05.measure测量
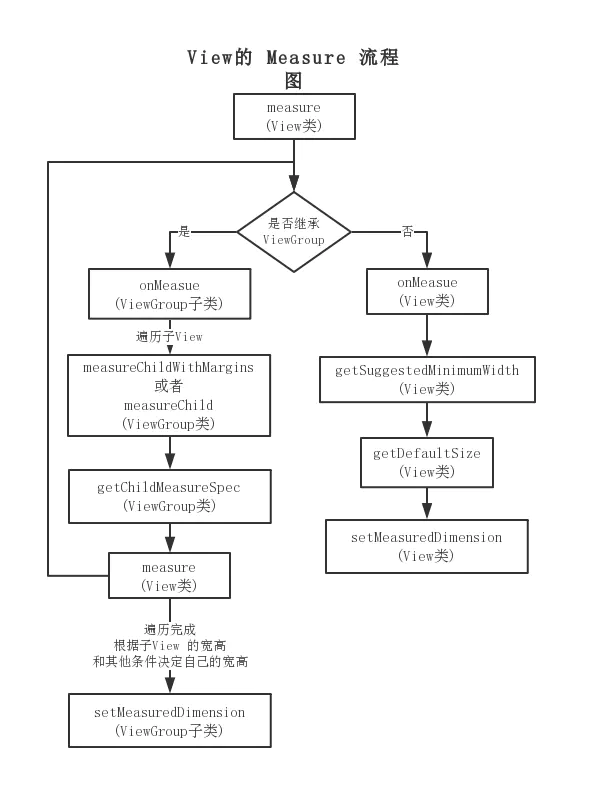
measure 流程
measure 前身流程 ViewRootImpl
ViewRootImpl 充当的是 View 和 window 之间的纽带。在 startActivity 之后,经过与 ActivityManagerService 的 IPC 交互,会在 ActivityThread 的 handleResumeActivity 方法中执行到 getWindow().addView,就是将根布局 Decor 添加到 window 中以显示。getWindow 会以 WindowManagerGloble 来执行 addView 方法,其中就会创建 ViewRootImpl 实例并调用其 setView 方法传入 Decor 布局,在 setView 中会执行到 performTranvesals 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// Activity Android29
// 在Activity的makeVisible调用WindowManager.addView
void makeVisible() {
if (!mWindowAdded) {
ViewManager wm = getWindowManager();
wm.addView(mDecor, getWindow().getAttributes());
mWindowAdded = true;
}
mDecor.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
WindowManager 的实现类是 WindowManagerImpl,最终调用的是 WindowManagerGlobal 的 addView,WindowManagerGlobal 是个单例
1
2
3
4
5
6
// WindowManagerImpl#addView
private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplay(), mParentWindow);
}
WindowManagerGlobal 的 addView
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params, Display display, Window parentWindow) {
ViewRootImpl root;
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
throw e;
}
}
最终调用 ViewRootImpl 的 setView
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
// ViewRootImpl Android29
View mView; // 如果是Activity,那么是DecorView
// 在WindowManagerGlobal#addView初始化ViewRootImpl并调用setView传递view进来,
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
mView = view;
// If the application owns the surface, don't enable hardware acceleration
if (mSurfaceHolder == null) {
// While this is supposed to enable only, it can effectively disable
// the acceleration too.
enableHardwareAcceleration(attrs); // 根据设置开启硬件加速
}
}
}
}
private void performTraversals() {
// ...
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
// ...
}
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
如果是 Activity,这个 mView,就是 DecorView,最终调用到 FrameLayout 的 measure 中去了,即 View#measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
DecorView 的 measureSpec 计算逻辑
如果所有子控件的 measureSpec 都是父控件结合自身的 measureSpec 和子 View 的 LayoutParams 来生成的。那么作为视图的顶级父类 DecorView 怎么获取自己的 measureSpec 呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
// 通过Window的root view的layout params设置计算出MeasureSpec
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
windowSize 是 widow 的宽高大小,所以我们可以看出 DecorView 的 measureSpec 是根据 window 的宽高大小和自身的 LayoutParams 来生成的
Activity 的 PhoneWindow 的 Window.LayoutParams 的 width 和 height 都是 MATCH_PARENT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// WindowManager.LayoutParams Android29
public class LayoutParams {
public LayoutParams() {
super(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
type = TYPE_APPLICATION;
format = PixelFormat.OPAQUE;
}
}
什么时候走 onMeasure
- 自身调用 requestLayout,一定走 onMeasure;其他 view 不一定,取决于有没有改变了大小
- setLayoutParams,会走 requestLayout
- setVisible,Gone 到 Visible 会走 requestLayout
View#measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
- 整个应用量算的起点是 ViewRootImpl 类,从它开始依次对子 View 进行量算,如果子 View 是一个 ViewGroup,那么又会遍历该 ViewGroup 的子 View 依次进行量算。也就是说,量算会从 View 树的根结点,纵向递归进行,从而实现自上而下对 View 树进行量算,直至完成对叶子节点 View 的量算。
- View 的父控件 ViewGroup 会调用 View 的 measure 方法,ViewGroup 会将一些宽度和高度的限制条件传递给 View 的 measure 方法
- 在 View 的 measure 方法会首先从成员变量中读取以前缓存过的量算结果,如果能找到该缓存值,那么就基本完事了,如果没有找到缓存值,那么 measure 方法会执行 onMeasure 回调方法,measure 方法会将上述的宽度和高度的限制条件依次传递给 onMeasure 方法。onMeasure 方法会完成具体的量算工作,并将量算的结果通过调用 View 的 setMeasuredDimension 方法保存到 View 的成员变量 mMeasuredWidth 和 mMeasuredHeight 中。
- 量算完成之后,View 的父控件就可以通过调用 getMeasuredWidth、getMeasuredState、getMeasuredWidthAndState 这三个方法获取 View 的量算结果。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
// View Android29
private LongSparseLongArray mMeasureCache;
public View() {
sAlwaysRemeasureExactly = targetSdkVersion <= Build.VERSION_CODES.M;
// 一些老的App希望在一次layou过程中,onMeasure方法总是被调用,也就是说如果targetSdkVersion的API版本低于KITKAT,即API level小于19,那么sIgnoreMeasureCache为true
sIgnoreMeasureCache = targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT;
}
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this); // 首先判断当前View的layoutMode是不是特例LAYOUT_MODE_OPTICAL_BOUNDS
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int oWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int oHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(widthMeasureSpec, optical ? -oWidth : oWidth);
heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(heightMeasureSpec, optical ? -oHeight : oHeight);
}
// 根据widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec计算key值,我们在下面用key值作为键,缓存我们量算的结果。key为当前widthMeasureSpec左移32位,相当于32~63位保存了widthMeasureSpec;heightMeasureSpec取低32位,也可以key=widthMeasureSpec(高32位)+heightMeasureSpec(低32位)
long key = (long) widthMeasureSpec << 32 | (long) heightMeasureSpec & 0xffffffffL;
// mMeasureCache是LongSparseLongArray类型的成员变量,其缓存着View在不同widthMeasureSpec、heightMeasureSpec下量算过的结果;如果mMeasureCache为空,我们就新new一个对象赋值给mMeasureCache
if (mMeasureCache == null) mMeasureCache = new LongSparseLongArray(2);
// mPrivateFlags是一个Int类型的值,其记录了View的各种状态位,如果(mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT,那么表示当前View需要强制进行layout(比如执行了View的forceLayout方法),foreceLayout为true
final boolean forceLayout = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
// mOldWidthMeasureSpec和mOldHeightMeasureSpec分别表示上次对View进行量算时的widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec,如果其中width或height有一个不同specChanged就为true
final boolean specChanged = widthMeasureSpec != mOldWidthMeasureSpec
|| heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec;
// 如果widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec有一个mode不是EXACTLY,isSpecExactly为false
final boolean isSpecExactly = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY
&& MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
// 如果已经测量的width/height和传递进来的size有一个不相等,matchesSpecSize为false
final boolean matchesSpecSize = getMeasuredWidth() == MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)
&& getMeasuredHeight() == MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// sAlwaysRemeasureExactly,API<=23为true,否则为false
// 需要layout条件:新旧measureSpce其中一个不相等且(API<=23 或measureSpecMode有一个不是EXACTLY 或已测量的大小和即将测量的大小有一个不一致)
final boolean needsLayout = specChanged
&& (sAlwaysRemeasureExactly || !isSpecExactly || !matchesSpecSize);
if (forceLayout || needsLayout) {
// 通过按位操作,重置View的状态mPrivateFlags,将其标记为未量算状态
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
// 对阿拉伯语、希伯来语等从右到左书写、布局的语言进行特殊处理
resolveRtlPropertiesIfNeeded();
// 在View真正进行量算之前,View还想进一步确认能不能从已有的缓存mMeasureCache中读取缓存过的量算结果
// 如果是强制layout导致的量算,那么将cacheIndex设置为-1,即不从缓存中读取量算结果
// 如果不是强制layout导致的量算,那么我们就用上面根据measureSpec计算出来的key值作为缓存索引cacheIndex。
int cacheIndex = forceLayout ? -1 : mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key);
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) { // 不读取缓存 或 API小于19,重新onMeasure
// 表示我们没有从缓存中找到量算过的尺寸或者是sIgnoreMeasureCache为true导致我们要忽略缓存结果,此处调用onMeasure方法,并把尺寸限制条件widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec传入进去,onMeasure方法中将会进行实际的量算工作,并把量算的结果保存到成员变量中
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); // 执行 onMeasure 方法
// onMeasure执行完后,通过位操作,重置View的状态mPrivateFlags,将其标记为在layout之前不必再进行量算的状态
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
// 如果运行到此处,那么表示当前的条件允许View从缓存成员变量mMeasureCache中读取量算过的结果,用上面得到的cacheIndex从缓存mMeasureCache中取出值,不必在调用onMeasure方法进行量算了
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
// 一旦我们从缓存中读到值,转换成可用的,我们就可以调用setMeasuredDimensionRaw方法将当前量算的结果到成员变量中
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
// 如果我们自定义的View重写了onMeasure方法,但是没有调用setMeasuredDimension()方法,
// 那么此处就会抛出异常,提醒开发者在onMeasure方法中调用setMeasuredDimension()方法
// Android是如何知道我们有没有在onMeasure方法中调用setMeasuredDimension()方法的呢?
// 方法很简单,还是通过解析状态位mPrivateFlags。
// setMeasuredDimension()方法中会将mPrivateFlags设置为PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET状态,即已量算状态,
// 此处就检查mPrivateFlags是否含有PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET状态即可判断setMeasuredDimension是否被调用
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) {
throw new IllegalStateException("View with id " + getId() + ": "
+ getClass().getName() + "#onMeasure() did not set the"
+ " measured dimension by calling"
+ " setMeasuredDimension()");
}
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
// mOldWidthMeasureSpec和mOldHeightMeasureSpec保存着最近一次量算时的MeasureSpec,在量算完成后将这次新传入的MeasureSpec赋值给它们
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;
// 最后用上面计算出的key作为键,量算结果作为值,将该键值对放入成员变量mMeasureCache中;将当前测量的宽左移32位高取低32位保存到mMeasureCache
mMeasureCache.put(key, ((long) mMeasuredWidth) << 32 | (long) mMeasuredHeight & 0xffffffffL);
}
- forceLayout 为 true,一定执行 onMeasure
- forceLayout 为 false,needsLayout 为 true,还要看 mMeasureCache 有没有缓存测量的结果,没有就走 onMeasure,有的话就取出来
