TouchDelegate 扩大事件区域
扩大点击区域(TouchDelegate)
Padding
给 View 设置 padding 即可实现,有些情况不能设置 padding,只能多包几层 view 了
TouchDelegate
什么是 TouchDelegate?
在 Android 开发中,TouchDelegate 是一个帮助类,它用来处理这样的情况:当你希望一个视图拥有比实际视图边界更大的触摸区域时。它允许父布局代替子视图 (View) 处理触摸事件,这在提升可点击区域大小时非常有用,特别是当你有一个视图的大小太小,不易于触摸操作。
API
TouchDelegate
1
2
3
4
// TouchDelegate.java
public class TouchDelegate {
public TouchDelegate(Rect bounds, View delegateView) {}
}
- View delegateView:指需要扩大点击区域的控件。
- Rect bounds:指 delegateView 响应事件的区域,一般比它的原始范围要大。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// View.java
/**
* Sets the TouchDelegate for this View.
*/
public void setTouchDelegate(TouchDelegate delegate) {
mTouchDelegate = delegate;
}
TouchDelegate 是 View. Java 的成员变量。View 对象一般是 delegateView 的祖先控件 (不仅仅是父控件,可以是祖先控件);如果设置为 delegateView,会出现 StackOverflowError。
Rect
如何获取 bounds?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
val rect = Rect()
// 获取mClickMeButton占据的矩形区域在其父View(也就是root)中的相对坐标
mClickMeButton.getHitRect(rect)
// rect.left mClickMeButton左边的边相对于parent左边的距离
// rect.right mClickMeButton右边的边相对于parent左边的距离 rect.right = rect+left + mClickMeButton.width
// rect.top mClickMeButton上边的边相对于parent上边的距离
// rect.bottom mClickMeButton下边的边相对于parent上边的距离 rect.bottom = rect+top + mClickMeButton.height
// Rect(490, 946 - 590, 1046) // width/height为100px
inset 上下左右分别都扩大 2*dx, 2*dy
1
2
3
4
5
6
public void inset(int dx, int dy) {
left += dx;
top += dy;
right -= dx;
bottom -= dy;
}
View.GetHitRect (outRect) 它用于计算视图在其父容器坐标系中的触摸区域(也称为命中矩形)并将其放入给定的 Rect 对象中。这个计算考虑到了视图的位置(由 mLeft、mTop、mRight 和 mBottom 属性给出)以及视图可能的变换(如缩放或旋转)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
// View.java
public void getHitRect(Rect outRect) {
if (hasIdentityMatrix() || mAttachInfo == null) {
// 如果视图没有变换或没有附加信息,则直接使用视图本身的边界坐标
outRect.set(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom);
} else {
// 否则,创建一个临时的 RectF 来应用变换
final RectF tmpRect = mAttachInfo.mTmpTransformRect;
tmpRect.set(0, 0, getWidth(), getHeight());
getMatrix().mapRect(tmpRect); // 应用视图的变换
// 将变换后的矩形转换回整数坐标,并设置到 outRect 中
outRect.set((int) tmpRect.left + mLeft, (int) tmpRect.top + mTop,
(int) tmpRect.right + mLeft, (int) tmpRect.bottom + mTop);
}
}
场景
场景一:父控件区域足够大,扩大单个 Button 点击范围
如下图,将 Button 的点击区域扩大 100 dp 像素
| 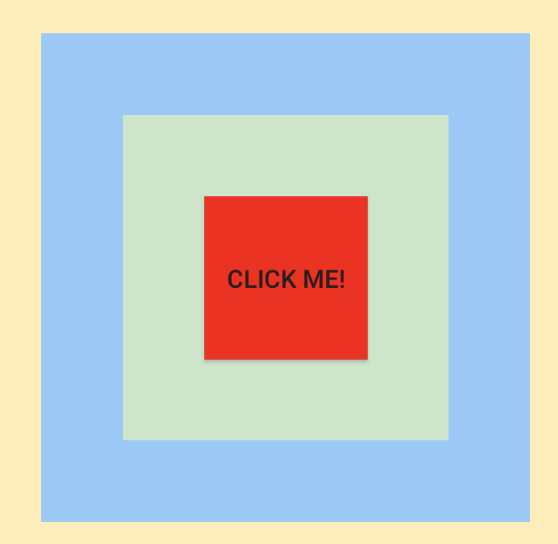 |
在红色和绿色区域都是可以点击的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
mClickMeButton.post {
// 方式1:
// val rect = Rect()
// ViewGroupUtils.getDescendantRect(mContentFrameLayout, mClickMeButton, rect)
// 方式2:
val rect = Rect()
// 获取iv_go占据的矩形区域在其父View(也就是root)中的相对坐标
mClickMeButton.getHitRect(rect)
rect.inset(-(50.dp), -(50.dp))
(mClickMeButton.parent as? ViewGroup)?.touchDelegate =
