fitsSystemWindows和WindowInsets
fitsSystemWindow
什么是 fitsSystemWindow? (API>=19)
fitsSystemWindows 是在 Android4.4(API19)中引入的。根据官方文档,如果某个 View 的 fitsSystemWindows 设为 true,那么该 View 的 padding 属性将由系统设置,用户在布局文件中设置的 padding 会被忽略。系统会为该 View 设置一个 paddingTop,值为 StatusBar 的高度。fitsSystemWindows 默认为 false。
System Windows 顾名思义就是系统窗口,系统在这里显示系统一些属性和操作区域,比如:状态栏,以及没有实体按键的虚拟导航栏。
fitsSystemWindow 什么时候生效?
- 设置了 fitsSystemWindows=true
配置 android:fitsSystemWindows=”true”,系统默认行为是给消费了 WindowInsets 事件的 View 添加系统状态栏或者导航栏高度的 padding
- 设置了
View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_FULLSCREEN或View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_HIDE_NAVIGATION中的一个 flag
fitsSystemWindows 必须结合透明状态栏才有效果(只有设置了
View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_HIDE_NAVIGATION(布局到导航栏,不隐藏导航栏)或View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_FULLSCREEN(布局到状态栏,不隐藏状态栏)之一),fitsSystemWindows 才会起作用;不然 StatusBar 的空间轮不到用户处理,这时会由 ContentView 的父控件处理,如果用 HierarchyView 工具查看,将会看到,ContentView 的父控件的 paddingTop 将会被设置。
设置了 WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_STATUS 或 WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_NAVIGATION 也会生效,因为他们生效后会默认添加 View.View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_FULLSCREEN/View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_HIDE_NAVIGATION。
- 如果多个 view 同时设置了 fitsSystemWindows,只有第一个会起作用。作用的 view 上面会加上 paddingTop 为状态栏高度
- fitsSystemWindow 生效后,view 原有的 padding 将失效
相关 API
setFitsSystemWindows(boolean fitSystemWindows) 设置 View 的 fitsSystemWindows
设置该 View 是否对系统栏(如状态栏)负责,插入内容;是否调用 fitSystemWindows(Rect) 的默认实现,true 表示使用系统默认实现;如果你自己定义实现了 fitSystemWindows(Rect),就不用设置该 Flag 了,你的实现会覆盖掉该 flag。
fitSystemWindows(Rect)/dispatchApplyWindowInsets(Rect) 分发
View#fitSystemWindows(Rect insets)过时
API20 过时,API20 用dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets)应用 insets 给 view。View#WindowInsets dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets)该方法用于替代过时的boolean fitSystemWindows(Rect insets)方法,分发 WindowInsets。
requestFitSystemWindows()/requestApplyInsets() 请求分发 WindowInsets,onApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets) 会被调用
requestFitSystemWindows()已过时,由requestApplyInsets()替代
1
2
3
4
5
6
@Deprecated
public void requestFitSystemWindows() {
if (mParent != null) {
mParent.requestFitSystemWindows();
}
}
View#requestApplyInsets(),实现就是调用 requestFitSystemWindows()
1
2
3
public void requestApplyInsets() {
requestFitSystemWindows();
}
上面 2 种的兼容写法:ViewCompat.requestApplyInsets
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public static void requestApplyInsets(@NonNull View view) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 20) {
view.requestApplyInsets(); // 需要API20及以上
} else if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 16) {
view.requestFitSystemWindows();
}
}
onApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets) 应用 WindowInsets
View#WindowInsets onApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets)复写 View,高版本用
自定义 View 来自定义行为适应 window insets- View#setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(OnApplyWindowInsetsListener listener) androidX 兼容低版本监听 View 适应 window insets
优先 View 的onApplyWindowInsets()方法
fitsSystemWindows 的默认行为和自定义行为
1、默认行为
android:fitsSystemWindows="true",根据 FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS 标志位,无论哪个版本,默认行为就是通过在 View 上设置和系统窗口一样高度的边框(padding )来确保你的内容不会出现到系统窗口下面。
- 如果某个 View 的
fitsSystemWindows设为 true,那么该 View 的 padding 属性将由系统设置,该 view 在布局文件中设置的 padding 会被忽略。系统会为该 View 设置一个 paddingTop,值为 StatusBar 的高度。fitsSystemWindows 默认为 false
2、自定义行为
- 复写 View 的
onApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets)方法 - 设置
OnApplyWindowInsetsListener
WindowInsets 和 OnApplyWindowInsetsListener
什么是 WindowInsets?