- 将当前测量的结果或取缓存的宽高结果存到 mMeasureCache 中去
View&ViewGroup 的测量
View 的测量
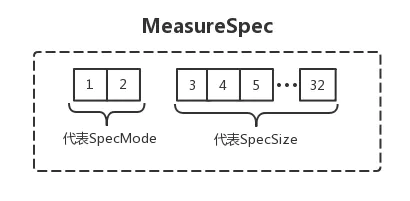
MeasureSpec
SpecMode 和 SpecSizwe
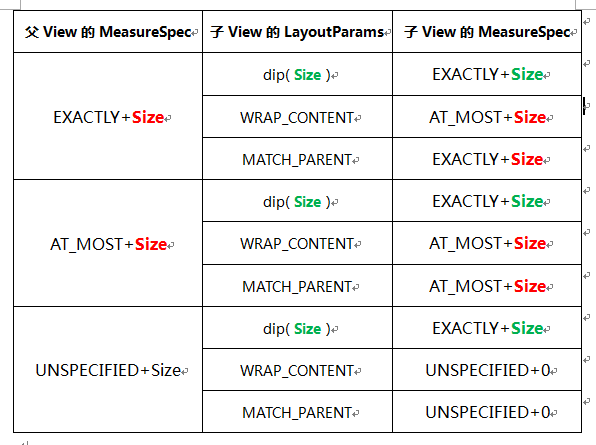
MeasureSpec 是一个 32bit 的 int 值,其中高 2 位为测量模式 SpecMode,低 30 位为测量的大小 SpecSize,在计算中使用位运算为了提高并优化效率。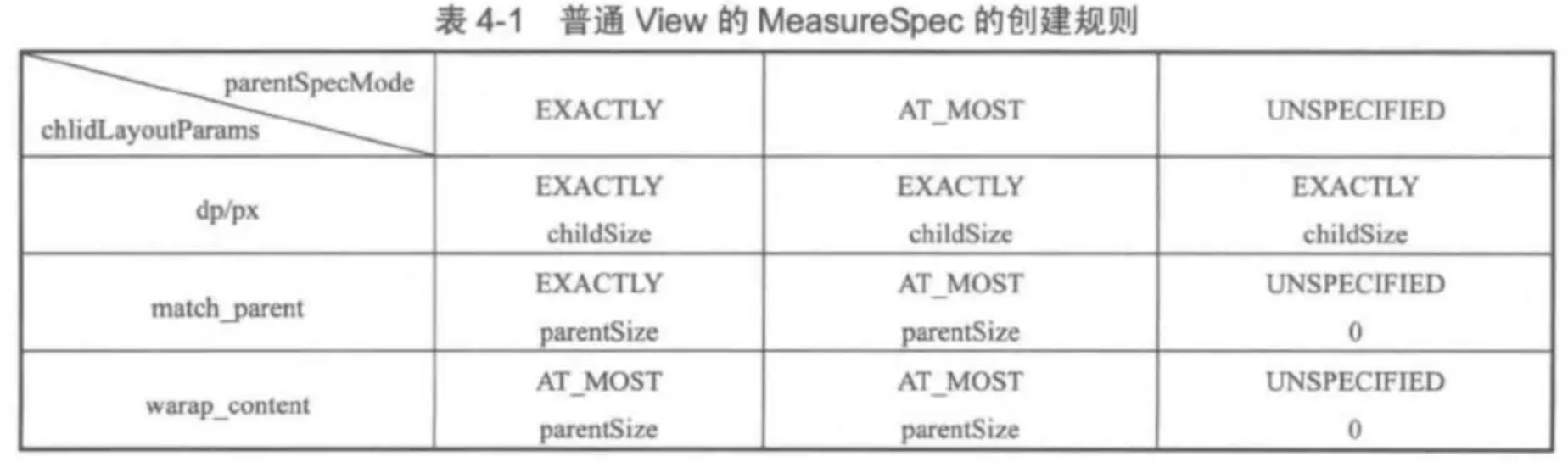
SpecMode 分类
测量模式分为 3 种:
- EXACTLY
精确模式,当我们将控件的layout_width/layout_height属性指定为具体的数值或者指定为 match_parent 时,系统使用的就是该模式。 - AT_MOST
最大值模式,当控件的layout_width/layout_height属性指定为 wrap_content 时,控件的大小一般随着控件的子空间或者内容的变化而变化,此时控件的尺寸只要不超过父控件允许的最大尺寸即可。 - UNSPECIFIED
父容器对当前 View 没有任何显示,子 View 可以取任意大小。一般用在系统内部,比如:Scrollview、ListView。。ScrollView 的子 View 的 height 为这个 mode
MeasureSpec 是 View 的测量规则。通常父控件要测量子控件的时候,会传给子控件 widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 这两个 int 类型的值。
计算
1
2
3
4
5
6
//将 Size 和 mode 组合成一个 int 值
int measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(size,mode);
//获取 size 大小
int size = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
//获取 mode 类型
int mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
View#onMeasure()
当 View 在 measure 方法中发现不得不进行实际的量算工作时,将会调用 onMeasure 方法,并且将尺寸限制条件 widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 作为参数传递给 onMeasure 方法。View 的 onMeasure 方法不是空方法,它提供了一个默认的具体实现。
1
2
3
4
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
onMeasure 方法详解
- 参数 1:widthMeasureSpec parent 所期望的值, 根据 parent 根据自身的 MeasureSpec+Padding 及 View 本身的 LayoutParams 共同决定的值 (xml 配置)
- 参数 2:heightMeasureSpec 同 widthMeasureSpec
onMeasure(int ,int)方法由measure(int, int)调用;- 约定:当重写了 onMeasure() 方法,必须调用
setMeasuredDimension(int, int)来保存 measure 的 width 和 height,如果没有做,那么会抛出IllegalStateException - onMeasure 默认测量策略是 background size,子类应该重写该方法提供更好的根据内容的测量策略
- onMeasure 被重写了,要保证 view 的测量的 width 和 height,不小于
getSuggestedMinimumWidth()和getSuggestedMinimumHeight()提供的值
widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 值是根据子 View 的布局参数(LayoutParams)和父容器的 MeasureSpec 值计算得来的,具
体计算逻辑封装在 getChildMeasureSpec() 里
getSuggestedMinimumWidth() 和 getSuggestedMinimumHeight() 返回 View 推荐的最小宽/高度
1
2
3
4
5
6
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
protected int getSuggestedMinimumHeight() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinHeight : max(mMinHeight, mBackground.getMinimumHeight());
}
- 如果 background 为 null,那么为 mMinWidth/mMinHeight(xml 中设置的 android:minWidth 和 android:minHeight)
- background 不为 null,background 的最小值和 mMinWidth/mMinHeight 中的大值,background 不能是 color
mMinWidth 和 mMinHeight 由 xml 中的 android:minWidth 和 android:minHeight 或
setMinimumWidth/Height()配置
int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size; // size表示的是View想要的尺寸信息,比如最小宽度或最小高度
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); // 从measureSpec中解析出specMode信息
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); // 从measureSpec中解析出specSize信息,不要将specSize与上面的size变量搞混
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: // 如果mode是UNSPECIFIED,表示View的父ViewGroup没有给View在尺寸上设置限制条件
result = size; // View直接用自己想要的尺寸size作为量算的结果
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize; //此处mode是AT_MOST或EXACTLY时,View就用其父ViewGroup指定的尺寸作为量算的结果
break;
}
return result;
}
- 如果 parent 期望的 mode 为 UNSPECIFIED,那么 View 的大小为 getSuggestedMinimumWidth() 和 getSuggestedMinimumHeight()
- 如果 parent 期望的 mode 为 AT_MOST 或 EXACTLY,那么 View 的大小为父容器给的尺寸 measureSpecSize
View 类默认的
onMeasure()方法只支持EXACTLY模式,如果自定义控件的时候不重写onMeasure()方法,就只能使用EXACTLY模式。控件可以响应你指定的具体宽高值或者 match_parent 属性。但是不支持 wrap_content 属性,必须要重写onMeasure()方法来指定 wrap_content 时的大小。
setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight)
必须由 onMeasure(int, int) 调用来保存测量的宽高
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// View
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) { // layoutMode是LAYOUT_MODE_OPTICAL_BOUNDS的特殊情况
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth;
measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight;
}
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
private void setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
// 将量算完成的宽度measuredWidth保存到View的成员变量mMeasuredWidth中
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
// 将量算完成的高度measuredHeight保存到View的成员变量mMeasuredHeight中
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
// 最后将View的状态位mPrivateFlags设置为已量算状态
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}
测量完成的尺寸的 state
View 的量算过程就完成了,但是 View 的父 ViewGroup 如何读取到 View 量算的结果呢?
