Gradle Task进阶
Task 的输入和输出
Task outcomes (Task 产出)
Task Outcome Task 结果标识有 5 种,从名字上能大概看出它们的含义: 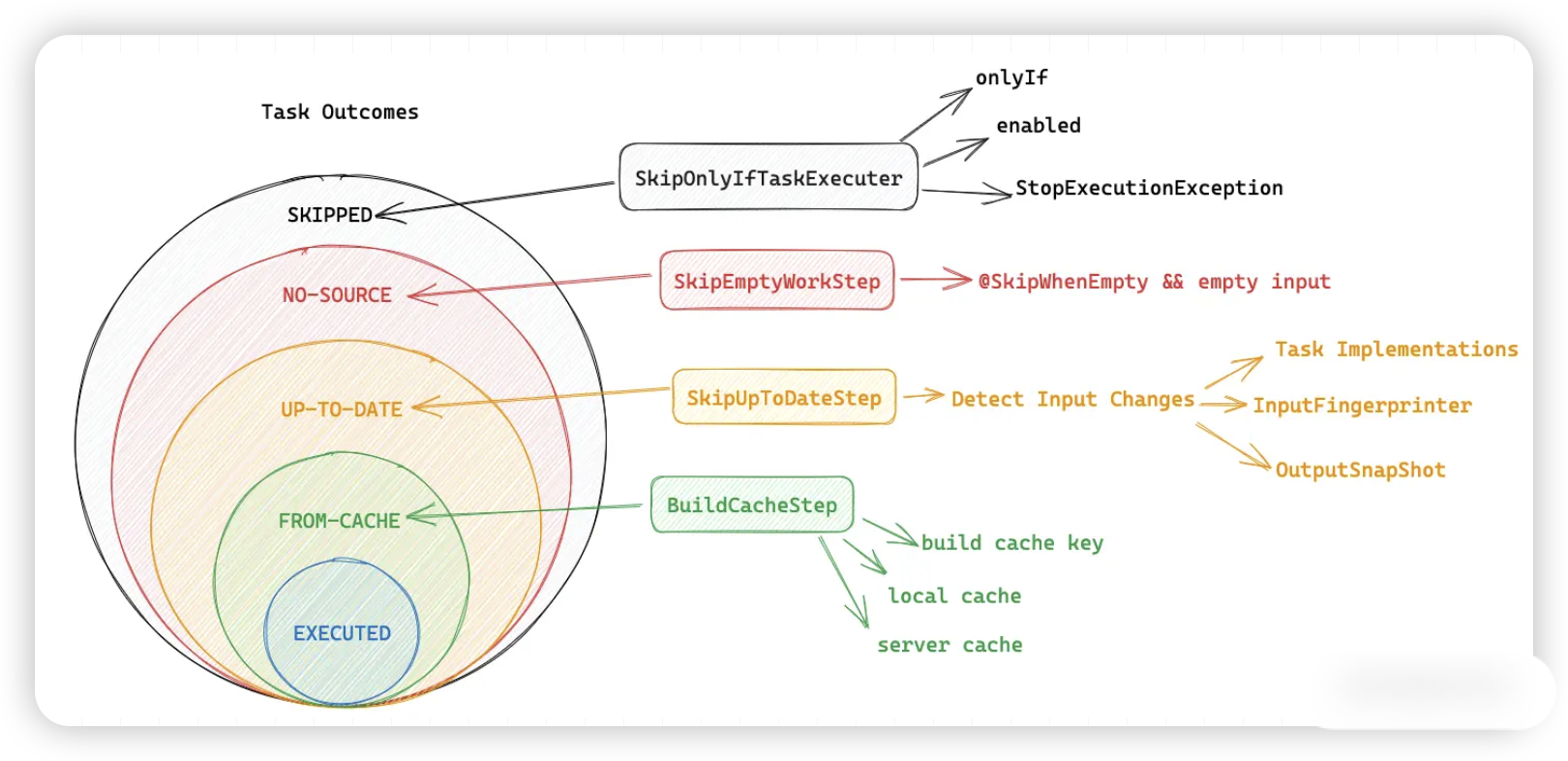
(no label) or EXECUTED
- (no label) or EXECUTED 表示 Task 执行了 action,常见。
- Task 有 action 且 Gradle 执行了
- Task 没有 action 且有部分 dependencies 执行了
UP-TO-DATE
- UP-TO-DATE 表示 Task 的输出(outputs)没有改变。
- Task 有 outputs 和 inputs 且没有 changed;See Incremental Build.
