LeakCanary2.x
LeakCanary
LeakCanary2.x 介绍
LeakCanary2.x 自动检测的对象:
- destroyed Activity instances
- destroyed Fragment instances
- destroyed fragment View instances
- cleared ViewModel instances
- destroyed Service instance
LeakCanary2.0+ 采用了新的 hprof 分析工具 shark 替换了原来的 haha,主要做了hprof 文件裁剪和实时监控。
hprof 文件裁剪
LeakCanary2.x 用 shark 组件来实现裁剪 hprof 文件功能,通过将所有基本类型数组替换为空数组(大小不变)
实时监控
在 Activity 或者 Fragment 的 destroy 生命周期后,可以检测 Activity 和 Fragment 是否被回收,来判断它们是否存在泄露的情况。
LeakCanary2.x 使用
如何初始化?
自动在主进程初始化
debugImplementation ‘com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:2.2’
会自动通过 MainProcessAppWatcherInstaller 进行注册
手动在主进程初始化
- 配置
<bool name="leak_canary_watcher_auto_install">false</bool> - 手动调用
AppWatcher.manualInstall()注册
如何判断注册成功?
在 Logcat 中过滤 tag 为 LeakCanary 输出如下 log:
LeakCanary is running and ready to detect memory leaks.
LeakCanary2.x 原理(v2.10)
AppWatcher
通过 MainProcessAppWatcherInstaller 主动注册或者手动注册,最终都是走到 AppWatcher.manualInstall(application),往下走:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
fun manualInstall(
application: Application,
retainedDelayMillis: Long = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(5),
watchersToInstall: List<InstallableWatcher> = appDefaultWatchers(application)
) {
// ... 一些条件校验
installCause = RuntimeException("manualInstall() first called here")
this.retainedDelayMillis = retainedDelayMillis
// ...
// Requires AppWatcher.objectWatcher to be set
LeakCanaryDelegate.loadLeakCanary(application)
// 遍历install开始监测对象
watchersToInstall.forEach {
it.install()
}
}
参数 2:retainedDelayMillis 默认 5 秒 参数 3:watchersToInstall 需要观察的对象,在 appDefaultWatchers 中有定义;可定义增加或删除观察的对象
看看 appDefaultWatchers():
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
val objectWatcher = ObjectWatcher(
clock = { SystemClock.uptimeMillis() },
checkRetainedExecutor = {
check(isInstalled) {
"AppWatcher not installed"
}
mainHandler.postDelayed(it, retainedDelayMillis)
},
isEnabled = { true }
)
fun appDefaultWatchers(
application: Application,
reachabilityWatcher: ReachabilityWatcher = objectWatcher
): List<InstallableWatcher> {
return listOf(
ActivityWatcher(application, reachabilityWatcher),
FragmentAndViewModelWatcher(application, reachabilityWatcher),
RootViewWatcher(reachabilityWatcher),
ServiceWatcher(reachabilityWatcher)
)
}
默认观察了 4 种对象:
- Activity 对象
- Fragment 对象
- View 对象
- Service 对象
接着看下 LeakCanaryDelegate.loadLeakCanary(application):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
internal object LeakCanaryDelegate {
val loadLeakCanary by lazy {
try {
val leakCanaryListener = Class.forName("leakcanary.internal.InternalLeakCanary")
leakCanaryListener.getDeclaredField("INSTANCE")
.get(null) as (Application) -> Unit
} catch (ignored: Throwable) {
NoLeakCanary
}
}
// ...
}
反射获取了 InternalLeakCanary 的 INSTANCE 字段,返回一个 InternalLeakCanary 对象(InternalLeakCanary 是一个 (Application)->Unit 的方法对象)
InternalLeakCanary 类定义:internal object InternalLeakCanary : (Application) -> Unit, OnObjectRetainedListener
其实最终调用的是 InternalLeakCanary 的 invoke 方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
override fun invoke(application: Application) {
_application = application
// 1
checkRunningInDebuggableBuild()
// 2
AppWatcher.objectWatcher.addOnObjectRetainedListener(this)
// 3
val gcTrigger = GcTrigger.Default
val configProvider = { LeakCanary.config }
val handlerThread = HandlerThread(LEAK_CANARY_THREAD_NAME)
handlerThread.start()
val backgroundHandler = Handler(handlerThread.looper)
// 4
heapDumpTrigger = HeapDumpTrigger(
application, backgroundHandler, AppWatcher.objectWatcher, gcTrigger,
configProvider
)
application.registerVisibilityListener { applicationVisible ->
this.applicationVisible = applicationVisible
heapDumpTrigger.onApplicationVisibilityChanged(applicationVisible)
}
registerResumedActivityListener(application)
addDynamicShortcut(application)
// We post so that the log happens after Application.onCreate()
mainHandler.post {
// https://github.com/square/leakcanary/issues/1981
// We post to a background handler because HeapDumpControl.iCanHasHeap() checks a shared pref
// which blocks until loaded and that creates a StrictMode violation.
