Lint
Lint
Lint 介绍
Android Studio 提供了 lint 工具来确认和纠正存在结构问题的代码,不需要执行你的 app 和写 test cases。每个被 lint 工具探测出来的问题会报告成一个描述信息和一个严重级别,
官网 lint 教程
https://developer.android.com/studio/write/lint.html
最新的 lint 规则
http://tools.android.com/tips/lint-checks
Lint 工作流程
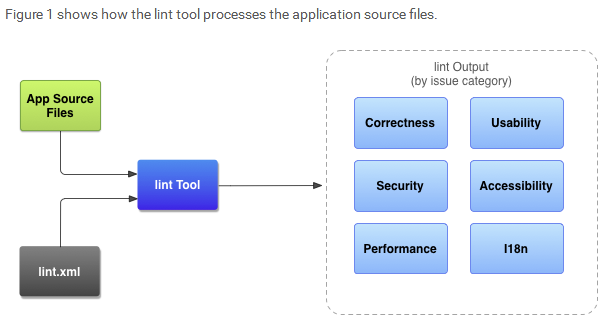
lint 扫描工作流程,如下图所示:
Application source files 组成 Android 项目文件,包括 Java、XML、icons 和 Proguard 配置文件。
The
lint.xmlfile lint 扫描规则配置文件,用来指定你想排除和自定义问题的严重级别The lint tool 一个静态代码扫描工具,你能在 Android Studio 中运行,也能在命令行中运行。lint 工具用来扫描检测存在质量和影响性能的的问题代码。强烈建议你在发布你的应用前纠正任何 lint 工具探测出来的问题
Results of lint checking 你能在 console 或者在 Android Studio 的
Inspection Results窗口查看
Lint 使用
命令行使用 Lint
- 针对一个 project 文件扫描
1
lint [flags] <project directory>
- 针对某一个问题(也叫 issue ID)的扫描,如对
myproject项目中的MissingPrefix(扫描 xml 属性中缺少了 android 名称空间前缀)的扫描:
1
lint --check MissingPrefix myproject
- 查看所有
flags和命令行的参数:
1
lint --help
在 Gradle 中使用 Lint
- 所有的
build variants(配置的 buildTypes)
1
gradlew lint
- 指定一个
build variant
1
gradlew lintDebug
配置 lint 压制警告
默认情况下,lint 扫描 lint 所支持多所有 issues。
你能配置 lint 不同的级别:
- Globally (entire project)
- Project module
- Production module
- Test module
- Open files
- Class hierarchy
- Version Control System (VCS) scopes
在 Android Studio 中配置 lint
Analyze→Inspect Code→Inspection Results
配置 lint 文件
指定 lint 检测参数在 lint.xml 文件中。lint.xml 由封闭的 <lint> 标签作为根节点,包含由一个或多个 <issue>,每个 <issue> 定义必须的 id 属性:
1
2
3
4
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<lint>
<!-- list of issues to configure -->
</lint>
你可以在 <issue> 标签,改变该 issue 的严重级别或者 disable lint check 通过 severity 属性
Tip: 查看 lint 支持的所有 issues,用
lint --list命令
一个简单的 lint.xml 案例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<lint>
<!-- Disable the given check in this project -->
<issue id="IconMissingDensityFolder" severity="ignore" />
<!-- Ignore the ObsoleteLayoutParam issue in the specified files -->
<issue id="ObsoleteLayoutParam">
<ignore path="res/layout/activation.xml" />
<ignore path="res/layout-xlarge/activation.xml" />
</issue>
<!-- Ignore the UselessLeaf issue in the specified file -->
<issue id="UselessLeaf">
<ignore path="res/layout/main.xml" />
</issue>
<!-- Change the severity of hardcoded strings to "error" -->
<issue id="HardcodedText" severity="error" />
</lint>
配置 lint 检测 Java 和 XML 源文件
你能配置 lint 不检测 Java 和 XML 源文件。
在 Settings→Editor→Inspections 可以配置
- 配置 lint 检测 Java
让 lint 不检测 Java 的类或者方法,加上@SuppressLint注解。
案例:不检测NewApi在onCreate方法,其他方法检测:
1
2
3
4
5
6
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
- 抑制所有的 lint issues,用
all
1
@SuppressLint("all")
- 配置 lint 检测 XML
用tool:ignore来关闭在 xml 中的 lint 检测,在你的lint.xml中添加下面名称空间以便 lint 工具认识该属性
1
namespace xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
下面这个案例展示你如何关闭 lint 检测 UnusedResourcesissue 在 <LinearLayout> 在 xml 的布局中,这个 igonre 属性可以在子节点中继承:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
tools:ignore="UnusedResources" >
<TextView
android:text="@string/auto_update_prompt" />
</LinearLayout>
检测多个,用逗号分隔:
1
tools:ignore="NewApi,StringFormatInvalid"
抑制所有,用 all:
1
tools:ignore="all"
用 Gradle 配置 lint 选项
google.github.io/android-gradle-dsl/current/com.android.build.gradle.internal.dsl.LintOptions.html
Android plugin for Gradle 允许你配置 lint 选项:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
def configDir = "${project.rootDir}/config/quality"
def reportsDir = "${project.buildDir}/reports"
// http://developer.android.com/intl/zh-cn/tools/help/lint.html
lintOptions {
abortOnError false // lint扫描到errors是否终止退出
absolutePaths true // 是否lint应该展示full path在errors ouput。默认相对路径。
checkReleaseBuilds true
// 是否在release build检测fatal errors,默认为true,一旦检测到严重级别为'fatal'的errors,release build立即终止
explainIssues true // 是否lint需要包含issue errors的解释(HTML和XML的报告故意做了这个解释,可以忽略)
lintConfig file("$configDir/lint/lint.xml") // 自己配置的lint.xml
xmlReport true // 默认为true
htmlReport true // 默认为true
xmlOutput file("$reportsDir/lint/lint-result.xml") // xml报告输出路径
htmlOutput file("$reportsDir/lint/lint-result.html") // html扫描报告输出路径
ignoreWarnings false // lint是否只扫描error而忽略errors
noLines true // 是否lint应该在errors的地方包含源码的行数(默认true)
// Turns off checks for the issue IDs you specify.
