触发,内调用 performDraw,里面调用 draw,里面先把 mDirty 清空,然后调 mAttachInfo.mHardwareRenderer.draw(mView, mAttachInfo, this); 里面调 updateRootDisplayList,里面调 updateViewTreeDisplayList,简单的说就是 performDraw 里面调用了 ThreadedRenderer#updateViewTreeDisplayList(View v),此时 v 是 DecorView,看下面的代码,此时 DecorView 的 PFLAG_INVALIDATED 没有被设置,所以根本不会被重绘。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
// View.ThreadedRenderer#updateViewTreeDisplayList
private void updateViewTreeDisplayList(View view) {
view.mPrivateFlags |= View.PFLAG_DRAWN;
view.mRecreateDisplayList = (view.mPrivateFlags & View.PFLAG_INVALIDATED)
== View.PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
view.mPrivateFlags &= ~View.PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
view.updateDisplayListIfDirty();
view.mRecreateDisplayList = false;
}
- 第二轮 doTraversal
此时触发 click 事件,调用 v1.requestLayout();,会把 DecorView 的 PFLAG_INVALIDATED 标志位给设置起来,并且触发 performTraversals。
此时 Button 动画还在刷新,所以又调用 ViewRootImpl#invalidate 把 mDirty 给设置成全屏,并且触发 performTraversals。
动画要的 performTraversals 和刷新要的 performTraversals 会合并成一个 doTraversal。内调用 performDraw,里面调用 draw,里面先把 mDirty 清空,然后调 mAttachInfo.mHardwareRenderer.draw(mView, mAttachInfo, this); 里面调 updateRootDisplayList,里面调 updateViewTreeDisplayList,简单的说就是 performDraw 里面调用了 ThreadedRenderer#updateViewTreeDisplayList(View v)
,此时 v 是 DecorView,注意此时 DecorView 的 PFLAG_INVALIDATED 标志位已经被设置了,所以会重绘,所以 ATextView 的 ondraw 会被调用。
如果我把 Button 改为 TextView,那么按下 TextView 就不会触发 ATextView 的 ondraw 了,因为没有按下动画。
源码分析
1
2
3
4
5
// View Androi29
static final int PFLAG_DRAWN = 0x00000020; // invalidate时会去除PFLAG_DRAWN,默认添加该flag
static final int PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID = 0x00008000; // invalidate时会去除PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID,默认添加该flag
static final int PFLAG_INVALIDATED = 0x80000000; // invalidate时添加PFLAG_INVALIDATED,添加了该flag会调用draw重绘
invaliate 源码分析
View#invalidate
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
// View Android29
// 如果View visible,会在未来某个时刻调用onDraw重绘View;必须在UI线程中调用,非UI线程中调用用postInvalidate
public void invalidate() {
invalidate(true);
}
public void invalidate(boolean invalidateCache) { // invalidateCache设置为true全更新;false如果view的尺寸未变就会跳过
invalidateInternal(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop, invalidateCache, true);
}
void invalidateInternal(int l, int t, int r, int b, boolean invalidateCache,
boolean fullInvalidate) {
if (mGhostView != null) {
mGhostView.invalidate(true);
return;
}
if (skipInvalidate()) {
return;
}
// Reset content capture caches
mCachedContentCaptureSession = null;
if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)) == (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)
|| (invalidateCache && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) == PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID)
|| (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_INVALIDATED) != PFLAG_INVALIDATED
|| (fullInvalidate && isOpaque() != mLastIsOpaque)) {
if (fullInvalidate) { // invalidate()方法这里为true
mLastIsOpaque = isOpaque();
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWN; // 去除PFLAG_DRAWN
}
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DIRTY; // 添加PFLAG_DIRTY
if (invalidateCache) { // invalidate()方法这里为true
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED; // 添加PFLAG_INVALIDATED
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID; // 去除PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID
}
// Propagate the damage rectangle to the parent view.
final AttachInfo ai = mAttachInfo;
final ViewParent p = mParent;
if (p != null && ai != null && l < r && t < b) {
final Rect damage = ai.mTmpInvalRect;
damage.set(l, t, r, b);
p.invalidateChild(this, damage); // 调用parent的invalidateChild
}
// ...