backgroundHandler.post {
SharkLog.d {
when (val iCanHasHeap = HeapDumpControl.iCanHasHeap()) {
is Yup -> application.getString(R.string.leak_canary_heap_dump_enabled_text)
is Nope -> application.getString(
R.string.leak_canary_heap_dump_disabled_text, iCanHasHeap.reason()
)
}
}
}
}
}
- checkRunningInDebuggableBuild() 校验是否在 debuggable 的包运行 LeakCanary,不在 debuggable 的包默认是不行;如果需要在非 debuggable 上运行,需要配置
<bool name="leak_canary_allow_in_non_debuggable_build">false</bool>为 true - addOnObjectRetainedListener() 方法,这里会给单例的
AppWatcher.objectWatcher对象注册一个 OnObjectRetainedListener 监听,当默认的那些 AppWatcher 对象 retain 了就会回调到这里来 - GcTrigger 通过调用 Runtime.getRuntime().gc() 方法触发虚拟机进行 GC 操作
- HeapDumpTrigger 管理触发 Heap Dump 的逻辑,有两个地方会触发 dumpHeap():
- retain 的对象超过阈值(5,应用可见的情况下),可以通过 Config 配置:
val retainedVisibleThreshold: Int = 5 // LeakCanary.Config
- 当 HeapDumpTrigger 回调
onDumpHeapReceived()方法时,会执行 dumpHeap();比如通知栏收到了 Notification 点击了
appDefaultWatchers() 4 种默认对象的泄漏检测
接着回到 LeakCanary 默认定义的几个 Watcher,我们以 ActivityWatcher 为例进行讲解。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
class ActivityWatcher(
private val application: Application,
private val reachabilityWatcher: ReachabilityWatcher // 1
) : InstallableWatcher {
private val lifecycleCallbacks =
object : Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks by noOpDelegate() {
override fun onActivityDestroyed(activity: Activity) {
reachabilityWatcher.expectWeaklyReachable( // 3
activity, "${activity::class.java.name} received Activity#onDestroy() callback"
)
}
}
override fun install() { // 2
application.registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks(lifecycleCallbacks)
}
override fun uninstall() { // 2
application.unregisterActivityLifecycleCallbacks(lifecycleCallbacks)
}
}
// AppWatcher.kt
val objectWatcher = ObjectWatcher(
clock = { SystemClock.uptimeMillis() },
checkRetainedExecutor = {
check(isInstalled) {
"AppWatcher not installed"
}
mainHandler.postDelayed(it, retainedDelayMillis)
},
isEnabled = { true }
)
- reachabilityWatcher 就是单例 AppWatcher 变量 objectWatcher,用于探测 retained 的对象
- install()/uninstall(),注册收集要监测的 Activity 对象,通过 registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks 来收集,在 Activity 的 onActivityDestroyed 中开始探测 Activity 是否泄漏
- **objectWatcher.expectWeaklyReachable **观测 Activity 对象是否泄漏
- objectWatcher 中第二个参数 checkRetainedExecutor 其实是
(Runnable)->Unit类型
- objectWatcher 中第二个参数 checkRetainedExecutor 其实是
接着来看看:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
class ObjectWatcher {
// 1
private val watchedObjects = mutableMapOf<String, KeyedWeakReference>()
// 2
private val queue = ReferenceQueue<Any>()
@Synchronized override fun expectWeaklyReachable(
watchedObject: Any,
description: String
) {
if (!isEnabled()) {
return
}
// 3
removeWeaklyReachableObjects()
val key = UUID.randomUUID().toString()
val watchUptimeMillis = clock.uptimeMillis()
val reference =
KeyedWeakReference(watchedObject, key, description, watchUptimeMillis, queue)
// 4
watchedObjects[key] = reference
// 5
checkRetainedExecutor.execute { moveToRetained(key) }
}
}
// 3
private fun removeWeaklyReachableObjects() {
// WeakReferences are enqueued as soon as the object to which they point to becomes weakly
// reachable. This is before finalization or garbage collection has actually happened.