- getMeasuredWidth() 和 getMeasuredHeight() 方法
- getMeasuredWidthAndState() 和 getMeasuredHeightAndState() 方法
- getMeasuredState() 方法
mMeasuredWidth/mMeasuredHeigth
mMeasuredWidth 是一个 Int 类型的值,其是由 4 个字节组成的。
背景:
我们先假设 mMeasuredWidth 只存储了量算完成的宽度信息,而且 View 的父 ViewGroup 可以通过相关方法得到该值。但是存在这样一种情况:View 在量算时,父 ViewGroup 给其传递的 widthMeasureSpec 中的 specMode 的值是 AT_MOST,specSize 是 100,但是 View 的最小宽度是 200,显然父 ViewGroup 指定的 specSize 不能满足 View 的大小,但是由于 specMode 的值是 AT_MOST,View 在 getDefaultSize 方法中不得不妥协,只能含泪将量算的最终宽度设置为 100。然后其父 ViewGroup 通过某些方法获取到该 View 的量算宽度为 100 时,ViewGroup 以为子 View 只需要 100 就够了,最终给了子 View 宽度为 100 的空间,这就导致了在 UI 界面上 View 特别窄,用户体验也就不好。
Android 为让其 View 的父控件获取更多的信息,就在 mMeasuredWidth 上下了很大功夫,虽然是一个 Int 值,但是想让它存储更多信息,具体来说就是把 mMeasuredWidth 分成两部分:
- 其高位的第一个字节 (25~32 位) 为第一部分,用于标记量算完的尺寸是不是达到了 View 想要的宽度,我们称该信息为量算的 state 信息。
- 其低位的三个字节 (1~24 位) 为第二部分,用于存储实际的量算到的宽度。
一个变量能包含两个信息,这个有点类似于 measureSpec;
1
2
3
4
5
// View Android29
public static final int MEASURED_SIZE_MASK = 0x00ffffff; // 测量宽/高真正size的mask
public static final int MEASURED_STATE_MASK = 0xff000000; // view宽/高state的mask
public static final int MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT = 16; // height state左移16位
public static final int MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL = 0x01000000; // 标记一个宽或高的state太小了
getMeasuredWidth() 和 getMeasuredHeight() 该组方法只返回量算结果中的的尺寸信息,去掉了高位字节的 state 信
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// View Android29
public final int getMeasuredWidth() {
return mMeasuredWidth & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;
}
public final int getMeasuredHeight() {
return mMeasuredHeight & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;
}
getMeasuredWidthAndState() 和 getMeasuredHeightAndState() 该组方法返回的量算结果中同时包含尺寸和 state 信息(如果 state 存在的话)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// View Android29
public final int getMeasuredWidthAndState() {
return mMeasuredWidth;
}
public final int getMeasuredHeightAndState() {
return mMeasuredHeight;
}
getMeasuredState() 该方法返回的 Int 值中同时包含宽度量算的 state 以及高度量算的 state,不包含任何的尺寸信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// View Android29
// 将宽度量算的state存储在Int值的第一个字节中,即高位首字节
// 将高度量算的state存储在Int值的第三个字节中
public final int getMeasuredState() {
return (mMeasuredWidth&MEASURED_STATE_MASK)
| ((mMeasuredHeight>>MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT)
& (MEASURED_STATE_MASK>>MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
}
由于我们已经用高位首字节存储了量算后宽度的 state,所以高度的 state 就不能存储在高位首字节了。Android 打算把它存储在第三个字节中。(mMeasuredHeight»MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT) 表示将 mMeasuredHeight 向右移 16 位,这样高度的 state 字节就从原来的第一个字节右移动到了第三个字节,由于高度的 state 向右移动了,所以其对应的掩码也有相应移动。(MEASURED_STATE_MASK»MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT) 表示 state 的掩码也从第一个字节右移 16 位到了第三个字节,即掩码从 0xff000000 变成了 0x0000ff00。然后用右移后的 state 与右移后的掩码执行按位与操作,这样就在第三个字节保留了高度的 state 信息,并且过滤掉了第 1、2、4 字节中的信息,即将这三个字节中的 24 个 bit 位置为 0 。 最后,将我们得到的宽度的 state 与高度的 state 进行按位或操作,这样就将宽度和高度的 state 都保存在一个 Int 值中:第一个字节存储宽度的 state,第三个字节存储高度的 state。
resolveSize/resolveSizeAndState
int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState)
参数:
- size View 需要的大小
- measureSpec 父容器约束的 MeasureSpec
- childMeasuredState 该 View 的子 view 的 state 联合信息;单个 view 传 0;viewGroup 调用 combineMeasuredStates 联合 state
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
// View Android29
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) {
final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
final int result;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (specSize < size) {
// 当specMode为AT_MOST,并且父控件指定的尺寸specSize小于View自己想要的尺寸时,