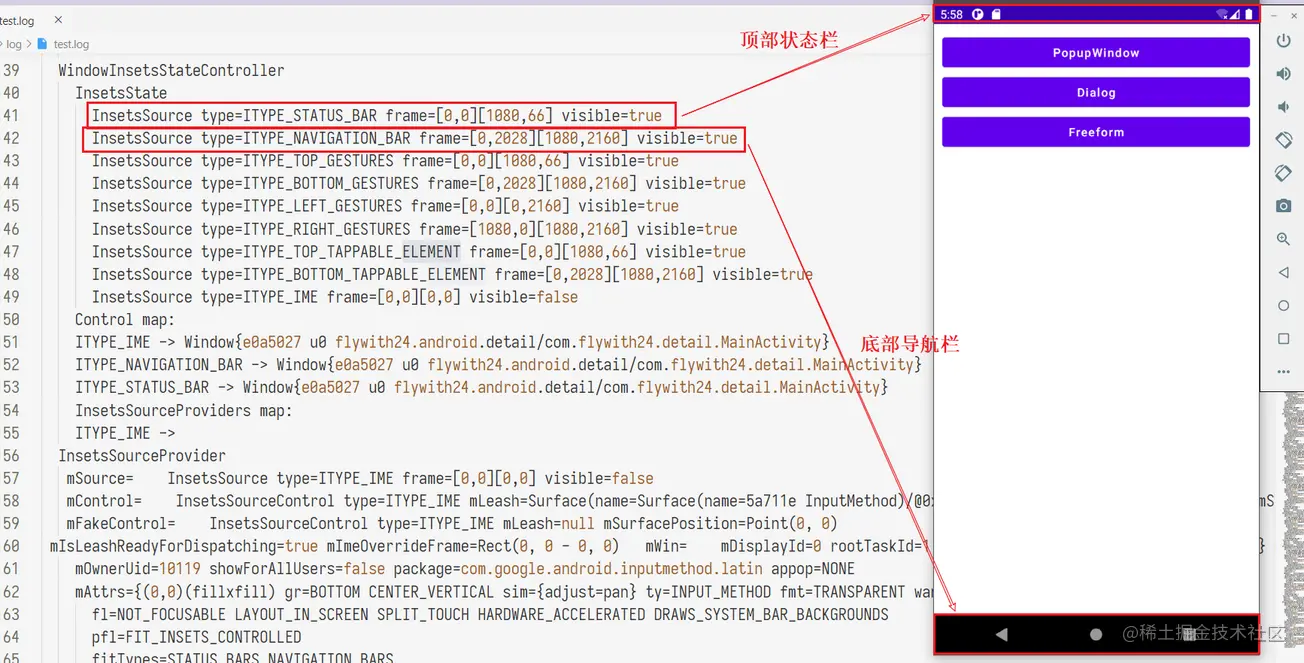
屏幕上除了开发者 app 绘制的内容还有系统的 Insets(插入物),Insets 区域负责描述屏幕的哪些部分会与系统 UI 相交。如 Starus bar 或 Navigation bar:
- STATUS_BAR,用于展示系统时间,电量,wifi 等信息
- NAVIGATION_BAR,虚拟导航栏(区别于实体的三大金刚键),形态有三大金刚键导航,手势导航两种。(有些设备形态如 TV 没有导航栏)
- IME,软键盘,用于输入文字
其中 STATUS_BAR 与 NAVIGATION_BAR 又被称为 System bar。
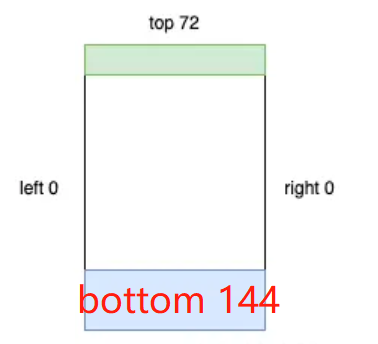
在源码中,Insets 对象拥有 4 个 int 值,用于描述矩形四个边的偏移:
不要把 Insets 的 top ,bottom,left,right 与 Rect 的搞混,前者描述的是偏移,后者是坐标。
WindowInsets 类型
SystemWindowInsets 是 WindowInsets 的最常见一种,另外还有 StableInsets(API v21) 和 WindowDecorInsets。
StableInsets 和 SystemWindowInsets 类似,表示被 StatusBar 等遮盖的区域,不同的是 StableInsets 不会随着 StatusBar 的隐藏和显示变化。沉浸式全屏下,StatusBar 可以通过手势呼出,StableInsets 不会发生变化。WindowDecorInsets 为预留属性,忽略。
WindowInsets API
- Insets getInsets(@InsetsType int typeMask)
之前的
getSystemWindowInsets()
1
2
3
4
5
val systemWindowInsets = insets.systemWindowInsets
val stableInsets = insets.stableInsets
val systemBarInsets = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars()) // 等同于systemWindowInsets
val systemBarInsets2 = insets.getInsetsIgnoringVisibility(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars()) // 等同于stableInsets
- Insets getInsetsIgnoringVisibility(@InsetsType int typeMask)
之前的
getStableInsets()
- boolean isVisible(@InsetsType int typeMask)
消费 WindowInsets
以 mSystemWindowInsets 为例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
private boolean mSystemWindowInsetsConsumed = false;
public WindowInsets consumeSystemWindowInsets() {
final WindowInsets result = new WindowInsets(this);
result.mSystemWindowInsets = EMPTY_RECT;
result.mSystemWindowInsetsConsumed = true;
return result;
}
public WindowInsets consumeSystemWindowInsets(boolean left, boolean top,
boolean right, boolean bottom) {
if (left || top || right || bottom) {
final WindowInsets result = new WindowInsets(this);
result.mSystemWindowInsets = new Rect(
left ? 0 : mSystemWindowInsets.left,
top ? 0 : mSystemWindowInsets.top,
right ? 0 : mSystemWindowInsets.right,
bottom ? 0 : mSystemWindowInsets.bottom);
return result;
}
return this;
}
mSystemWindowInsets 的消费分为全部消费和部分消费,如果不存在消费,则返回对象本身,如果消费了,则返回将消费部分置为 0 的对象 copy(一个新的 copy WindowInsets 对象)
判断 WindowInsets 是否消费掉:
1
2
3
4
// 判断WindowInsets是否被消费掉
public boolean isConsumed() {
return mSystemWindowInsetsConsumed && mWindowDecorInsetsConsumed && mStableInsetsConsumed;
}
可见要消费掉 WindowInsets,需要同时消耗掉 mSystemWindowInsets, mWindowDecorInsets, mStableInsets。
WindowInsets 小结
WindowInsets 是一个描述了屏幕上的各个插入空间的一个类,其在后期中可以扩展,WindowInsets 在消耗后将不再继续传递。对于普通的 View 而言,要消耗 WindowInsets 必须先设置 View 的 fitsSystemWindows 的属性为 true。这也是为什么对普通 View 层级设置 fitsSystemWindows 属性为 true 却只有一个顶层的生效而已。单对于一些特殊的 View 而言,则是另外一番情况了
OnApplyWindowInsetsListener
如果 OnApplyWindowInsetsListener 不生效,需要设置 WindowCompat.setDecorFitsSystemWindows(activity.window, false) //this is backward compatible version,即设置 View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_FULLSCREEN 或 View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_HIDE_NAVIGATION 中一个即可。
setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener never called
接口 OnApplyWindowInsetsListener
1
2
3
public interface OnApplyWindowInsetsListener {
WindowInsetsCompat onApplyWindowInsets(View v, WindowInsetsCompat insets);
}
OnApplyWindowInsetsListener 参数
- v View 需要被处理 window insets 的 view
- insets WindowInsetsCompat 被处理的 WindowInsets
OnApplyWindowInsetsListener 返回值
返回消费过后的 WindowInsets。完全消费后,其他的 view 就无法消费了
- 消费 insets 部分
1
2
3
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(root) { v, insets ->
insets.inset(0, (10.dp), 0, 0) // 表示在原有insets基础上减去10dp
}
- 完全消费
1
2
3
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(root) { v, insets ->
WindowInsetsCompat.CONSUMED
}
View.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(API>=20)
API>=20,替代
View#onApplyWindowInsets,设置了View#setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener就不会调用View#onApplyWindowInsets了
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(API>=21)
优先于 View 的 setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener
- 自定义 View 处理 WindowInset
控件 titlebar 留出 insetTop 的 margin,防止遮挡了 insetTop
1
2
3
4
5
6
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(titlebar) { _, insets ->
val p = titlebar.layoutParams as? ConstraintLayout.LayoutParams
p?.topMargin = insets.systemWindowInsetTop
titlebar.layoutParams = p
insets
}
consumeSystemWindowInsets
insets.consumeSystemWindowInsets() // 消费掉了,后面的子 View 就不会分发了
透明到状态栏并处理布局被状态栏遮挡(兼容 API19 的)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
initImmersionBar().statusBarColor(R.color.transparent).statusBarDarkFont(false).init()
iv_back_my_goods.setOnClickListener { onBackPressed() }
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(my_goods_title_container_id) { _, insets ->
val p = my_goods_title_container_id.layoutParams as? ConstraintLayout.LayoutParams
p?.topMargin = insets.systemWindowInsetTop
my_goods_title_container_id.layoutParams = p
insets
}
} else if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
my_goods_title_container_id.fitsSystemWindows = true
}
ViewCompat.requestApplyInsets(contentView)
ViewUtils.doOnApplyWindowInsets 更方便使用 OnApplyWindowInsetsListener
- initialPadding View 的原始 padding
- requestApplyInsetsWhenAttached() 可以支持 view 未 attach 调用(等到 attach 是再次请求
View.requestApplyInsets())
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
public static void doOnApplyWindowInsets(
@NonNull View view, @NonNull final ViewUtils.OnApplyWindowInsetsListener listener) {
// Create a snapshot of the view's padding state.
final RelativePadding initialPadding =
new RelativePadding(
ViewCompat.getPaddingStart(view),
view.getPaddingTop(),
ViewCompat.getPaddingEnd(view),
view.getPaddingBottom());
// Set an actual OnApplyWindowInsetsListener which proxies to the given callback, also passing
// in the original padding state.