- Task 有 action,但是 task 告诉 Gradle 它的 outputs 没有 changed
- Task 没有 action, 但有部分 dependencies 是 update-to-date,skipped 或 from cache;See also Lifecycle Tasks.
- Task 没有 action 且没有 dependencies
FROM-CACHE
- FROM-CACHE 可以从缓存中复用上一次的执行结果 (Task 的 outputs 从上一次构建找到)
- Task 有 outputs 从 build cache 找到 See Build Cache.
SKIPPED
- SKIPPED 跳过(Task 没有执行 actions)
- Task 被显示的 excluded 从 cli See Excluding tasks from execution.
$ gradle dist --exclude-task helloTask
- Task 的
onlyIf返回的 false See Using a predicate.
- Task 被显示的 excluded 从 cli See Excluding tasks from execution.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
tasks.register('customTask') {
onlyIf {
}
enabled = false
}
// onlyIf和enabled都可以控制Task执行条件,如果其结果是false,那这个Task就不需要被执行
SkipOnlyIfTaskExecuter 就是用来判断这个的,Task 的 SKIPPED 标识就是这里处理的。
NO-SOURCE
- NO-SOURCE Task 不需要执行它的 actions
- 有 outputs 和 inputs,但没有 no sources。例如,source files 是
.java的 JavaCompile.
- 有 outputs 和 inputs,但没有 no sources。例如,source files 是
Task 输入输出
一般情况下,任务需要一些输入并生成一些输出。我们可以将 Java 编译过程视为 Task 的一个示例,Java 源文件作为 Task 的输入,而生成的类文件,即编译的结果,是 Task 的输出。
| 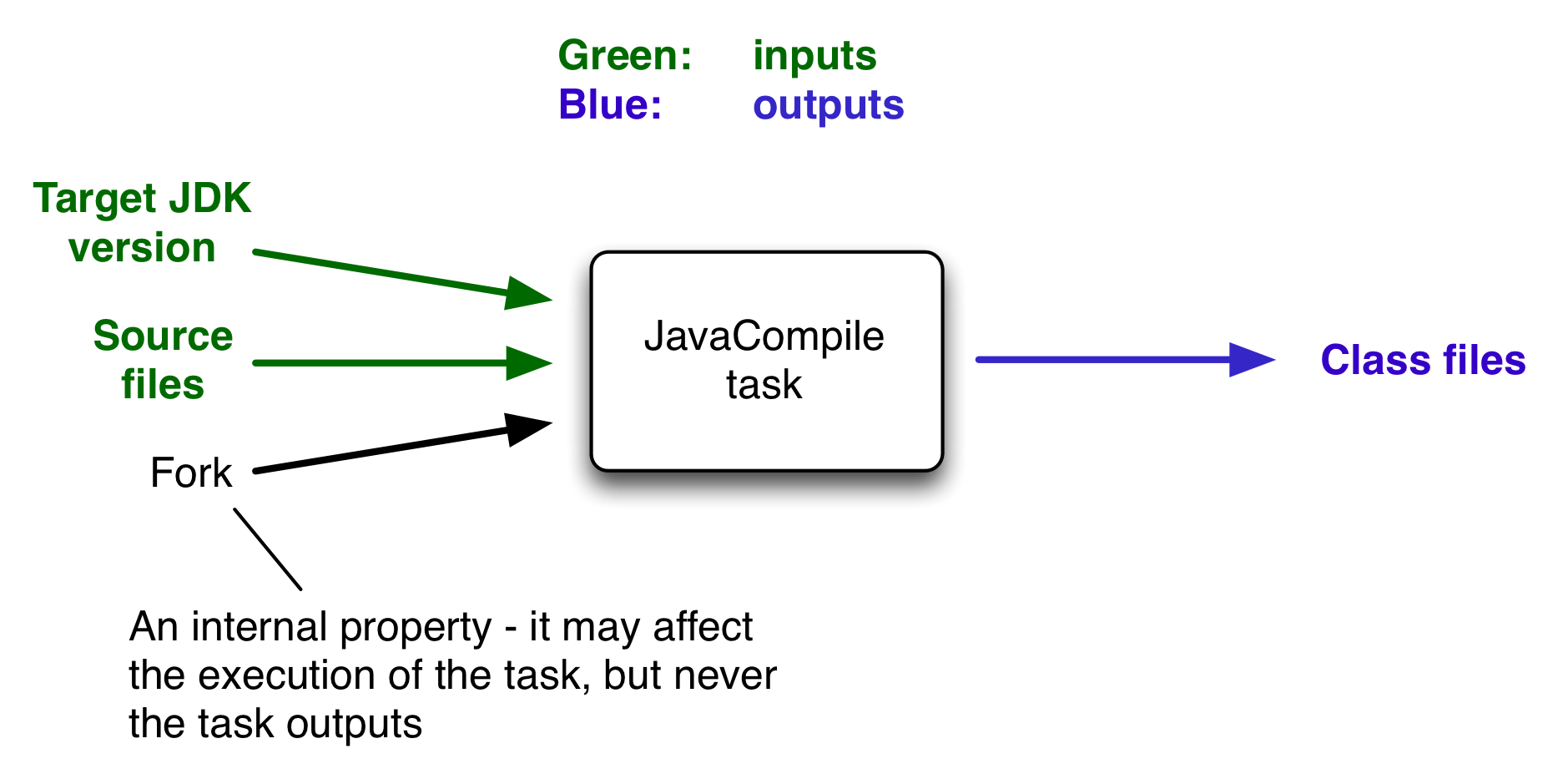 |
输入的一个重要特征是,它会影响一个或多个输出,如上图,根据源文件的内容和您要运行代码的 Java 运行时的最低版本,会生成不同的字节码。
编写 Task 时,需要告诉 Gradle 哪些 Task 属性是输入,哪些是输出。 如果 Task 属性影响输出,请务必将其注册为输入,否则当它不是时,Task 将被视为最新状态。相反,如果属性不影响输出,请不要将属性注册为输入,否则 Task 可能会在不需要时执行。还要注意可能为完全相同的输入生成不同输出的非确定性 Task,这些 Task 不应配置为增量构建,因为 UP-TO-DATE 检查将不起作用。
Gradle Task Incremental 增量更新
Task 增量更新概述