// 我们就会用掩码MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL向量算结果加入尺寸太小的标记
// 这样其父ViewGroup就可以通过该标记其给子View的尺寸太小了,
// 然后可能分配更大一点的尺寸给子View
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
default:
result = size;
}
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}
int resolveSize(int size, int measureSpec) 不关心 state,只取低 32 位的 size 信息
1
2
3
4
// View Android29
public static int resolveSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
return resolveSizeAndState(size, measureSpec, 0) & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;
}
combineMeasuredStates(int curState, int newState)
1
2
3
4
// View Android29
public static int combineMeasuredStates(int curState, int newState) {
return curState | newState;
}
和 getDefaultSize 的区别
- 如果 MeasureSpce Mode 都是 EXACTLY/UNSPECIFIED,getDefaultSize 和 resolveSizeXXX 都一样
- 如果 MeasureSpce Mode 都是 AT_MOST,getDefaultSize 返回的尺寸为 measureSpce Size 即和父容器给的大小一样;但 resolveSizeXXX 取的是 view 需要的大小和 measureSpecSize 中的最小值
onMeasure 模板代码
重写 View#onMeasure() 目的,就是为了给 View 一个 wrap_content 属性下的默认大小。
- 重写 onMeasure() 模板代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 没有必要再让 view 自己测量一遍了,浪费资源,此处面试的时候普遍会问。
// super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 计算期望的 size
int size = (int) ((PADDING + RADIUS) * 2);
// 获取父 View 传递来的可用大小
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
// 开始计算
int result = 0;
switch (widthMode) {
// 不超过
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
// 在 AT_MOST 模式下,取二者的最小值
if (widthSize < size) {
result = widthSize;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
// 精准的
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
// 父 View 给多少用多少
result = widthSize;
break;
// 无限大,没有指定大小
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
// 使用计算出的大小
result = size;
break;
default:
result = 0;
break;
}
// 设置大小
setMeasuredDimension(result, result);
}
这段模版代码其实 Android SDK 里面早就有了很好的封装 : resolveSize(int size, int measureSpec) 和 resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) ,两行代码直接搞定。
- 利用 resolveSizeXXX
1
2
3
4
5
6
override fun onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec: Int, heightMeasureSpec: Int) {
val w = resolveSizeAndState(DEFAULT_SIZE, widthMeasureSpec, 0)
val h = resolveSizeAndState(DEFAULT_SIZE, heightMeasureSpec, 0)
setMeasuredDimension(w, h)
LogUtils.i("${this.javaClass.simpleName} onMeasure")
}
ViewGroup 的测量
总结
- 一般 ViewGroup 是先测量子 View,再测量自己;而 ViewPager 特殊,是先测量自己再测量子 View
ViewGroup 提供的 measure child 方法
measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
measure 所有不为 GONE 的 child
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
measureChildWithMargins(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed, int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed)
measure child,包含了子 view 的 margin 和 parent 已经用了宽高尺寸 (widthUsed/heightUsed)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int parentHeightMeasureSpec) 包括父控件的 padding
带上父控件的 MeasureSpec 和 padding,让 child 自己测量,主要是调用 getChildMeasureSpec,调用 child 的 measure() 测量子 View 控件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// ViewGroup#measureChild
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
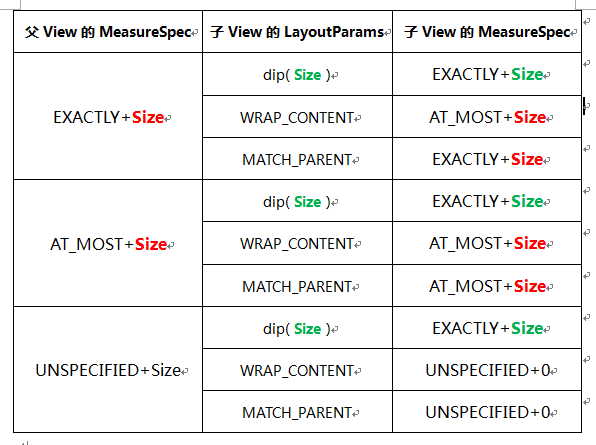
int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension)
measureChildren 最难的部分:计算出 MeasureSpec,该方法用于计算出正确的 MeasureSpec
- 参数 1 spec 父容器的 MeasureSpec
- 参数 2 padding 父容器的 padding 或者加上自身的 margin
- 参数 3 childDimension View 想要的大小,一般是定义在 xml 中,封装成了 LayoutParams
getChildMeasureSpec 源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
// ViewGroup
sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec = targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.M;