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(
view,
new androidx.core.view.OnApplyWindowInsetsListener() {
@Override
public WindowInsetsCompat onApplyWindowInsets(View view, WindowInsetsCompat insets) {
return listener.onApplyWindowInsets(view, insets, new RelativePadding(initialPadding));
}
});
// Request some insets.
requestApplyInsetsWhenAttached(view);
}
/** Requests that insets should be applied to this view once it is attached. */
public static void requestApplyInsetsWhenAttached(@NonNull View view) {
if (ViewCompat.isAttachedToWindow(view)) {
// We're already attached, just request as normal.
ViewCompat.requestApplyInsets(view);
} else {
// We're not attached to the hierarchy, add a listener to request when we are.
view.addOnAttachStateChangeListener(
new View.OnAttachStateChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onViewAttachedToWindow(@NonNull View v) {
v.removeOnAttachStateChangeListener(this);
ViewCompat.requestApplyInsets(v);
}
@Override
public void onViewDetachedFromWindow(View v) {}
});
}
}
/** Simple data object to store the initial padding for a view. */
public static class RelativePadding {
public int start;
public int top;
public int end;
public int bottom;
public RelativePadding(int start, int top, int end, int bottom) {
this.start = start;
this.top = top;
this.end = end;
this.bottom = bottom;
}
public RelativePadding(@NonNull RelativePadding other) {
this.start = other.start;
this.top = other.top;
this.end = other.end;
this.bottom = other.bottom;
}
/** Applies this relative padding to the view. */
public void applyToView(View view) {
ViewCompat.setPaddingRelative(view, start, top, end, bottom);
}
}
/**
* Wrapper around {@link androidx.core.view.OnApplyWindowInsetsListener} which also passes
* the initial padding set on the view. Used with {@link doOnApplyWindowInsets(View,ViewUtils.OnApplyWindowInsetsListener)}.
*/
public interface OnApplyWindowInsetsListener {
/**
* When {@link View#setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(View.OnApplyWindowInsetsListener) set} on a
* View, this listener method will be called instead of the view's own {@link
* View#onApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets)} method. The {@code initialPadding} is the view's
* original padding which can be updated and will be applied to the view automatically. This
* method should return a new {@link WindowInsetsCompat} with any insets consumed.
*/
WindowInsetsCompat onApplyWindowInsets(
@NonNull View view, @NonNull WindowInsetsCompat insets, @NonNull RelativePadding initialPadding);
}
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
ViewUtils.doOnApplyWindowInsets(tv1) { v, insets, initialPadding ->
val systemBarInsets = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars())
val systemBarInsets2 =
insets.getInsetsIgnoringVisibility(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars())
val statusBarInsets = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.statusBars())
val navigationBarInsets = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.navigationBars())
val imeInsets = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime())
Log.i(
"hacket",
"${v.javaClass.simpleName}-onApplyWindowInsets: systemBarInsets=$systemBarInsets,systemBarInsets2=$systemBarInsets2,statusBarInsets=$statusBarInsets,navigationBarInsets=$navigationBarInsets,imeInsets=$imeInsets\n initialPadding=${initialPadding.toStr()}"
)
root.setPadding(
0,
systemBarInsets.top + initialPadding.top,
0,
systemBarInsets.bottom + initialPadding.bottom
)
insets
}
ViewUtils.doOnApplyWindowInsets 提供给自定义 View 处理 WindowInsets 用的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
/**
* Wrapper around {@link androidx.core.view.OnApplyWindowInsetsListener} that can
* automatically apply inset padding based on view attributes.
*/
public static void doOnApplyWindowInsets(
@NonNull View view, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
doOnApplyWindowInsets(view, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes, null);
}
/**
* Wrapper around {@link androidx.core.view.OnApplyWindowInsetsListener} that can
* automatically apply inset padding based on view attributes.