TouchDelegate(rect, mClickMeButton)
}
场景二:父控件区域很小,扩大单个 Button 点击范围
粉红色 ViewGroup 区域只比 Button 大一点,将 Button 点击区域扩大 500 像素。
| 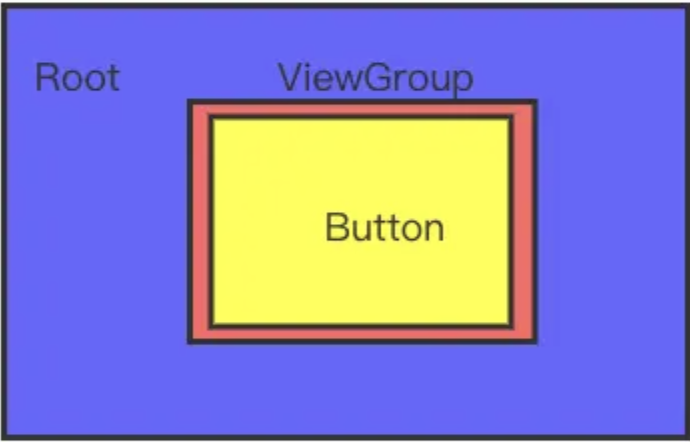 |
那就用 Root,而不是用 ViewGroup 设置 TouchDelegate
某 ViewGroup 想扩大它的后代 View 的点击区域,必须保证 ViewGroup 有足够的空间,否则寻找空间足够大的祖先控件来扩大后代 View 的点击区域
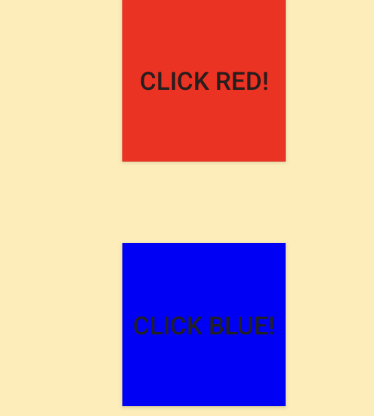
场景三:同时有多个 Button 想扩大点击区域
如下图,同时扩大 Button 1、Button 2 的点击区域 50 dp 像素:
|  |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
mContentLinearLayout.post {
val blueRect = Rect()
ViewGroupUtils.getDescendantRect(mContentLinearLayout, mBlueButton, blueRect)
blueRect.inset(-(50.dp), -(50.dp))
mContentLinearLayout.touchDelegate = TouchDelegate(blueRect, mBlueButton)
val redRect = Rect()
ViewGroupUtils.getDescendantRect(mContentLinearLayout, mRedButton, redRect)
redRect.inset(-(50.dp), -(50.dp))
mContentLinearLayout.touchDelegate = TouchDelegate(redRect, mRedButton)
}
只有 mRedButton 的点击区域扩大了 500 像素,mBlueButton 的点击区域并没有扩大,这是系统默认的 TouchDelegate 的局限性,只能给一个后代 View 扩大点击区域
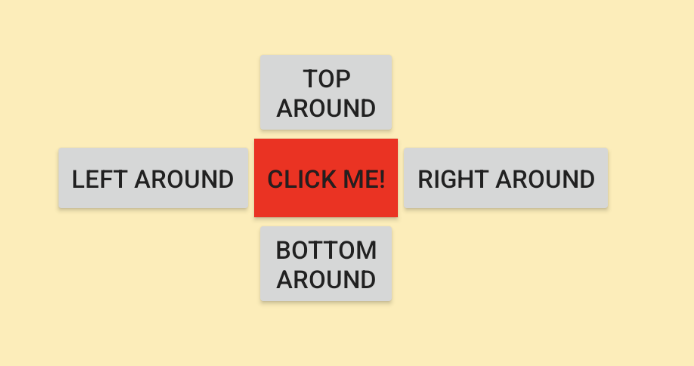
场景四:扩大点击区域的 Button 周围填充了其它 View
|  |
1
2
3
4
5
6
mClickMeButton.post {
val rect = Rect()
ViewGroupUtils.getDescendantRect(mContentFrameLayout, mClickMeButton, rect)
rect.inset(-500, -500)
mContentFrameLayout.touchDelegate = TouchDelegate(rect, mClickMeButton)
}
当用户点击在 left、top 等 View 上,即使已经将 Button 1 的点击扩大了 500 px,Button 1 也无法获取点击事件。因为只有当 ViewGroup 的所有子 View 都不处理事件,才会轮到 TouchDelegate 去分发事件。
原因: 事件分发的流程,TouchDelegate 是在 onTouchEvent() 里面的,是需要等 ViewGroup 的 dispatchTouchEvent 先执行完毕后才执行,如果 delegateView 的附近, ViewGroup 中如果已经有其他子 View 能响应事件,那就不会走到 TouchDelegate 中去
TouchDelegate 局限性
Android 7.0 bug
| [浅谈TouchDelegate的坑与用法. 最近要实现如下图所示的布局: | by Wan Xiao | Medium](https://medium.com/@wanxiao1994/%E6%B5%85%E8%B0%88touchdelegate%E7%9A%84%E5%9D%91%E4%B8%8E%E7%94%A8%E6%B3%95-851f6f9d535) |
在 delegateView 上 设置了 TouchDelegate
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
root.post {
val bounds = Rect()
// 获取iv_go占据的矩形区域在其父View(也就是root)中的相对坐标
iv_go.getHitRect(bounds)
// 计算扩展后的矩形区域Bounds相对于root的坐标,left、top、right、bottom分别为View2在各个方向上的扩展范围
bounds.left -= 20.dp
bounds.top -= 20.dp
bounds.right += 20.dp
bounds.bottom += 20.dp
iv_go.touchDelegate = TouchDelegate(bounds, iv_go)
}
直接报错了:
1
2
3
java.lang.StackOverflowError: stack size 8188KB at android.view.MotionEvent.isTargetAccessibilityFocus(MotionEvent.java:2502) at android.view.View.dispatchTouchEvent(View.java:14987) at android.view.TouchDelegate.onTouchEvent(TouchDelegate.java:151)
at android.view.View.onTouchEvent(View.java:16970)
at android.view.View.dispatchTouchEvent(View.java:15076)
为什么?
查看 View.onTouchEvent