/**
* 目标是将父控件的测量规格和child view的布局参数LayoutParams相结合,得到一个
* 最可能符合条件的child view的测量规格。
* @param spec 父控件的测量规格
* @param padding 父控件里已经占用的大小
* @param childDimension child view布局LayoutParams里的尺寸
* @return child view 的测量规格
*/
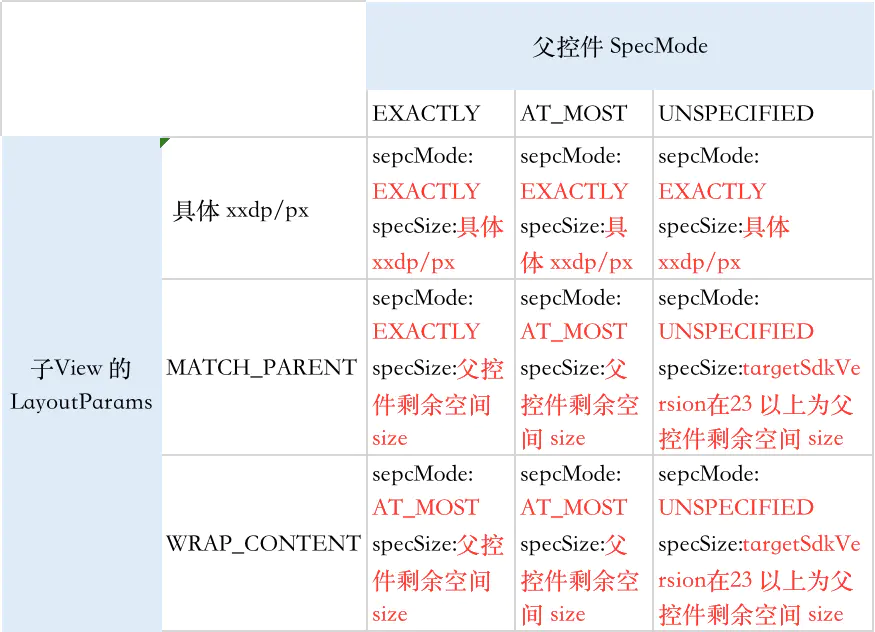
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
// 获取父容器(这里指的是FrameLayout)的测量模式和尺寸大小
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
// 这个尺寸应该减去内边距的值
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
// 声明临时变量存值
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: // 父容器尺寸大小是一个确定的值
if (childDimension >= 0) { //如果childDimension是一个具体的值 那么就将该值作为结果
resultSize = childDimension;
// 而这个值也是被确定的
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) { //如果子元素的布局参数为MATCH_PARENT
// 那么就将父容器的大小作为结果
resultSize = size;
// 因为父容器的大小是被确定的所以子元素大小也是可以被确定的
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) { //如果子元素的布局参数为WRAP_CONTENT
// 那么就将父容器的大小作为结果
resultSize = size;
// 但是子元素的大小包裹了其内容后不能超过父容器
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: // 父容器尺寸大小拥有一个限制值
if (childDimension >= 0) { //如果childDimension是一个具体的值
// 那么就将该值作为结果
resultSize = childDimension;
// 而这个值也是被确定的
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
//如果子元素的布局参数为MATCH_PARENT,那么就将父容器的大小作为结果
resultSize = size;
// 注释1:因为父容器的大小是受到限制值的限制所以子元素的大小也应该受到父容器的限制
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) { //如果子元素的布局参数为WRAP_CONTENT
// 那么就将父容器的大小作为结果
resultSize = size;
// 但是子元素的大小包裹了其内容后不能超过父容器
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: // 父容器尺寸大小未受限制
if (childDimension >= 0) {
//如果childDimension是一个具体的值,那么就将该值作为结果
resultSize = childDimension;
// 而这个值也是被确定的
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) { //如果子元素的布局参数为MATCH_PARENT
// 注释2:因为父容器的大小不受限制而对子元素来说也可以是任意大小所以不指定也不限制子元素的大小;AndroidM(API23)及以上为父容器最大值
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) { //如果子元素的布局参数为WRAP_CONTENT
// 因为父容器的大小不受限制而对子元素来说也可以是任意大小所以不指定也不限制子元素的大小;AndroidM(API23)及以上为父容器最大值
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
// 返回封装后的测量规格
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
总结如下图:
注:parentSize 为父容器中目前可使用的大小;AndroidM(API23) 及以上 UNSPECIFIED resultSize 不为 0 了,而是父容器期望大小。
- 对于应用层 View ,其 MeasureSpec 由父容器的 MeasureSpec 和自身的 LayoutParams 来共同决定
- 对于不同的父容器和 view 本身不同的 LayoutParams,view 就可以有多种 MeasureSpec
- 当 view 采用固定宽高的时候,不管父容器的 MeasureSpec 是什么,view 的 MeasureSpec 都是精确模式并且其大小遵循 Layoutparams 中的大小;
- 当 view 的宽高是 match_parent 时,这个时候如果父容器的模式是精准模式,那么 view 也是精准模式并且其大小是父容器的剩余空间,如果父容器是最大模式,那么 view 也是最大模式并且其大小不会超过父容器的剩余空间;
- 当 view 的宽高是 wrap_content 时,不管父容器的模式是精准还是最大化,view 的模式总是最大化并且大小不能超过父容器的剩余空间
- Unspecified 模式,这个模式主要用于系统内部多次 measure 的情况下,一般来说,我们不需要关注此模式 (这里注意自定义 View 放到 ScrollView 的情况 需要处理)。
常用布局的 onMeasure
常见布局测量及选择
FrameLayout 布局特点
- FrameLayout 的宽或高为 wrap_content(不为 Exactly)时,且子 view 大于 1 个的宽或高为 match_parent,测量 2 次
- 其他情况测量 1 次
LinearLayout 布局特点
- 没有 layout_weight 时,只 measure 一次(横向或者纵向)
- 设置了 layout_weight,先 measure 没有设置的,再 measure 一次设置的了,共 2 次
如果不使用 weight 属性,LinearLayout 会在当前方向上进行一次 measure 的过程,如果使用 weight 属性,LinearLayout 会避开设置过 weight 属性的 view 做第一次 measure,完了再对设置过 weight 属性的 view 做第二次 measure。由此可见,weight 属性对性能是有影响的,而且本身有大坑,请注意避让。
RelativeLayout 布局特点
- RelativeLayout 布局灵活一点
- RelativeLayout 实现复杂的布局,可以更少的层级
- RelativeLayout 总共 measure2 次,horizontal 和 vertical 各一次
RelativeLayout 在 measure 上是有性能损耗的,由于需要分别计算子 View 在横、竖两个方向上的尺寸,在每次 measure 过程中,子 View 需要被 measure 两次,所以在使用 RelativeLayout 时,一定要控制布局的深度,减少嵌套的情况
- 用 padding 替代 margin
View 的 measure 方法里对绘制过程做了一个优化,如果我们或者我们的子 View 没有要求强制刷新,而父 View 给子 View 的传入值也没有变化(也就是说子 View 的位置没变化),就不会做无谓的 measure。但是上面已经说了 RelativeLayout 要做两次 measure,而在做横向的测量时,纵向的测量结果尚未完成,只好暂时使用 myHeight 传入子 View 系统,假如子 View 的 Height 不等于(设置了 margin)myHeight 的高度,那么 measure 中上面代码所做得优化将不起作用,这一过程将进一步影响 RelativeLayout 的绘制性能。而 LinearLayout 则无这方面的担忧。解决这个问题也很好办,如果可以,尽量使用 padding 代替 margin。