*/
public static void doOnApplyWindowInsets(
@NonNull View view,
@Nullable AttributeSet attrs,
int defStyleAttr,
int defStyleRes,
@Nullable final ViewUtils.OnApplyWindowInsetsListener listener) {
TypedArray a =
view.getContext()
.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.Insets, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
final boolean paddingBottomSystemWindowInsets =
a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Insets_paddingBottomSystemWindowInsets, false);
final boolean paddingLeftSystemWindowInsets =
a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Insets_paddingLeftSystemWindowInsets, false);
final boolean paddingRightSystemWindowInsets =
a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Insets_paddingRightSystemWindowInsets, false);
a.recycle();
doOnApplyWindowInsets(
view,
new ViewUtils.OnApplyWindowInsetsListener() {
@NonNull
@Override
public WindowInsetsCompat onApplyWindowInsets(
View view,
@NonNull WindowInsetsCompat insets,
@NonNull ViewUtils.RelativePadding initialPadding) {
if (paddingBottomSystemWindowInsets) {
initialPadding.bottom += insets.getSystemWindowInsetBottom();
}
boolean isRtl = isLayoutRtl(view);
if (paddingLeftSystemWindowInsets) {
if (isRtl) {
initialPadding.end += insets.getSystemWindowInsetLeft();
} else {
initialPadding.start += insets.getSystemWindowInsetLeft();
}
}
if (paddingRightSystemWindowInsets) {
if (isRtl) {
initialPadding.start += insets.getSystemWindowInsetRight();
} else {
initialPadding.end += insets.getSystemWindowInsetRight();
}
}
initialPadding.applyToView(view);
return listener != null
? listener.onApplyWindowInsets(view, insets, initialPadding)
: insets;
}
});
}
WindowInsets 分发原理(基于 API31)
View 中的 4 个标记
static final int OPTIONAL_FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS = 0x00000800
如果设置了该 flag,忽略其 insets;该 flag 只支持到 Android R(API30/Android11),现在用
PFLAG4_FRAMEWORK_OPTIONAL_FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS
static final int PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS = 0x20
该 flag 表示正在 apply insets 中
private static final int FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS = 0x00000002
FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS,表示 View 会通过调整 padding 来适配 system window,通过 setFitsSystemWindows() 设置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
/**
* This view will adjust its padding to fit sytem windows (e.g. status bar)
*/
private static final int FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS = 0x00000002;
public void setFitsSystemWindows(boolean fitSystemWindows) {
setFlags(fitSystemWindows ? FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS : 0, FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS);
}
public static final int SYSTEM_UI_LAYOUT_FLAGS = SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_HIDE_NAVIGATION|SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_FULLSCREEN
该 flag 可以影响与系统 UI 的布局
WindowInsets 分发原理分析
ViewRootImpl#dispatchApplyInsets
dispatchApplyInsets 的调用链:
1
2
3
4
5
ViewRootImpl.scheduleTraversals() →
mTraversalRunnable(TraversalRunnable)→
doTraversal() →
performTraversals() →
dispatchApplyInsets() →
源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
// ViewRootImpl
private void performTraversals() {
final View host = mView; // DecorView
// ...
if (mFirst) {
// ...
dispatchApplyInsets(host);
}
// ...
if (mApplyInsetsRequested && !(mWillMove || mWillResize)) {
dispatchApplyInsets(host);
if (mLayoutRequested) {
}
// ...
if (dispatchApplyInsets || mLastSystemUiVisibility !=
mAttachInfo.mSystemUiVisibility || mApplyInsetsRequested) {
mLastSystemUiVisibility = mAttachInfo.mSystemUiVisibility;
dispatchApplyInsets(host);
// We applied insets so force contentInsetsChanged to ensure the
// hierarchy is measured below.
dispatchApplyInsets = true;
}
}
void dispatchApplyInsets(View host) {
WindowInsets insets = getWindowInsets(true /* forceConstruct */);
final boolean dispatchCutout = (mWindowAttributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode
== LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS);
if (!dispatchCutout) {
// Window is either not laid out in cutout or the status bar inset takes care of
// clearing the cutout, so we don't need to dispatch the cutout to the hierarchy.
insets = insets.consumeDisplayCutout();
}
host.dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
}
接着看 ViewGroup#dispatchApplyWindowInsets:
ViewGroup#dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets)
WindowInsets 的分发和事件分发有点类似。
ViewGroup 的 dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets),就是不停的调用子 View 的 dispatchApplyWindowInsets,直到有子 View 消费掉。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// ViewGroup
@Override
public WindowInsets dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
insets = super.dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets); // 1.
if (insets.isConsumed()) { // 2.
return insets;
}
if (View.sBrokenInsetsDispatch) { // 3.
return brokenDispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
} else {
return newDispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
}
}
- 调用父类的 dispatchApplyWindowInsets 方法
- 如果 insets 被 consumed 了,那么返回该 insets
- 如果 View.sBrokenInsetsDispatch 的值为 true 走
brokenDispatchApplyWindowInsets();否则走newDispatchApplyWindowInsets() - sBrokenInsetsDispatch 给 AndroidR(Android11/API30) 之前用,Android11 之前的版本有 bug;
我们先看看 brokenDispatchApplyWindowInsetsh() 和 newDispatchApplyWindowInsets():
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
private WindowInsets brokenDispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
insets = getChildAt(i).dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
if (insets.isConsumed()) {
break;
}
}
return insets;
}
private WindowInsets newDispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
getChildAt(i).dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
}
return insets;
}
- brokenDispatchApplyWindowInsets 从所有子 view 中,找到了一个子 view 的 dispatchApplyWindowInsets 消费了,那么就循环结束了,不继续分发了
- newDispatchApplyWindowInsets 遍历所有子 view 调用 dispatchApplyWindowInsets
View#dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets)
先看看 View#dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// View
/**
* Flag indicating that we're in the process of applying window insets.