增量构建 是当 Task 的输入和输出没有变化时,跳过 action 的执行,当 Task 输入或输出发生变化时,在 action 中只对发生变化的输入或输出进行处理,这样就可以避免一个没有变化的 Task 被反复构建,当 Task 发生变化时也只处理变化部分,这样可以提高 Gradle 的构建效率,缩短构建时间。
任何构建工具的一个重要部分是能够避免做已经完成的工作。编译源文件后,除非发生影响输出的某些变化,例如修改源文件或删除输出文件,否则无需重新编译它们。编译可能需要大量时间,因此在不需要时跳过步骤可以节省大量时间。
Gradle 提供这种开箱即用的增量构建的功能,当你在编译时,Task 在控制台输出中标记为 UP-TO-DATE,这意味着增量构建正在工作。
Task 增量构建的两种形式
- Task 完全可以复用,输入和输出都没有任何变化,即
UP-TO-DATE,默认支持 - 第二种,有部分变化,只需要针对变化的部分进行操作;
完全复用
示例 :编写一个复制文件的 Task,不支持增量编译的
在编写 Task 的时候,我们需要使用注解来声明输入和输出。@InputXXX 表示输入,@OutputXXX 表示输出。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
abstract class CopyTask : DefaultTask() {
// 指定输入
// @InputFile
@InputFiles
var from: FileCollection? = null
// 输出
@OutputDirectory
var to: Directory? = null
@TaskAction
fun execute() {
val fromInput = from ?: return
val toOutput = to ?: return
val file = fromInput.singleFile
if (file.isDirectory) {
fromInput.asFileTree.forEach {
println("===============>>>> copy dir file=$it")
copyFileToDir(it, toOutput)
}
} else {
println("------------------>>>>>> copy file file=$file")
copyFileToDir(file, toOutput)
}
}
private fun copyFileToDir(src: File, dir: Directory) {
val destFile = File(dir.asFile.path, src.name)
if (!destFile.exists()) {
destFile.createNewFile()
}
destFile.outputStream().use { output ->
src.inputStream().use { input ->
input.copyTo(output)
}
} }
}
// 使用
tasks.register<CopyTask>("myCopyTask") {
group = "test"
// from = fileTree("src") // Expected directory 'src' to contain exactly one file, however, it contains more than one file.