var ref: KeyedWeakReference?
do {
ref = queue.poll() as KeyedWeakReference?
if (ref != null) {
watchedObjects.remove(ref.key)
}
} while (ref != null)
}
// 5
@Synchronized private fun moveToRetained(key: String) {
removeWeaklyReachableObjects()
val retainedRef = watchedObjects[key]
if (retainedRef != null) {
retainedRef.retainedUptimeMillis = clock.uptimeMillis()
onObjectRetainedListeners.forEach { it.onObjectRetained() }
}
}
- watchedObjects 保存了 KeyedWeakReference 的 HashMap,key 为随机生成的数;正常回收的对象会被移除,留下来的可能是泄漏的
- queue WeakReference 的 ReferenceQueue 在对象被回收后,会将指向对象的 WeakReference 放到 queue 中去。
- **removeWeaklyReachableObjects() 【将正常回收的对象从 watchObjects 移除】 **遍历 queue,如果找到了 ref 不为 null 的(不为 null 说明对象被回收了),那么从 watchObjects 中移除掉,因为观测的这个对象已经被回收了,watchObjects 中留下来的可能是泄漏的对象 retained 了
- 将要观察的对象包装成一个 KeyedWeakReference,保存到 watchedObjects 中去
- 执行 checkRetainedExecutor.execute【延迟 5 秒看对象回收情况】,checkRetainedExecutor 定义是在 APPWatcher 的 objectWatcher,延迟五秒会调用 moveToRetained(),也就是说在 Activity 回调 onDestroy5 秒后执行;在 moveToRetained 中,首先调用 removeWeaklyReachableObjects() 将已经回收的对象移除掉,watchedObjects 中留下来的对象可能是内存泄漏的对象,回调 OnObjectRetainedListener,最终回调到 InternalLeakCanary 的
onObjectRetained()方法
其他的
AndroidXFragmentDestroyWatcher和ViewModelClearedWatcher都是类似的逻辑
HeapDumpTrigger 触发 dump heap 的逻辑
接着前面,在 5 秒后如果还存在于 watchedObjects 中,就会回调到 InternalLeakCanary 的 onObjectRetained() 方法,最终会调用到 HeapDumpTrigger 的 scheduleRetainedObjectCheck() 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class InternalLeakCanary {
fun scheduleRetainedObjectCheck(delayMillis: Long = 0L) { // 这里的delayMillis为0L
val checkCurrentlyScheduledAt = checkScheduledAt
if (checkCurrentlyScheduledAt > 0) {
return
}
checkScheduledAt = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis
backgroundHandler.postDelayed({ // 是在子线程中dump
checkScheduledAt = 0
checkRetainedObjects()
}, delayMillis)
}
}
接着看 checkRetainedObjects():
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
private fun checkRetainedObjects() {
// ...
// 1. 已经被回收过后的retained对象的总和
var retainedReferenceCount = objectWatcher.retainedObjectCount
if (retainedReferenceCount > 0) {
// 2
gcTrigger.runGc()
retainedReferenceCount = objectWatcher.retainedObjectCount
}
// 3
if (checkRetainedCount(retainedReferenceCount, config.retainedVisibleThreshold)) return
val now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis()
val elapsedSinceLastDumpMillis = now - lastHeapDumpUptimeMillis
// 4
if (elapsedSinceLastDumpMillis < WAIT_BETWEEN_HEAP_DUMPS_MILLIS) {
onRetainInstanceListener.onEvent(DumpHappenedRecently)
showRetainedCountNotification(
objectCount = retainedReferenceCount,
contentText = application.getString(R.string.leak_canary_notification_retained_dump_wait)
)
scheduleRetainedObjectCheck(
delayMillis = WAIT_BETWEEN_HEAP_DUMPS_MILLIS - elapsedSinceLastDumpMillis
)
return
}
dismissRetainedCountNotification()
val visibility = if (applicationVisible) "visible" else "not visible"
// 5
dumpHeap(
retainedReferenceCount = retainedReferenceCount,
retry = true,
reason = "$retainedReferenceCount retained objects, app is $visibility"
)
}
- **retainedReferenceCount **已经被回收过后的 retained 对象的总和,会调用 removeWeaklyReachableObjects 先判断下
- 如果存在一个 retained 对象,手动触发一下 GC;再重新计算下retainedReferenceCount
- 如果 retained 的对象小于 5 个(默认),不走下面逻辑了
- 如果 retained 的对象大于等于 5 个;距离上次 dump 时间小于 60 秒,只展示通知,delay dump heap
- retained 大于等于 5 个且距离时间大于等于 60 秒,就直接 dump heap
LeakCanary 如何分析 hprof 文件?