}
}
private boolean skipInvalidate() {
return (mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != VISIBLE && mCurrentAnimation == null &&
(!(mParent instanceof ViewGroup) ||
!((ViewGroup) mParent).isViewTransitioning(this));
}
View 的 invalidate 会调到 invalidateInternal,设置 flag 位 PFLAG_INVALIDATED,取消 flag 位 PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;并调用 ViewGroup 的 invalidateChild
ViewGroup#invalidateChild
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
// ViewGroup Android29
protected ViewParent mParent;
public final void invalidateChild(View child, final Rect dirty) {
final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
if (attachInfo != null && attachInfo.mHardwareAccelerated) { // 硬件加速
// HW accelerated fast path
onDescendantInvalidated(child, child);
return;
}
ViewParent parent = this;
// 如果child在做动画
final boolean drawAnimation = (child.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION) != 0;
do {
View view = null;
if (parent instanceof View) {
view = (View) parent;
}
if (drawAnimation) {
if (view != null) {
view.mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION; // 子view做动画,给自身也添加这个flag
} else if (parent instanceof ViewRootImpl) {
((ViewRootImpl) parent).mIsAnimating = true;
}
}
// ...
parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty);
// ...
} while (parent != null); // 直到parent为null;ViewGroup的invalidateChildInParent一般都不为null,只有ViewRootImpl才返回null
}
public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(final int[] location, final Rect dirty) {
if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID)) != 0) { // 只要设置了PFLAG_DRAWN或PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID,就不为null;而PFLAG_DRAWN默认添加了
return mParent;
}
return null;
}
- 硬件加速的话调用 onDescendantInvalidated,递归调用,直到 ViewRootImpl 的 onDescendantInvalidated;
- 未开启硬件加速,invalidateChild 内部有个 do while 循环,不停调用父 view 的 invalidateChildInParent,一直到调用 ViewRootImpl 的 invalidateChildInParent。
ViewRootImpl#onDescendantInvalidated/invalidateChildInParent
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
// ViewRootImpl Android29
public boolean mIsAnimating; // 由PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION位标记
public class ViewRootImpl {
// 硬件加速
public void onDescendantInvalidated(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View descendant) {
// TODO: Re-enable after camera is fixed or consider targetSdk checking this
// checkThread();
if ((descendant.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION) != 0) {
mIsAnimating = true;
}
invalidate();
}
@UnsupportedAppUsage
void invalidate() {
mDirty.set(0, 0, mWidth, mHeight);
if (!mWillDrawSoon) {
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
// 未硬件加速
public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(int[] location, Rect dirty) { // ViewRootImpl的都返回null
checkThread();
if (DEBUG_DRAW) Log.v(mTag, "Invalidate child: " + dirty);
if (dirty == null) {
invalidate();
return null;
} else if (dirty.isEmpty() && !mIsAnimating) {
return null;
}
// ...
invalidateRectOnScreen(dirty);
return null;
}
private void invalidateRectOnScreen(Rect dirty) {
final Rect localDirty = mDirty;
// Add the new dirty rect to the current one
localDirty.union(dirty.left, dirty.top, dirty.right, dirty.bottom);
// Intersect with the bounds of the window to skip
// updates that lie outside of the visible region
final float appScale = mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale;
final boolean intersected = localDirty.intersect(0, 0,
(int) (mWidth * appScale + 0.5f), (int) (mHeight * appScale + 0.5f));
if (!intersected) {
localDirty.setEmpty();
}
if (!mWillDrawSoon && (intersected || mIsAnimating)) { // mWillDrawSoon默认false,在动画mIsAnimating=true
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
}
在 ViewRootImpl 中,不管是否开启硬件加速,scheduleTraversals 都会被调用。
ViewRootImpl#scheduleTraversals
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
// ViewRootImpl
final class TraversalRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
doTraversal();
}
}
final TraversalRunnable mTraversalRunnable = new TraversalRunnable();
void scheduleTraversals() {
if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = true;
mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
mChoreographer.postCallback(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) {
scheduleConsumeBatchedInput();
}
notifyRendererOfFramePending();
pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();
}
}
void doTraversal() {
if (mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = false;
mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().removeSyncBarrier(mTraversalBarrier);
// ...
performTraversals();
// ...
}
}
private void performTraversals() {
// ...
performDraw();
// ...
}
private void performDraw() {
boolean canUseAsync = draw(fullRedrawNeeded);
}
private boolean draw(boolean fullRedrawNeeded) {
boolean animating = mScroller != null && mScroller.computeScrollOffset();
final float appScale = mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale;
final boolean scalingRequired = mAttachInfo.mScalingRequired;
if (fullRedrawNeeded) {
dirty.set(0, 0, (int) (mWidth * appScale + 0.5f), (int) (mHeight * appScale + 0.5f));
}
if (!dirty.isEmpty() || mIsAnimating || accessibilityFocusDirty) {
if (mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer != null && mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.isEnabled()) { // 硬件加速并开启
// Draw with hardware renderer.