// disable 'TypographyFractions','TypographyQuotes'
// Turns on checks for the issue IDs you specify. These checks are in
// addition to the default lint checks.
// enable 'RtlHardcoded','RtlCompat', 'RtlEnabled'
// To enable checks for only a subset of issue IDs and ignore all others,
// list the issue IDs with the 'check' property instead. This property overrides
// any issue IDs you enable or disable using the properties above.
// check 'NewApi', 'InlinedApi'
// If set to true, turns off analysis progress reporting by lint.
// quiet true
}
baseline
手动允许 inspections
手动允许 lint 配置,通过 Analyze → Inspect Code,结果在 Inspection Results 窗口展示。
设置 inspection scope 和 profile
选择你想要分析的文件 (inspection scope) 和你想要允许的安全规则 (inspection profile):
- 在 Android,打开你的 project,选择你想要分析的 project,一个 folder,或一个 file。
- 在菜单中,选择
Analyze → Inspect Code - 在
Specify Inspection Scope对话框,review 你的设置 (不同 AS 版本可能不太一样)
- Under Inspection profile, keep the default profile (Project Default).
- Click OK 运行这个 Inspection
Review 和编辑 inspection profile
Android Lint 可以忽略的检查规则
1、ContentDescription
Summary: Image without contentDescription
ImageView 和 ImageButton 控件缺少 android:contentDescription 属性;对于一些视力有障碍的用户,由于这两个控件没有 text,这时用户点击这个控件。开了 Accessible 权限,android 系统会自动使用人声朗读控件上 android:contentDescription 属性说指向的内容。
Priority: 3 / 10
Severity: Warning
Category: Accessibility
Non-textual widgets like ImageViews and ImageButtons should use the
contentDescription attribute to specify a textual description of the widget
such that screen readers and other accessibility tools can adequately describe
the user interface.
Note that elements in application screens that are purely decorative and do
not provide any content or enable a user action should not have accessibility
content descriptions. In this case, just suppress the lint warning with a
tools:ignore=”ContentDescription” attribute.
Note that for text fields, you should not set both the hint and the
contentDescription attributes since the hint will never be shown. Just set the
hint. See
http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/accessibility/checklist.html#spec
al-cases.
2、RtlHardcoded
Summary: Using left/right instead of start/end attributes
用 gravity、paddingLeft、layout_marginLeft 等 left,right 用 start,end 代替。保证 right-to-left 布局能用
Priority: 5 / 10
Severity: Warning
Category: Internationalization:Bidirectional Text
Using Gravity#LEFT and Gravity#RIGHT can lead to problems when a layout is
rendered in locales where text flows from right to left. Use Gravity#START and
Gravity#END instead. Similarly, in XML gravity and layout_gravity attributes,
use start rather than left.
For XML attributes such as paddingLeft and layout_marginLeft, use paddingStart
and layout_marginStart. NOTE: If your minSdkVersion is less than 17, you
should add both the older left/right attributes as well as the new start/right
attributes. On older platforms, where RTL is not supported and the start/right
attributes are unknown and therefore ignored, you need the older left/right
attributes. There is a separate lint check which catches that type of error.
| (Note: For Gravity#LEFT and Gravity#START, you can use these constants even when targeting older platforms, because the start bitmask is a superset of the left bitmask. Therefore, you can use gravity=”start” rather than gravity=”left | start”.) |
3、RtlSymmetry
Summary: Padding and margin symmetry
如果指定了 margin 或者 padding 的一半,left 和 right 应该都要指定,对称性
Priority: 6 / 10
Severity: Warning
Category: Internationalization:Bidirectional Text
If you specify padding or margin on the left side of a layout, you should
probably also specify padding on the right side (and vice versa) for
right-to-left layout symmetry.