布局抉择
- 优先考虑布局层级,优先考虑 RelativeLayout 和 ConstraintLayout
- 用 LinearLayout 的嵌套布局层次和 RelativeLayout 差不多的情况下,优先用 LinearLayout 或者 FrameLayout,性能更高点
- RelativeLayout 的子 View 如果高度和 RelativeLayout 不同,则会引发效率问题,当子 View 很复杂时,这个问题会更加严重。如果可以,尽量使用 padding 代替 margin。
FrameLayout 的 onMeasure
FrameLayout 测量小结
- 当 FrameLayout 的宽或高属性为
wrap_content属性时,同时有 2 个及以上的子 view 的宽或高属性为match_parent时,则所有子 view 会 measure 两次
FrameLayout#onMeasure 分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
// FrameLayout#onMeasure
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
// 父View传过来的layoutparams包含wrap_content属性
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
// 设置子View的宽度和高度,这里widthUsed 和 heightUsed都是0,说明子view想要多大就是多大
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 累加子View的宽高和上下左右margin,统计所有子view中的最大宽度和高度,作为父view自己的宽高
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// 子View指定了match_parent属性,需要在测量一次,先加到数组里
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// 省略Foreground计算代码,非本文重点
// 第一次测量完成,让每个view按照自己想要的大小,同时FrameLayout自己的getMeasuredWidth() /
// getMeasureHeight() 已经有值了
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
// 有超过1个子View设置了match_parent属性,需要重新测量FrameLayout的宽高
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// 设置子view的宽度为当前FrameLayout测量后的宽度(这里getMeasuredWidth 就是上面setMeasuredDimension 后的宽度)
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
// 非match_parent: 将子view margin算入子view的宽度中
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// 高度与宽度同理,都是设置子view的宽或高为FrameLayout的宽或高
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
// 更新child的宽度
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
- 第一次 measure 后,子 view 按照自己想要的大小,如果
measureMatchParentChildren=true(即 FrameLayout 的宽或高不为EXACTLY) 且子 view 的宽或高为MATCH_PARENT,那么添加到mMatchParentChildren - 如果 mMatchParentChildren 大于 1,那么进行子 View 的第 2 次 measure
FrameLayout 什么情况下子 view 会 measure 两次?
- FrameLayout 自身的 MeasureSpec.Mode 不等于 MeasureSpec.EXACTLY。
- 有两个或以上子 view 设置了 match_parent
为什么这种情况 FrameLayout 会测量两次呢?
- 首先看 ViewGroup#getChildMeasureSpec
如果 FrameLayout 的 SpecMode 是 AT_MOST 或 UNSPECIFIED,而子 view 的 layout 属性时 MATCH_PARENT 或 WRAP_CONTENT,则子 view 的 SpecMode 会变成和父 view 一样
FrameLayout 测量 2 次条件是 FrameLayout 不为 Exactly,且大于 1 个子 View 为 match_parent,首次 measure 后,子 View 的 SpecMode 为 AT_MOST,由子 View 自己决定大小。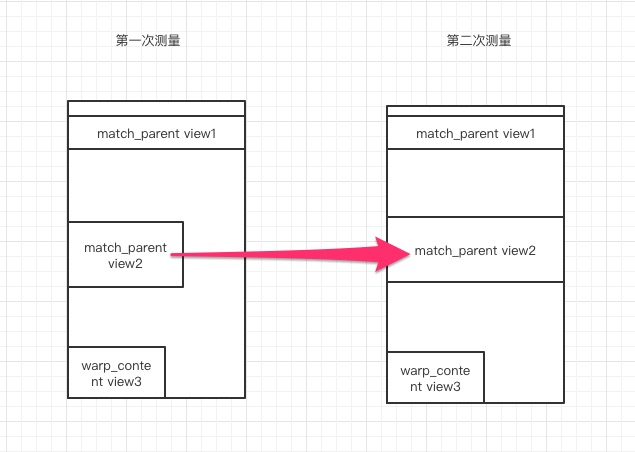
以宽度为例说明,因为 FrameLayout 可能包含多个子 view,第一次测量后,设置了 match_parent 的 view1 和 view2 变为 wrap_content,child.getMeasuredWidth 为 wrap_content 的宽度,即子 view 自己的宽度。
由于有多个 match_parent 的子 view,父 view 需要重新调整自己的宽度为最大的子 view 的宽度,所以所有的子 view 需要在根据父 view 的宽度重新调整一下自己的宽度,最终导致子 view measure 两次。
RelativeLayout 有没有 measure 两次子 View 的问题?为什么?
没有。
RelativeLayout 自定义了 getChildMeasureSpec() 方法。
LinearLayout 的 onMeasure
onMeasure
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// LinearLayout 类
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
//如果方向是垂直方向,就进行垂直方向的测量
measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
//进行水平方向的测量
measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
measureVertical 和 measureHorizontal 过程类似,我们对 measureVertical 进行分析。(以下源码有所删减)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
// LinearLayout 类
void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
mTotalLength = 0;
float totalWeight = 0;
final int count = getVirtualChildCount();
//获取 LinearLayout 的宽高模式 SpecMode
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
boolean skippedMeasure = false;
// See how tall everyone is. Also remember max width.