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// View.java
public boolean onTouchEvent(@NonNull MotionEvent event) {
if (mTouchDelegate != null) {
if (mTouchDelegate.onTouchEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
}
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: // ...
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: // ...
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: // ...
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: // ...
}
}
如果有 TouchDelegate,调用 TouchDelegate的onTouchEvent();如果符合条件,又会调用 delegateView 的 dispatchTouchEvent(),就会陷入了死循环了,不停的调用来调用去,然后就 StackOverflowError 了。
一个 ViewGroup 下设置多个 TouchDelegate
现状: 默认 TouchDelegate 只能设置一个,后面设置的会覆盖前面的。
解决:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
class ExpandTouchAreaDelegate(private val rootView: View) :
TouchDelegate(null, rootView) {
private var mDelegateView: View? = null
private var mDelegateTargeted = false
private val targetView = mutableMapOf<View, (rect: Rect) -> Rect>()
fun addTargetView(view: View, changeBound: (rect: Rect) -> Rect) {
targetView[view] = changeBound
}
override fun onTouchEvent(event: MotionEvent): Boolean {
val x = event.x.toInt()
val y = event.y.toInt()
var sendToDelegate = false
var handled = false
when (event.action) {
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> {
mDelegateView = isInTarget(rootView, x, y)
mDelegateTargeted = mDelegateView != null
sendToDelegate = true
}
MotionEvent.ACTION_UP,
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> {
sendToDelegate = mDelegateTargeted
}
MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL -> {
sendToDelegate = mDelegateTargeted
mDelegateTargeted = false
}
else -> {}
}
if (sendToDelegate) {
mDelegateView?.let {
event.setLocation((it.width / 2).toFloat(), (it.height / 2).toFloat())
handled = it.dispatchTouchEvent(event)
}
}
return handled
}
private fun isInTarget(rootView: View, x: Int, y: Int): View? {
targetView.keys.forEach {
if (targetView[it]?.invoke(rectInParentView(rootView, it))?.contains(x, y) == true)
return it
} return null
}
private fun rectInParentView(parent: View, child: View): Rect {
val childRect = Rect()
child.getGlobalVisibleRect(childRect)
val parentLocation = IntArray(2)
parent.getLocationOnScreen(parentLocation)
childRect.offset(-parentLocation[0], -parentLocation[1])
return childRect
}
}
支持触摸拖动的 TouchDelegate
原理
先看 View.OnTouchEvent (MotionEvent event)
- 如果设置了 TouchDelegate,则调用它的 onTouchEvent,如果返回 true,调用结束,否则往下走
- 处理 OnClickListener,OnLongClickListener 等事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// View.java
public boolean onTouchEvent(@NonNull MotionEvent event) {
// ...