4、HardcodedText
Summary: Hardcoded text
在布局中硬编码
Priority: 5 / 10
Severity: Warning
Category: Internationalization
Hardcoding text attributes directly in layout files is bad for several
reasons:
- When creating configuration variations (for example for landscape or
portrait)you have to repeat the actual text (and keep it up to date when
making changes) - The application cannot be translated to other languages by just adding new
translations for existing string resources.
There are quickfixes to automatically extract this hardcoded string into a
resource lookup.
5、SetTextI18n
Summary: TextView Internationalization
Priority: 6 / 10
Severity: Warning
Category: Internationalization
When calling TextView#setText
- Never call Number#toString() to format numbers; it will not handle fraction
separators and locale-specific digits properly. Consider using String#format
with proper format specifications (%d or %f) instead.
不要调用Number#toString()格式化数字,它不会处理小数点分隔符和地区数字特性。考虑用String#format()加上格式符 (%d 或 %f) - Do not pass a string literal (e.g. “Hello”) to display text. Hardcoded text
can not be properly translated to other languages. Consider using Android
resource strings instead.
不要传递一个 String 文本。硬编码不好翻译成其他语言,考虑用 Android resource 替代。 - Do not build messages by concatenating text chunks. Such messages can not be
properly translated.
More information:
http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/resources/localization.html
SetJavaScriptEnabled
Summary: Using setJavaScriptEnabled
开启 setJavaScriptEnabled 可能导致 XSS 漏洞
Priority: 6 / 10
Severity: Warning
Category: Security
Your code should not invoke setJavaScriptEnabled if you are not sure that your
app really requires JavaScript support.
More information:
http://developer.android.com/guide/practices/security.html
Android Lint 检查规则
官网最新 lint check 规则
http://tools.android.com/tips/lint-checks
Correctness 正确性检查
1、AdapterViewChildren
Summary: AdapterViews cannot have children in XML
确保没有在 XML 文件中定义 AdapterViews 的子 view
Priority: 10 / 10
Severity: Warning
Category: Correctness
AdapterViews such as ListViews must be configured with data from Java code,
such as a ListAdapter.
More information:
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/AdapterView.html
2、OnClick
Summary: onClick method does not exist
确保 XML 文件声明的 OnClick 的调用函数在代码中实际存在(必须以 public 修饰,一个参数为 View)
Priority: 10 / 10
Severity: Error
Category: Correctness
The onClick attribute value should be the name of a method in this View’s
context to invoke when the view is clicked. This name must correspond to a
public method that takes exactly one parameter of type View.
Must be a string value, using ‘;’ to escape characters such as ‘\n’ or
‘\uxxxx’ for a unicode character.
3、StopShip
Summary: Code contains STOPSHIP marker
代码注释中有// SHOPSHIP 的地方应该被 lint 扫描,需要解决掉
Priority: 10 / 10
Severity: Warning
Category: Correctness
NOTE: This issue is disabled by default!
You can enable it by adding –enable StopShip
Using the comment // STOPSHIP can be used to flag code that is incomplete but
checked in. This comment marker can be used to indicate that the code should
not be shipped until the issue is addressed, and lint will look for these.
4、MissingPermission
Summary: Missing Permissions
代码中需要运行权限的地方没有加权限
Priority: 9 / 10
Severity: Error
Category: Correctness
This check scans through your code and libraries and looks at the APIs being
used, and checks this against the set of permissions required to access those
APIs. If the code using those APIs is called at runtime, then the program will
crash.
Furthermore, for permissions that are revocable (with targetSdkVersion 23),
client code must also be prepared to handle the calls throwing an exception if
the user rejects the request for permission at runtime.
5、MissingSuperCall
Summary: Missing Super Call
需要调用 super. 地方
Priority: 9 / 10
Severity: Error
Category: Correctness
Some methods, such as View#onDetachedFromWindow, require that you also call
the super implementation as part of your method.
6、ResAuto
Summary: Hardcoded Package in Namespace
资源文件中的 namespace 不要 hardcode,需要用 http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto,不要用以前的那种加包名的方式
Priority: 9 / 10
Severity: Fatal
Category: Correctness
In Gradle projects, the actual package used in the final APK can vary; for
example,you can add a .debug package suffix in one version and not the other.
Therefore, you should not hardcode the application package in the resource;
instead, use the special namespace http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto
which will cause the tools to figure out the right namespace for the resource
regardless of the actual package used during the build.
7、SuspiciousImport
Summary: ‘import android.R’ statement
检查代码中是否有 'import android.R'
Priority: 9 / 10
Severity: Warning
Category: Correctness
Importing android.R is usually not intentional; it sometimes happens when you
use an IDE and ask it to automatically add imports at a time when your
project’s R class it not present.
Once the import is there you might get a lot of “confusing” error messages
because of course the fields available on android.R are not the ones you’d
expect from just looking at your own R class.
8、UsesMinSdkAttributes
Summary: Minimum SDK and target SDK attributes not defined
检查是否在 AndroidManifest.xml 文件中定义了 minimum SDK 和 target SDK 这两个属性
Priority: 9 / 10
Severity: Warning
Category: Correctness
The manifest should contain a element which defines the minimum API
Level required for the application to run, as well as the target version (the
highest API level you have tested the version for.)