*/
static final int PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS = 0x20;
public WindowInsets dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
try {
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS; // 1.
if (mListenerInfo != null && mListenerInfo.mOnApplyWindowInsetsListener != null) { // 2.
return mListenerInfo.mOnApplyWindowInsetsListener.onApplyWindowInsets(this, insets);
} else {
return onApplyWindowInsets(insets); // 3.
}
} finally {
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS; // 4.
}
}
- 设置了
PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS,PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETSflag 表示在请求 window insets - 如果设置了
mOnApplyWindowInsetsListener,那么走mOnApplyWindowInsetsListener.onApplyWindowInsets - 如果没有设置 mOnApplyWindowInsetsListener,那么走
View.onApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets) - 最后清除掉 mPrivateFlags3 的值
PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS
在 View 的
dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets)可以看到,如果通过setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(OnApplyWindowInsetsListener listener)设置了监听,会调用 Listener 的onApplyWindowInsets;否则调用 View 自己的onApplyWindowInsets()方法,自定义 View 可以实现该方法来实现处理 WindowInsets。
来看看 View.onApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets):
View#onApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public WindowInsets onApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
if ((mPrivateFlags4 & PFLAG4_FRAMEWORK_OPTIONAL_FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS) != 0
&& (mViewFlags & FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS) != 0) { // 1.
return onApplyFrameworkOptionalFitSystemWindows(insets);
}
if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_FITTING_SYSTEM_WINDOWS) == 0) { // 2.
// 系统回调调用
// We weren't called from within a direct call to fitSystemWindows,
// call into it as a fallback in case we're in a class that overrides it
// and has logic to perform.
if (fitSystemWindows(insets.getSystemWindowInsets())) {
return insets.consumeSystemWindowInsets(); // 4.
}
} else {
// 直接调用
// We were called from within a direct call to fitSystemWindows.
if (fitSystemWindowsInt(insets.getSystemWindowInsets())) { // 3.
return insets.consumeSystemWindowInsets(); // 4.
}
}
return insets;
}
- 该方法应该被子类重写掉,否则走默认行为;如果设置了 OnApplyWindowInsetsListener,该方法不会走;
- 系统调用,系统就是在该 View 添加 padding
- 检查 mPrivateFlags3 这个 Flag 是否设置了 PFLAG3_FITTING_SYSTEM_WINDOWS,这里由于我们没有设置过,所以走 if 代码流程。
- fitSystemWindowsInt();这里要注意传递给 fitSystemWindows 方法的参数,是 getSystemWindowInsetsAsRect 方法的返回值。
- fitSystemWindows 或者 fitSystemWindowsInt 返回了 true,则调用 WindowInsets 的 consumeSystemWindowInsets 说明此 View 消费了这个 WindowInsets。
接着看 fitSystemWindows() 和 fitSystemWindowsInt()
ViewfitSystemWindows(Rect)/fitSystemWindowsInt(Rect)
先看 fitSystemWindows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
@Deprecated
protected boolean fitSystemWindows(Rect insets) {
if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS) == 0) { // 1.
if (insets == null) {
// Null insets被定义为已经消费的insets;所以返回false
return false;
}
try {
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_FITTING_SYSTEM_WINDOWS;
return dispatchApplyWindowInsets(new WindowInsets(insets)).isConsumed();
} finally {
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_FITTING_SYSTEM_WINDOWS;
}
} else { // 2.
// 默认情况,走这里
return fitSystemWindowsInt(insets);
}
}
- 检查 mPrivateFlags3 是否设置了 PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS 这个 Flag,这里肯定是设置了的,因为在 View 的 dispatchApplyWindowInsets 方法开始调用时设置了这个 Flag,调用结束时取消了这个 Flag。
- 这里会走 fitSystemWindowsInt
接着看 fitSystemWindowsInt:
View.boolean fitSystemWindowsInt(insets),一系列条件给 View 设置 padding;fitSystemWindowsInt 就是调 computeFitSystemWindows 和 internalSetPadding;computeFitSystemWindows 是计算 padding,而 internalSetPadding 就正式设置 padding,padding 设置好了,子 view 就会小一些,被约束在 padding 里面。注意一点 fitSystemWindowsInt 只有 FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS 这个 flag 为 true 才会进去,flag 不对直接返回 false。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
private boolean fitSystemWindowsInt(Rect insets) {
if ((mViewFlags & FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS) == FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS) { // 1.