// 如果设置了mTouchDelegate,先交给mTouchDelegate处理
if (mTouchDelegate != null) {
if (mTouchDelegate.onTouchEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
}
// 处理click、longclick
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: // ...
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: // ...
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: // ...
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: // ...
}
}
TouchDelegate.OnTouchEvent (MotionEvent event):
- Down 事件,判断手指是否落在事件扩大范围内
- 非 Down 事件,判断手指是否超出了 slopBounds,slopBounds 是在 bounds 的区域上再扩大一定的范围,如果超出,向 delegateView 发送一个负值事件坐标;所以触摸事件即使超出了 mBounds,只要没有超出 mBounds+mSlop,delegateView 还是可以响应点击事件,否则收到的是个负值 event 坐标,无法响应点击事件
- 如果分发事件,将事件坐标设置为 delegateView 的中心点
- 如果手机超出了最大范围,将事件坐标设置为负值分发,那么 delegateView 就不会处理该点击事件了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
// TouchDelegate.java
private View mDelegateView;
private Rect mBounds;
private Rect mSlopBounds;
public TouchDelegate(Rect bounds, View delegateView) {
// delegateView相对于parent的坐标
mBounds = bounds;
// 表示用户在触摸屏上滑动时需要超过的最小距离阈值,该滑动才会被识别为真正的滚动而非点击。三星A51是17px
mSlop = ViewConfiguration.get(delegateView.getContext()).getScaledTouchSlop();
// mSlopBounds复制bounds
mSlopBounds = new Rect(bounds);
// mSlopBounds将bounds的四周扩大17px
mSlopBounds.inset(-mSlop, -mSlop);
// 要扩大的view
mDelegateView = delegateView;
}
public boolean onTouchEvent(@NonNull MotionEvent event) {
int x = (int)event.getX();
int y = (int)event.getY();
boolean sendToDelegate = false; // 是否让delegate处理
boolean hit = true;
boolean handled = false;
switch (event.getActionMasked()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: // down事件
// 判断手指是否落在扩大范围内
mDelegateTargeted = mBounds.contains(x, y);
sendToDelegate = mDelegateTargeted;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
sendToDelegate = mDelegateTargeted;
if (sendToDelegate) {
Rect slopBounds = mSlopBounds;
// 非down事件,说明移动了,看是否在mSlop内,如果不在,就说明该手势是滑动了,不是点击,hit设置为false
if (!slopBounds.contains(x, y)) {
hit = false;
}
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
sendToDelegate = mDelegateTargeted;
mDelegateTargeted = false;
break; }
if (sendToDelegate) { // 需要发送事件给delegateView
if (hit) { // 命中
// Offset event coordinates to be inside the target view
// 将事件左边设置为delegateView的中心
event.setLocation(mDelegateView.getWidth() / 2, mDelegateView.getHeight() / 2);
} else { // 未命中
// Offset event coordinates to be outside the target view (in case it does
// something like tracking pressed state)
int slop = mSlop;
// 将事件设置为负数,不在delegateView中,不会响应delegate的click事件了
event.setLocation(-(slop * 2), -(slop * 2));
}
// 分发事件给delegateView
handled = mDelegateView.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
return handled;
}
MotionEvent.setLocation(newX, newY)用于将新的坐标设置给 MotionEvent;这对于修改事件的位置很有用,比如将触摸事件转发到另一个视图时。原理是用新的坐标减去旧的坐标得到插值 delt 去 offsetLocation
总结
- 设置 TouchDelegate,必须在需要扩大点击区域的 View 的祖先 View 上;设置在 delegateView 上会出现
StackOverflowError。 - 如果祖先 View 空间比子 View 需要的区域还小,无法正确扩大点击区域。
- 如果 View 周边有其它的 View 消耗事件,那么扩大点击区域可能无效。
- 系统默认情况,无法给多个 View 扩大点击区域。
- 设置了 TouchDelegate,当手指在扩大范围内按下,但在扩大范围外抬起,如果是在
mBounds+ViewConfiguration.get(delegateView.getContext()).getScaledTouchSlop()内,那么点击事件还是能响应的,如果在这之外了就不能响应事件了
封装
去掉 getScaledTouchSlop,只在?
Ref
- juejin.cn/post/6940985171000688653
- Android TouchDelegate 详解及优化
https://www.jianshu.com/p/cb5181418c7a