More information:
http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/manifest/uses-sdk-element.html
9、WrongViewCast
Summary: Mismatched view type
检查对 XML 中定义的 View 在 Java 代码中进行强转换时是否正确
Priority: 9 / 10
Severity: Fatal
Category: Correctness
Keeps track of the view types associated with ids and if it finds a usage of
the id in the Java code it ensures that it is treated as the same type.
10、AaptCrash
Summary: Potential AAPT crash
不要在 style 文件中定义 android:id 属性,可以在 ids.xml 文件中定义
Priority: 8 / 10
Severity: Fatal
Category: Correctness
Defining a style which sets android:id to a dynamically generated id can cause
many versions of aapt, the resource packaging tool, to crash. To work around
this, declare the id explicitly with instead.
More information:
https://code.google.com/p/android/issues/detail?id=20479
11、GradleCompatible
Summary: Incompatible Gradle Versions
不兼容的 Gradle 版本
Priority: 8 / 10
Severity: Error
Category: Correctness
There are some combinations of libraries, or tools and libraries, that are
incompatible, or can lead to bugs. One such incompatibility is compiling with
a version of the Android support libraries that is not the latest version (or
in particular, a version lower than your targetSdkVersion.)
12、GradlePluginVersion
Summary: Incompatible Android Gradle Plugin
不兼容的 Android Gradle Plugin 版本
Priority: 8 / 10
Severity: Error
Category: Correctness
Not all versions of the Android Gradle plugin are compatible with all versions
of the SDK. If you update your tools, or if you are trying to open a project
that was built with an old version of the tools, you may need to update your plugin version number.
13、IllegalResourceRef
Summary: Name and version must be integer or string, not resource
versionCode 和 versionName 必须是 integer 或 string
Priority: 8 / 10
Severity: Warning
Category: Correctness
For the versionCode attribute, you have to specify an actual integer literal;
you cannot use an indirection with a @dimen/name resource. Similarly, the
versionName attribute should be an actual string, not a string resource url.
14、MergeMarker
Summary: Code contains merge marker
代码中存在 merge 标志(<<<),这种情况一般是意外留下的
Priority: 8 / 10
Severity: Error
Category: Correctness
Many version control systems leave unmerged files with markers such as <<< in
the source code. This check looks for these markers, which are sometimes
accidentally left in, particularly in resource files where they don’t break
compilation.