Rect localInsets = sThreadLocal.get();
boolean res = computeFitSystemWindows(insets, localInsets);
applyInsets(localInsets);
return res;
}
return false;
}
protected boolean computeFitSystemWindows(Rect inoutInsets, Rect outLocalInsets) {
WindowInsets innerInsets = computeSystemWindowInsets(new WindowInsets(inoutInsets),
outLocalInsets);
inoutInsets.set(innerInsets.getSystemWindowInsetsAsRect());
return innerInsets.isSystemWindowInsetsConsumed();
}
public WindowInsets computeSystemWindowInsets(WindowInsets in, Rect outLocalInsets) { // 2.
boolean isOptionalFitSystemWindows = (mViewFlags & OPTIONAL_FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS) != 0
|| (mPrivateFlags4 & PFLAG4_FRAMEWORK_OPTIONAL_FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS) != 0;
if (isOptionalFitSystemWindows && mAttachInfo != null) {
OnContentApplyWindowInsetsListener listener =
mAttachInfo.mContentOnApplyWindowInsetsListener;
if (listener == null) {
// The application wants to take care of fitting system window for
// the content.
outLocalInsets.setEmpty();
return in;
}
Pair<Insets, WindowInsets> result = listener.onContentApplyWindowInsets(this, in);
outLocalInsets.set(result.first.toRect());
return result.second;
} else {
outLocalInsets.set(in.getSystemWindowInsetsAsRect());
return in.consumeSystemWindowInsets().inset(outLocalInsets);
}
}
private void applyInsets(Rect insets) { // 3.
mUserPaddingStart = UNDEFINED_PADDING;
mUserPaddingEnd = UNDEFINED_PADDING;
mUserPaddingLeftInitial = insets.left;
mUserPaddingRightInitial = insets.right;
internalSetPadding(insets.left, insets.top, insets.right, insets.bottom);
}
- 检查该 View 是否设置了
FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS这个 Flag,也就是是否设置了属性android:fitsSystemWindows="true"(默认false),如果没有设置,说名该 View 不会消费这个事件,直接返回 false。 - computeFitSystemWindows 方法计算自己是否消费这次事件
- 调用 internalSetPadding 方法设置 View 自己的 padding 值
Android11 的 computeSystemWindowInsets 迷糊,看看旧版本的 View#computeSystemWindowInsets()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public static final int SYSTEM_UI_LAYOUT_FLAGS = SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_HIDE_NAVIGATION | SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_FULLSCREEN;
public WindowInsets computeSystemWindowInsets(WindowInsets in, Rect outLocalInsets) {
if ((mViewFlags & OPTIONAL_FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWS) == 0 // fitsSystemWindow为false
|| mAttachInfo == null // view未attach
|| ((mAttachInfo.mSystemUiVisibility & SYSTEM_UI_LAYOUT_FLAGS) == 0 // SYSTEM_UI_LAYOUT_FLAGS未设置 没有设置内容沉浸到状态栏和虚拟导航栏两者
&& !mAttachInfo.mOverscanRequested)) {
outLocalInsets.set(in.getSystemWindowInsets());
return in.consumeSystemWindowInsets().inset(outLocalInsets);
} else {
// The application wants to take care of fitting system window for
// the content... however we still need to take care of any overscan here.
final Rect overscan = mAttachInfo.mOverscanInsets;
outLocalInsets.set(overscan);
return in.inset(outLocalInsets);
}
}
WindowInsets 分发在不同版本表现不同
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
@Override
public WindowInsets dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