分析 hprof 文件的工作主要是在 HeapAnalyzerService 类中完成的;用 Sharp 分析 hprof 来分析
原理小结
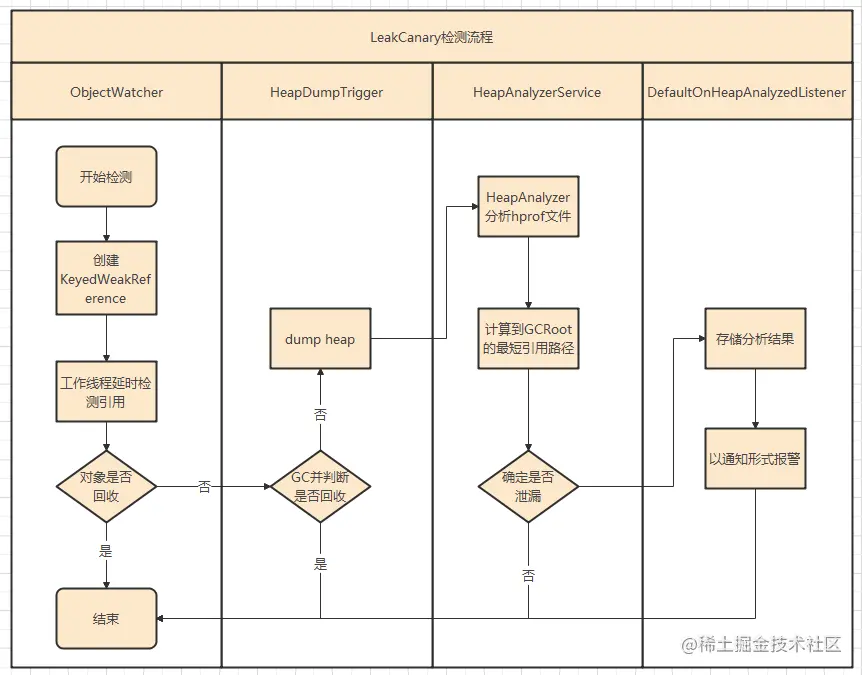
默认可以监听 Activity、Fragment、View 和 ViewModel 的泄漏,以 Activity 为例:
- 监听 Activity 生命周期
- 在 Activity onDestroy 的时候,创建一个弱引用 KeyedWeakReference 到 Activity 对象并关联一个引用队列 queue,key 是一个随机数(和当前 Activity 绑定),将 key 和 KeyedWeakReference 保存到 watchedObjects 里面
- 然后在延迟默认 5 秒后,开始检测是否内存泄漏,具体检测步骤:
- 1、判断 queue 中是否有该 Activity 的 KeyedWeakReference 对象,有则说明 Activity 被回收了,移除 watchedObjects 里面对应的 key
- 2、判断 watchedObjects 里面是否有当前要检测的 Activity 的 key,如果没有,说明 Activity 对象已经被回收了,没有内存泄漏;如果有,只能说明 Activity 对象还没有被回收,可能此时已经没有被引用,不一定是内存泄漏
- 手动触发一次 GC
- dump heap 分析 hprof 文件,构建可能泄漏的对象与 GC Root 的引用链,如果存在则泄漏了
- 存储结果并使用 Notification 提醒用户存在泄漏
弱引用和引用队列搭配使用,如果弱引用持有的对象被回收,Java 虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。也就是说如果 KeyedWeakReference 持有的 Activity 对象被回收,该 KeyedWeakReference 就会加入到引用队列 queue 中。 LeakCanary 就是利用这个原理。
LeakCanary 疑问?
为什么 LeakCancary 不能用于线上?
- 泄漏后生成
.hprof文件增加手机负担,引起手机卡顿等问题。.hprof 文件较大,信息回捞成问题。 - 多次调用 GC,可能会对线上性能产生影响
- 同样的泄漏问题,会重复生成 .hprof 文件,重复分析并写入磁盘
LeakCanary 为什么卡顿?解决?
自定义 Heap Dump 执行器,默认的是 AndroidDebugHeapDumper
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
LeakCanary.config = LeakCanary.config.copy(
// 自定义 Heap Dump 执行器
heapDumper = {
// KOOM
ForkJvmHeapDumper.getInstance().dump(it.absolutePath)
}
)
- dump 放到子进程