15、MissingLeanbackLauncher
16、MissingRegistered
…
自定义 Lint 规则
自定义 lint 接入方案
全局
把此 jar 拷贝到 ~/.android/lint/ 目录中即可
AAR 壳
另一种实现方式是将 jar 置于一个 aar 中,如果某个工程想要接入执行自定义的 lint 规则,只需依赖这个发布后的 aar 即可,如此一来,新增的 lint 规则就可将影响范围控制在单个项目内了。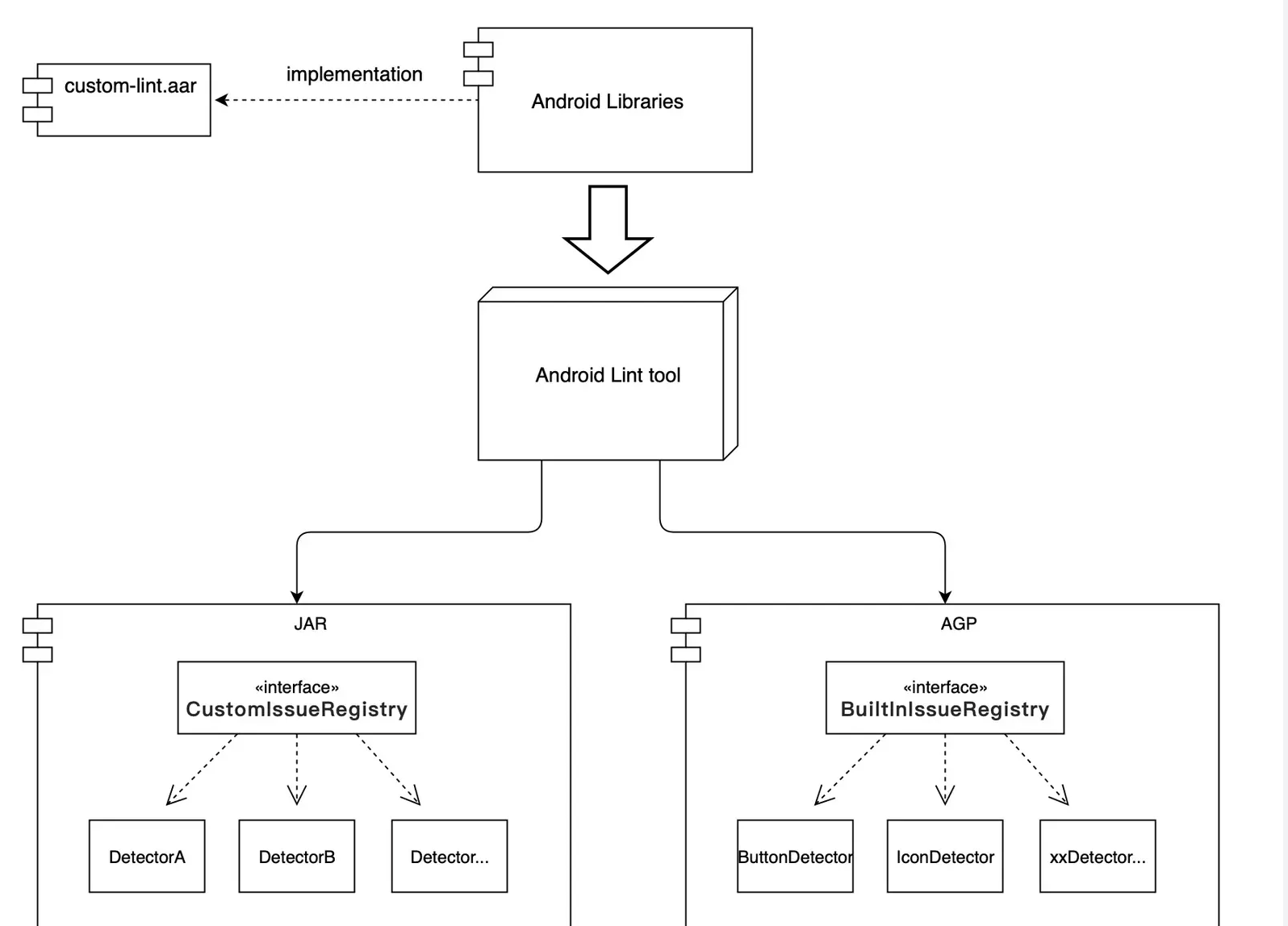
自定义 Lint 规则
创建 java-library & 配置 lint 依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
plugins {
id "java-library"
id "kotlin"
}
java {
sourceCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17
targetCompatibility = JavaVersion.VERSION_17
}
jar {
manifest {
// Only use the "-v2" key here if your checks have been updated to the
// new 3.0 APIs (including UAST)
attributes("Lint-Registry-V2": "me.hacket.lint.todo.MyCustomIssueRegistry")
}
}
configurations {
lintJarOutput
}
dependencies {
lintJarOutput files(jar)
}
defaultTasks "assemble"
dependencies {
def kotlin_version = "1.9.10"
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:$kotlin_version"
def lint_version = "31.1.2"
// 官方提供的Lint相关API,并不稳定,每次AGP升级都可能会更改,且并不是向下兼容的
compileOnly "com.android.tools.lint:lint-api:$lint_version"
// 目前Android中内置的lint检测规则
compileOnly "com.android.tools.lint:lint-checks:$lint_version}"
testImplementation "com.android.tools.lint:lint-tests:$lint_version"
testImplementation "junit:junit:4.13.2"
}
如果你创建 module 时选择的是 kotlin 语言,还可能会遇到以下这个坑: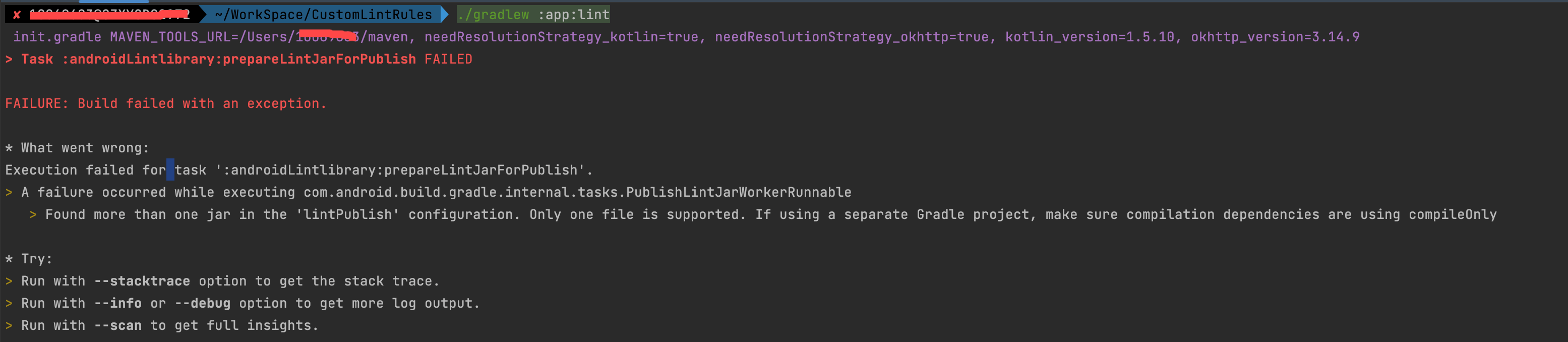
只需要将 kotlin 标准库依赖方式改为 compileOnly 即可:
compileOnly “org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:$kotlin_version”
编写 lint-rules
- KotlinTodoDetector
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
@Suppress("UnstableApiUsage")
class KotlinTodoDetector : Detector(), Detector.UastScanner {
override fun getApplicableMethodNames(): List<String> {
return listOf("TODO")
}
override fun visitMethodCall(context: JavaContext, node: UCallExpression, method: PsiMethod) {
println("KotlinTodoDetector >>> matched TODO in [${method.parent.containingFile}]")
if (context.evaluator.isMemberInClass(method, "kotlin.StandardKt__StandardKt")) {
val deleteFix = fix()
.name("Delete this TODO method")
.replace()
.all()
.with("")
.build()
context.report(
ISSUE,
context.getLocation(node),
"You must fix `TODO()` first.", deleteFix
)
}
}
companion object {
private const val ISSUE_ID = "KotlinTodo"
val ISSUE = Issue.create(
ISSUE_ID,
"Detecting `TODO()` method from kotlin/Standard.kt.",
"""
You have unimplemented method or undo work marked by `TODO()`,
please implement it or remove dangerous TODO.