//遍历子 View ,查看每一个子类有多高,并且记住最大的宽度。
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
//measureNullChild() 恒返回 0,
mTotalLength += measureNullChild (i);
continue;
}
//如果子控件时 GONE 状态,就跳过,不进行测量。
//也可以看出,如果子 View 是 INVISIBLE 也是要测量大小的。
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
//getChildrenSkipCount 也是恒返回为 0 的。
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
continue;
}
//获取子控件的参数信息。
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
totalWeight += lp.weight;
//子控件是否设置了权重 weight
final boolean useExcessSpace = lp.height == 0 && lp.weight > 0;
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && useExcessSpace) {
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
//如果设置了权重,就将 skippedMeasure 标记为 true。
//后面会根据 skippedMeasure 的值和其他条件来决定是否进行重新绘制。
//所以说,在 LinearLayout 中使用了 weight 权重,会导致测量两次,比较耗时。
//可以考虑使用 RelativeLayout 或者 ConstraintLayout
skippedMeasure = true;
} else {
if (useExcessSpace) {
lp.height = LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
}
//计算已经使用过的高度
final int usedHeight = totalWeight == 0 ? mTotalLength : 0;
/*这句代码是关键,从字面意思就可以理解出,该方法是在 layout
之前进行子 View 的测量。*/
measureChildBeforeLayout(child, i, widthMeasureSpec, 0,
heightMeasureSpec, usedHeight);
}
}
}
那么我们再查看 measureChildBeforeLayout 方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//LinearLayout 类
void measureChildBeforeLayout(View child, int childIndex,
int widthMeasureSpec, int totalWidth, int heightMeasureSpec,
int totalHeight) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, totalWidth,
heightMeasureSpec, totalHeight);
}
测量多次问题
- 在 LinearLayout 中,如果为 GONE 的 child 和没有 weight 的 child 在 onMeasure 方法中永远只会被测量一次
- 对于 children 应该分开来看,因为有可能在一次 onMeasure()的执行过程中,其中一部分 child 被测量的 1 次,另外的 child 被测量了 2 次。
- 由于使用了 weight,这个 LinearLayout 中的【一部分(有可能是区青年布)】child 被测量了 2 次 “
RelativeLayout
ConstraintLayout
ScrollView 的 onMeasure
ScrollView 测量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="@color/green_50"
android:tag="ScrollView">
<me.hacket.assistant.samples.ui.base.MySpecFrameLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/red_A100"
android:tag="MySpecFrameLayout">
<me.hacket.assistant.samples.ui.base.MySpecView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:tag="MySpecView" />
</me.hacket.assistant.samples.ui.base.MySpecFrameLayout>
</ScrollView>
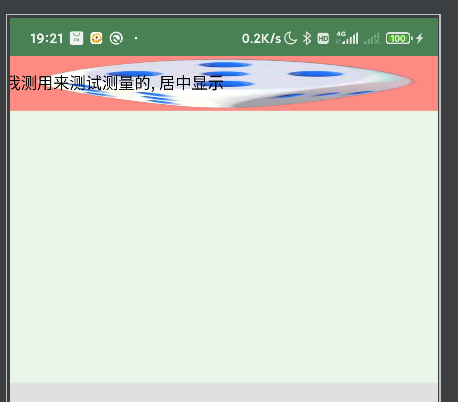
MySpecView 的 width 和 heigh 都设置为 wrap_content,MySpecView 显示不出来。
分析:ScrollView 重写了 measureChildWithMargins() 方法,heightMode 改成了 MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED,widthMode 还是父容器传过来的;MySpectView 的 heightMeasureSpec 为 MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED,MySpectView 走的默认的 onMeasure。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
protected int getSuggestedMinimumHeight() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinHeight : max(mMinHeight, mBackground.getMinimumHeight());
}
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
可以看到走的 getDefaultSize(),如果 specMode==MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED,那么 result=size,getSuggestedMinimumHeight()。如果 mBackground!=null 的话,值为 mMinHeight 和 mBackground 的最大值,如果 mBackground==null,值为 mMinHeight
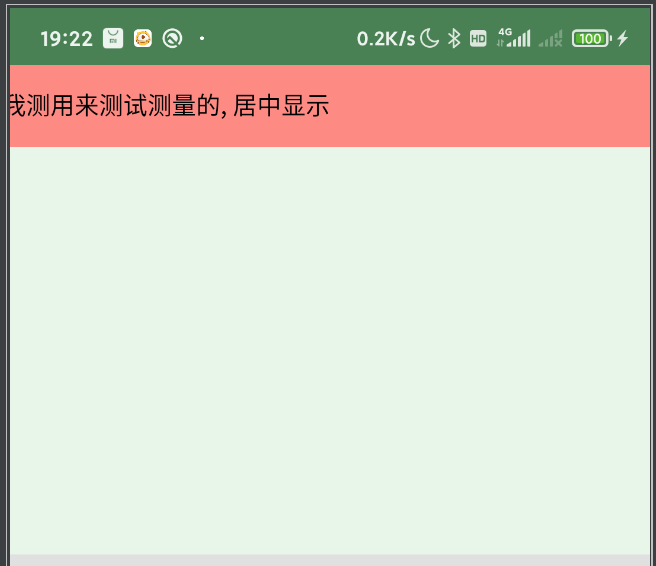
解决:
- 设置一个 background,不能设置为 color(height 为 background 的 drawable 的高度,widget 为 widthMeasureSpecSize 即 scrollView 的宽度)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="@color/green_50"
android:tag="ScrollView">
<me.hacket.assistant.samples.ui.base.MySpecFrameLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/red_A100"
android:tag="MySpecFrameLayout">
<me.hacket.assistant.samples.ui.base.MySpecView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/dice_five"
android:tag="MySpecView" />
</me.hacket.assistant.samples.ui.base.MySpecFrameLayout>
</ScrollView>
- 设置一个 minHeight
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="@color/green_50"
android:tag="ScrollView">
<me.hacket.assistant.samples.ui.base.MySpecFrameLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/red_A100"
android:tag="MySpecFrameLayout">
<me.hacket.assistant.samples.ui.base.MySpecView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:minHeight="50dp"
android:tag="MySpecView" />
</me.hacket.assistant.samples.ui.base.MySpecFrameLayout>
</ScrollView>
源码分析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
public class ScrollView {
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if (!mFillViewport) {
return;
}
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {
return;
}
if (getChildCount() > 0) {
final View child = getChildAt(0);
final int widthPadding;
final int heightPadding;
final int targetSdkVersion = getContext().getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion;
final FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
if (targetSdkVersion >= VERSION_CODES.M) {
widthPadding = mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
heightPadding = mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
} else {
widthPadding = mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight;
heightPadding = mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom;
}
final int desiredHeight = getMeasuredHeight() - heightPadding;
if (child.getMeasuredHeight() < desiredHeight) {
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(
widthMeasureSpec, widthPadding, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
desiredHeight, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
@Override
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
int childWidthMeasureSpec;
int childHeightMeasureSpec;
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec, mPaddingLeft
+ mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int verticalPadding = mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom;
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeSafeMeasureSpec(
Math.max(0, MeasureSpec.getSize(parentHeightMeasureSpec) - verticalPadding),
MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int usedTotal = mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin +
heightUsed;
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeSafeMeasureSpec(
Math.max(0, MeasureSpec.getSize(parentHeightMeasureSpec) - usedTotal),
MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}