insets = super.dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
if (insets.isConsumed()) {
return insets;
}
if (View.sBrokenInsetsDispatch) {
return brokenDispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
} else {
return newDispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
}
}
private WindowInsets brokenDispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
insets = getChildAt(i).dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
if (insets.isConsumed()) { // AndroidR之前版本,某个view consumed了,后面的view就不会dispatchApplyWindowInsets
break;
}
}
return insets;
}
private WindowInsets newDispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { // AndroidR及以上版本,兄弟间view consumed,不会影响其他兄弟view
getChildAt(i).dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
}
return insets;
}
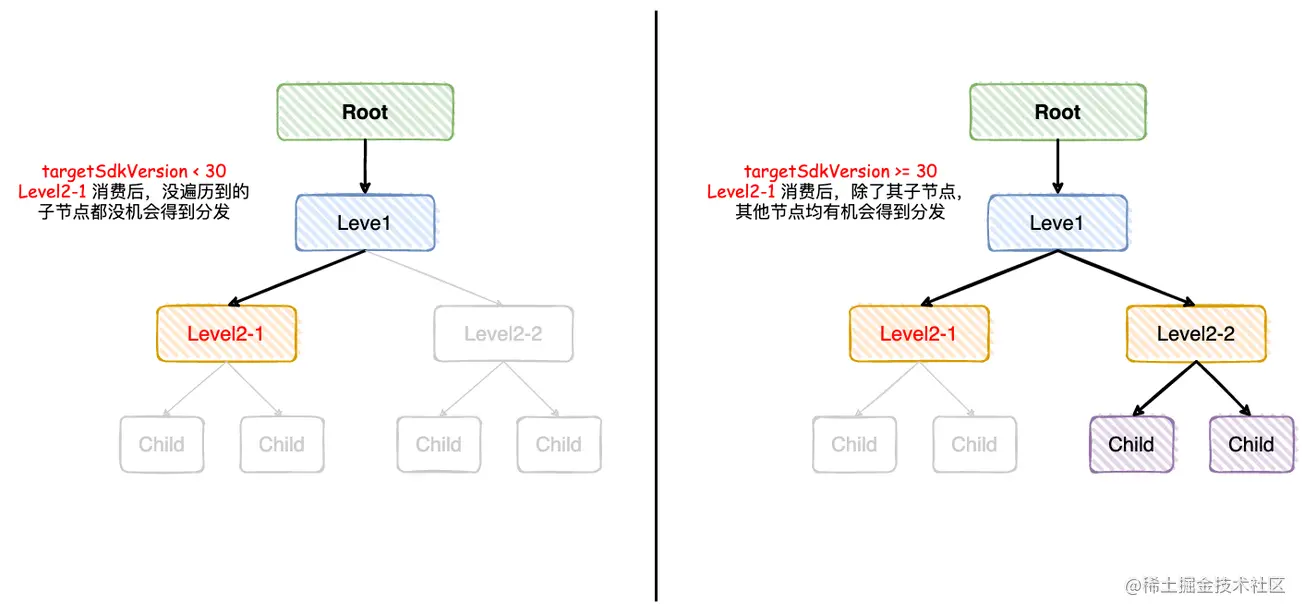
- AndroidR(Android11/API30) 之前版本
targetSdkVersion < 30 ,如果某个节点消费了 Insets,所有没遍历到的节点都不会收到 WindowInsets 的分发;即兄弟节点和子节点就不会 dispatchApplyWindowInsets 了 - AndroidR 及以上版本
当 app 运行在 Android 11 以上版本的设备上且 targetSdkVersion >=30,如果某个节点消费了 Insets,该节点的所有子节点不会收到 WindowInsets 分发,但其兄弟节点可以分发
WindowInsets 分发原理总结
- WindowInsets 分发简单总结
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
ViewRootImpl.scheduleTraversals() →
mTraversalRunnable(TraversalRunnable)→
doTraversal() →
performTraversals() →
dispatchApplyInsets() →
ViewGroup.dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets) →
View.dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets) →
View.mOnApplyWindowInsetsListener.onApplyWindowInsets(View,WindowInsets)或onApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets) →
View.fitSystemWindowsInt(Rect) →
View.computeFitSystemWindows() →
View.applyInsets(Rect)
- 自定义 view 复写 onApplyWindowInsets() 方法或设置了
mOnApplyWindowInsetsListener,默认的 fitsSystemWindows 行为就失效了;OnApplyWindowInsetsListener的onApplyWindowInsets优先于View.onApplyWindowInsets调用 - fitsSystemWindows 默认为 false
- 默认的 fitsSystemWindows 行为生效条件:setFitsSystemWindows(true) 或 xml 布局
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"(即设置了FITS_SYSTEM_WINDOWSflag) - 默认的 fitsSystemWindows 行为是为 view 添加 padding,该 View 本身的 padding 就失效了
系统控件对 WindowInsets 处理
- 基本布局
FrameLayout、LinearLayout、RelativeLayout等采用默认的行为,即设置 padding - 像
DrawerLayout、CollapsingToolbarLayout、CoordinatorLayout、AppBarLayout,ViewPager自定义了行为
见部分特殊View的WindowInsets分发逻辑.md
Ref
- WindowInsets 在 View 下的的分发(一)
https://www.jianshu.com/p/756e94fa2e09 - 令人困惑的 fitsSystemWindows 属性
http://www.jianshu.com/p/5cc3bd23be7b - 从 fitSystemWindows 说起
https://www.jianshu.com/p/9614a9ad0111 - 随手记 Android 沉浸式状态栏的踩坑之路
https://juejin.im/post/5a25f6146fb9a0452405ad5b - 带你彻底弄懂状态栏透明的细节 —— 深入分析 fitsSystemWindows
https://juejin.im/entry/59469d3f61ff4b006cf363ca - Why would I want to fitsSystemWindows?
https://medium.com/androiddevelopers/why-would-i-want-to-fitssystemwindows-4e26d9ce1eec - Android Detail:Window 篇—— WindowInsets 与 fitsSystemWindow
https://juejin.cn/post/7038422081528135687 - [Digging] Android Translucent Status Bar1/2/3 系列
- [Digging] Android Translucent Status Bar
- [Digging] Android Translucent Status Bar2
- [Digging] Android Translucent Status Bar3
- [Digging]android:fitsSystemWindows