""",
category = Category.CORRECTNESS,
priority = 9,
severity = Severity.ERROR,
implementation = Implementation(KotlinTodoDetector::class.java, Scope.JAVA_FILE_SCOPE),
)
}
}
我们需要检测的对象是 java/kt 源文件,这里只需要继承自 Detector 并实现 Detector.UastScanner 接口即可。当然,我们也可以选择按组合方式实现更多其他 Scanner,这取决于我们希望扫描的文件范围。目前支持的扫描范围有:
- UastScanner:扫描 Java 或者 kotlin 源文件
- ClassScanner:扫描字节码或编译的类文件
- BinaryResourceScanner:扫描二进制资源文件(res/raw/bitmap 等)
- ResourceFolderScanner:扫描资源文件夹
- XmlScanner:扫描 xml 格式文件
- GradleScanner:扫描 Gradle 格式文件
- OtherFileScanner:其他类型文件
检测 java/kt 源文件,可以通过 getApplicableMethodNames 指定扫描的方法名,其他还有 类名、文件名、属性名 等等,并通过 visitMethodCall 接受检测到的方法。这里我们只需要检测 Kotlin 标准库中的 Standard.kt 中的 TODO 方法,匹配到后通过 context.report 来报告具体问题,这里需要指定一个 Issue 对象来描述问题具体信息,相关字段如下:
- id : 唯一值,应该能简短描述当前问题。利用 Java 注解或者 XML 属性进行屏蔽时,使用的就是这个 id。
- summary : 简短的总结,通常 5-6 个字符,描述问题而不是修复措施。
- explanation : 完整的问题解释和修复建议。
- category : 问题类别。常见的有:CORRECTNESS、SECURITY、COMPLIANCE、USABILITY、LINT 等等。
- priority : 优先级。1-10 的数字,10 为最重要/最严重。
- severity : 严重级别:Fatal, Error, Warning, Informational, Ignore。
- Implementation : 为 Issue 和 Detector 提供映射关系,Detector 就是当前 Detector。声明扫描检测的范围 Scope,Scope 用来描述 Detector 需要分析时需要考虑的文件集,包括:Resource 文件或目录、Java 文件、Class 文件等。
还可以设置出现该 issue 上报时的默认解决方案 fix,这里我们创建了一个 deleteFix 实现开发者快速移除报错位置的 TODO 代码。
最后,只需要自定义一个 Registry 声明自己需要检测的 Issues 即可:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
@Suppress("UnstableApiUsage")
class MyCustomIssueRegistry : IssueRegistry() {
init {
println("MyCustomIssueRegistry, run...")