mIsAnimating = false;
mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.draw(mView, mAttachInfo, this);
} else {
if (!drawSoftware(surface, mAttachInfo, xOffset, yOffset, scalingRequired, dirty, surfaceInsets)) { // mView.draw(canvas);
return false;
}
}
}
if (animating) {
mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
调用链:ViewRootImpl#scheduleTraversals → TraversalRunnable → doTraversal → performTraversals
performTraversals 一般都会调用 performDraw 进而调 draw,在 draw 内,如果发现 mDirty 非空就会调:
- 硬件加速且开启 mAttachInfo.mHardwareRenderer.draw(mView, mAttachInfo, this);
- 硬件加速未设置会未开启,drawSoftware(),最终调用 View#draw(Canvas)
ThreadedRenderer#draw(View view, AttachInfo attachInfo, DrawCallbacks callbacks)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// ThreadedRenderer Android29
void draw(View view, AttachInfo attachInfo, DrawCallbacks callbacks) {
updateRootDisplayList(view, callbacks);
}
private void updateRootDisplayList(View view, DrawCallbacks callbacks) {
updateViewTreeDisplayList(view);
}
private void updateViewTreeDisplayList(View view) {
view.mPrivateFlags |= View.PFLAG_DRAWN; // 添加PFLAG_DRAWN标记
view.mRecreateDisplayList = (view.mPrivateFlags & View.PFLAG_INVALIDATED)
== View.PFLAG_INVALIDATED; // 设置mRecreateDisplayList,如果有PFLAG_INVALIDATED,为true;我们在invalidate时会添加该PFLAG_INVALIDATED,所以这里会是true
view.mPrivateFlags &= ~View.PFLAG_INVALIDATED; // 重置PFLAG_INVALIDATED
view.updateDisplayListIfDirty();
view.mRecreateDisplayList = false; // 重置mRecreateDisplayList
}
此时 view 是 DecorView,DecorView 的 updateViewTreeDisplayList 会调 updateDisplayListIfDirty,现在看 View#updateDisplayListIfDirty
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
public RenderNode updateDisplayListIfDirty() {
// ...
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) == 0
|| !renderNode.hasDisplayList()
|| (mRecreateDisplayList)) {
// Don't need to recreate the display list, just need to tell our
// children to restore/recreate theirs
if (renderNode.hasDisplayList()
&& !mRecreateDisplayList) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK;
dispatchGetDisplayList(); // 分发是否绘制
return renderNode; // no work needed
}
// If we got here, we're recreating it. Mark it as such to ensure that
// we copy in child display lists into ours in drawChild()
mRecreateDisplayList = true;
// ...
try {
if (layerType == LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE) {
buildDrawingCache(true);
Bitmap cache = getDrawingCache(true);
if (cache != null) {
canvas.drawBitmap(cache, 0, 0, mLayerPaint);
}
} else {
computeScroll();
canvas.translate(-mScrollX, -mScrollY);
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK;
// Fast path for layouts with no backgrounds
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) == PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) { // 如果是ViewGroup,那么会添加这个标记,设置setWillNotDraw(false)取消该标记,就会调用draw
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// ...
} else { // 如果是View或调用了setWillNotDraw(false),那么走到这里draw
draw(canvas);
}
}
}
// ...
} else {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK;
}
return renderNode;
}
updateDisplayListIfDirty 调用 dispatchGetDisplayList
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
// ViewGroup Android29
protected void dispatchGetDisplayList() {
final int count = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = children[i];
if (((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null)) {
recreateChildDisplayList(child);
}
}
final int transientCount = mTransientViews == null ? 0 : mTransientIndices.size();
for (int i = 0; i < transientCount; ++i) {
View child = mTransientViews.get(i);
if (((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null)) {
recreateChildDisplayList(child);
}
}
if (mOverlay != null) {
View overlayView = mOverlay.getOverlayView();
recreateChildDisplayList(overlayView);
}
if (mDisappearingChildren != null) {
final ArrayList<View> disappearingChildren = mDisappearingChildren;
final int disappearingCount = disappearingChildren.size();
for (int i = 0; i < disappearingCount; ++i) {
final View child = disappearingChildren.get(i);
recreateChildDisplayList(child);
}
}
}
private void recreateChildDisplayList(View child) {
child.mRecreateDisplayList = (child.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_INVALIDATED) != 0;
child.mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
child.updateDisplayListIfDirty();
child.mRecreateDisplayList = false;
}
dispatchGetDisplayList 的代码很简单,循环调用 recreateChildDisplayList,让子 view recreate display。
recreateChildDisplayList,内部给 mRecreateDisplayList 赋值,然后调用 updateDisplayListIfDirty,此时对象变成了 DecorView 的 child
requestLayout 源码分析
Ref
- 从源码看 invalidate 和 requestLayout 的区别
https://blog.csdn.net/litefish/article/details/52859300 - invalidate 和 requestLayout 流程认识
https://cruise1008.github.io/2016/04/30/how-does-invalidate-and-requestLayout-work/