}
override val issues: List<Issue>
get() = listOf(
// JcenterDetector.ISSUE,
KotlinTodoDetector.ISSUE,
)
override val minApi: Int
get() = 8 // works with Studio 4.1 or later; see com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Api / ApiKt
override val api: Int
get() = CURRENT_API
override val vendor: Vendor
get() = Vendor(
vendorName = "hacket",
contact = "shengfanzeng@gmail.com"
)
}
Lint 发布
出于灵活性和可用性角度考虑自然选择 aar 壳的方式。经过这几年 lint 的发展,实现起来也很简单:只需要创建一个 Android-Library module,然后稍微配置下 gradle 即可:
1
2
3
dependencies {
lintPublish(project(":lint"))
}
此处的 lintPublish 配置允许我们引用另一个 module,它会获取该组件输出的 jar 并将其打包为 lint.jar 然后放到自身的 AAR 中
Lint 接入
在 app 模块中依赖一下 androidLintlibrary 这个组件
./gradlew :app:lint 即可看到控制台输出以下内容: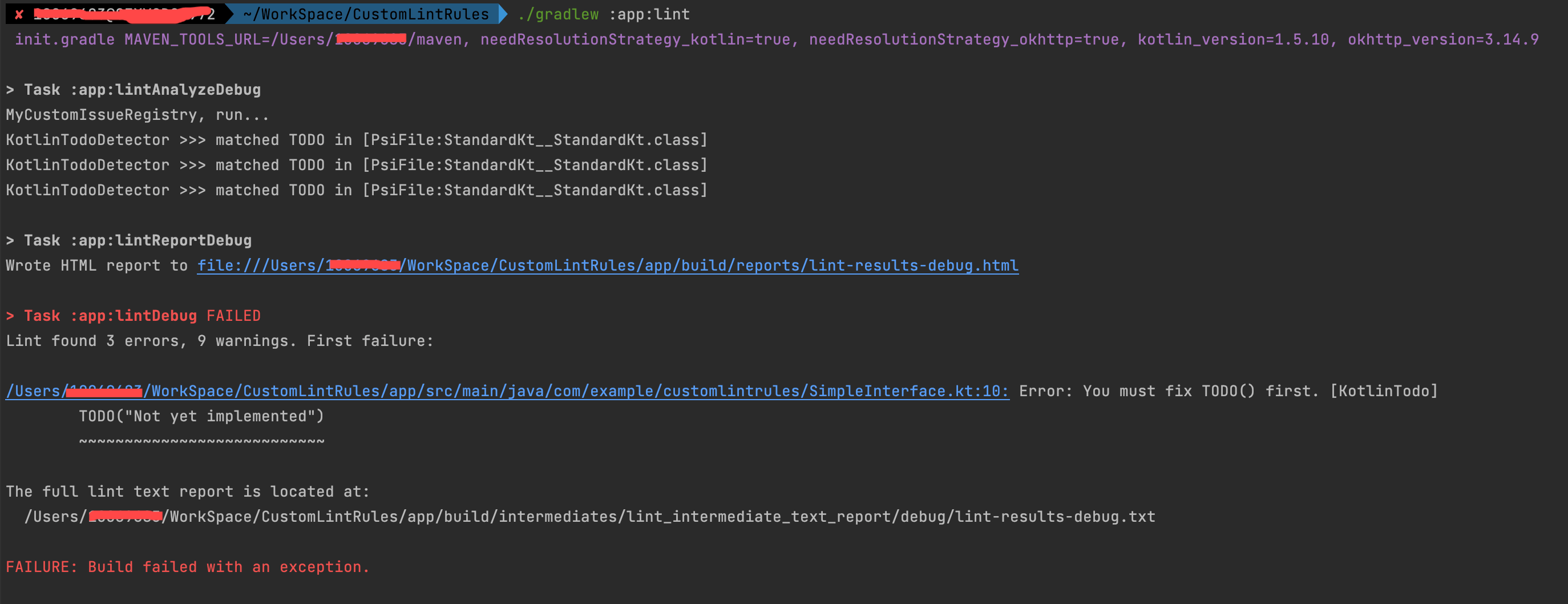
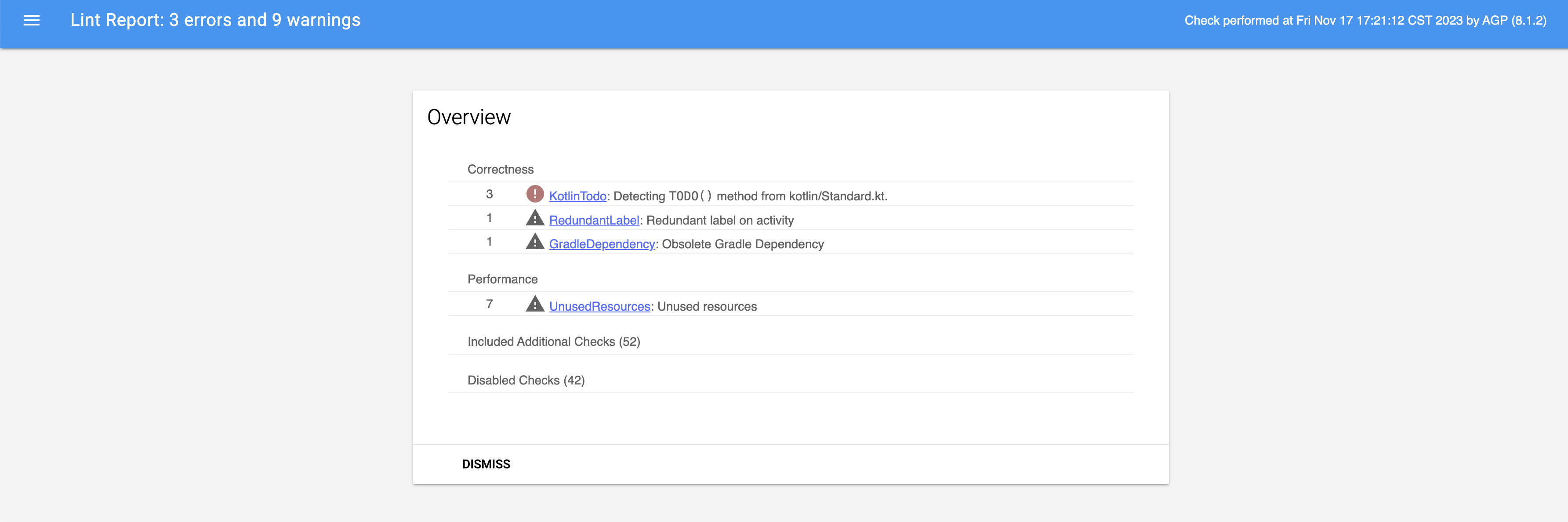
AGP4.0 lint
AGP 4.0 开始,Android studio 支持了独立的 com.android.lint 插件,进一步降低了自定义 lint 的成本,通过在 manifest 中注册自定义 Registry 改为通过服务表单注册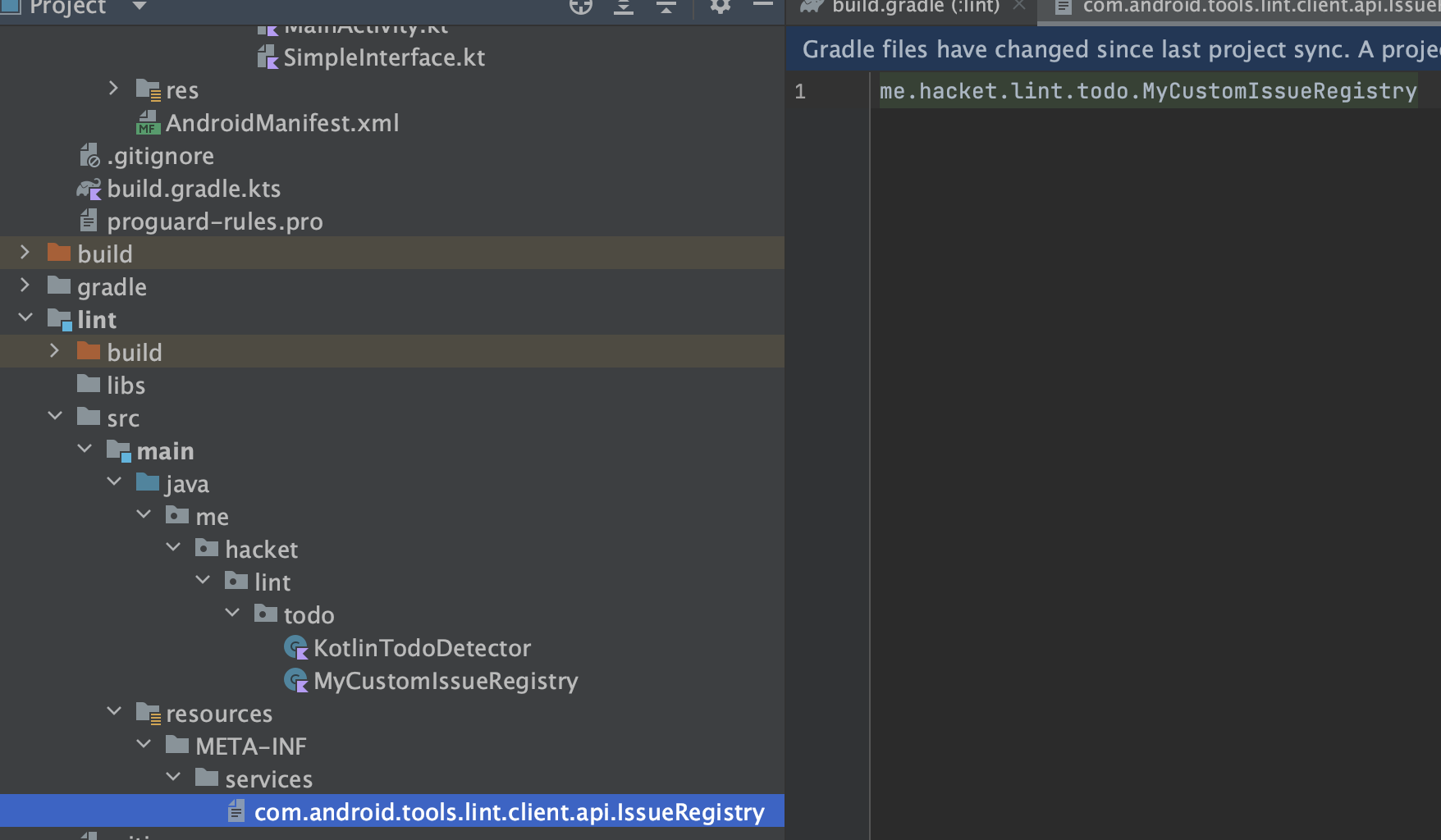
1
2
3
plugins {
id 'com.android.lint'
}
示例
用 Logger 替代 Log
Ref
- Android Lint(官方)
- Android Lint API Guide(官方)
- Android 自定义 Lint 实践
http://tech.meituan.com/android_custom_lint.html - 浅谈 Android 自定义 Lint 规则的实现 (一)
http://www.carrotsight.com/2016/01/29/浅谈Android自定义Lint规则的实现 (一).html#