from = files("from")
to = layout.projectDirectory.dir("to")
}
测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 当前目录
├── app
│ ├── from
│ │ └── txt1.txt
# 测试
./gradlew CopyTask --info
# 此时的目录结构:
├── app
│ ├── from
│ │ └── txt1.txt
│ └── to
│ └── txt1.txt
第 1 次执行的日志:
| 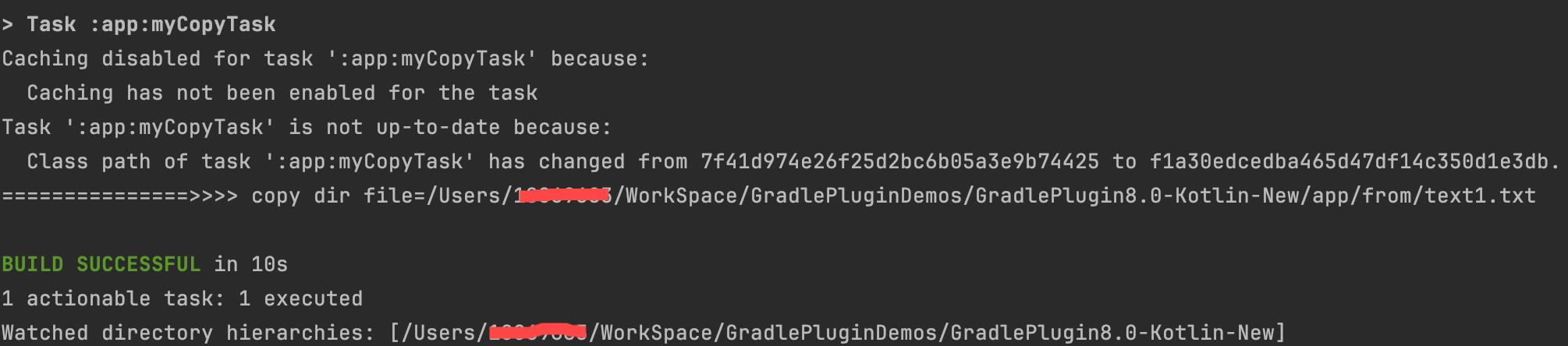 |
第 2 次执行的日志:
| 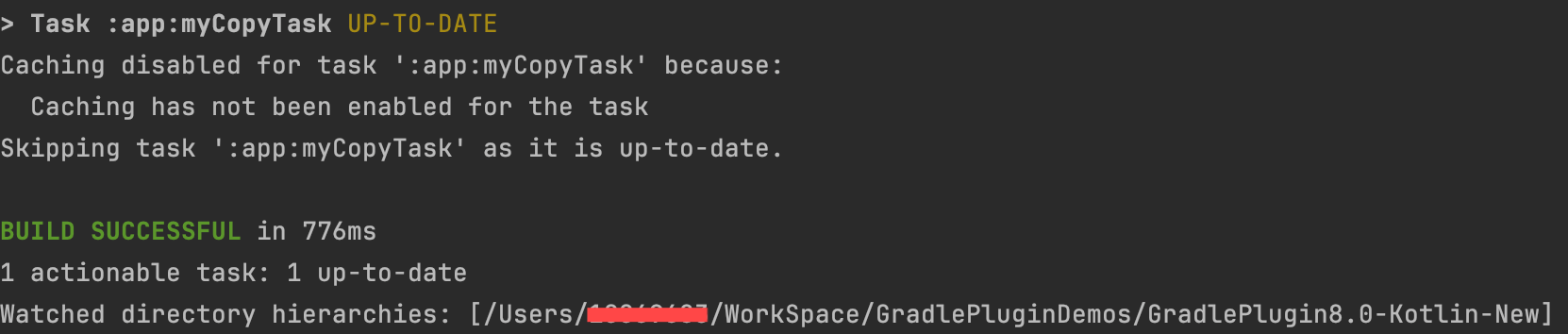 |
Task 的执行结果已经由 executed 变为 up-to-date 了,说明我们的增量构建已经生效了。
虽然说此时增量构建已经生效了,但完成度还不够,还需要有颗粒度更细的处理。
部分增量构建
场景:基于上面的场景,在 from 文件夹下增加一个 text2.txt 文件,并支持增量构建。
在 text1.txt 复制后,再执行 task,两个 text 又复制了一遍
| 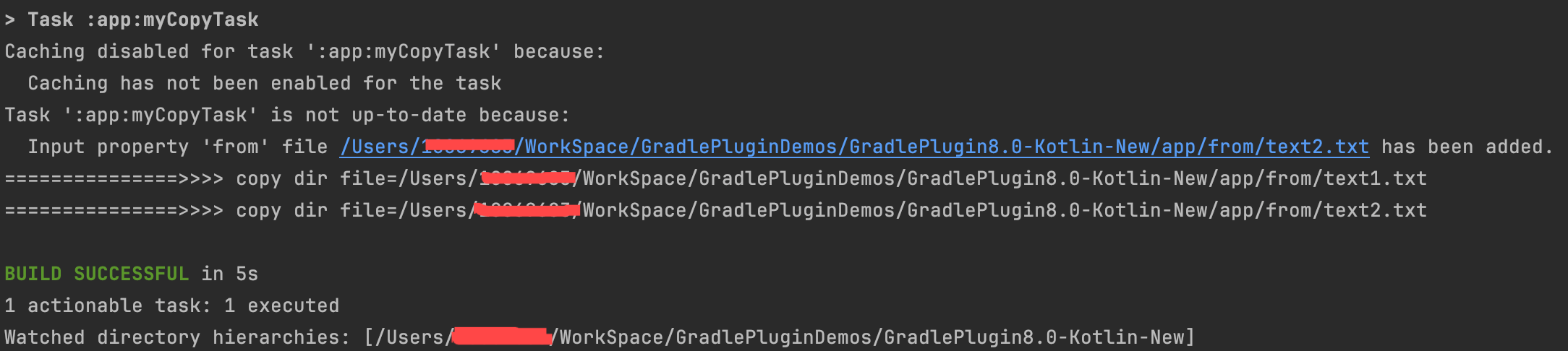 |
增加一个
txt2.txt文件再次执行上面的命令时,会发现text1.txt文件被再次复制了一遍。这是因为我们的输入有了变化,CopyTask 的 Action 就会全量构建,而我们想要的效果是只复制
text2.txt文件就好了。只对新增或修改的文件做复制操作,没有变化的文件不进行复制。 而要实现这种效果,就得让 Action 方法支持增量构建。
给 action 方法增加一个 InputChanges 参数,带 InputChanges 类型参数的 Action 方法表示这是一个增量任务操作方法,该参数告诉 Gradle,该 Action 方法仅需要处理更改的输入,此外,Task 还需要通过使用 @Incremental 或 @SkipWhenEmpty 来指定至少一个增量文件输入属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
abstract class CopyTask : DefaultTask() {
// 指定增量输入属性
@Incremental
@InputFiles
var from: FileCollection? = null
// 输出
@OutputDirectory
var to: Directory? = null
@TaskAction
fun execute(inputChanges: InputChanges) {
val fromInput = from ?: return
val toOutput = to ?: return
val incremental = inputChanges.isIncremental
println("isIncremental = $incremental")
inputChanges.getFileChanges(fromInput).forEach {
println("file change file= ${it.file}, isDirectory=${it.file.isDirectory}, Type = ${it.changeType}")
if (it.fileType != FileType.DIRECTORY) {
println("file= ${it.file}, fileType = ${it.fileType}")
if (it.changeType != ChangeType.REMOVED) {
copyFileToDir(it.file, toOutput)
}
} else {
println("file= ${it.file}, fileType = ${it.fileType}, DIRECTORY?")
}
}
}
private fun copyFileToDir(src: File, dir: Directory) {
val destFile = File(dir.asFile.path, src.name)
if (!destFile.exists()) {
destFile.createNewFile()
}
destFile.outputStream().use { output ->
src.inputStream().use { input ->
input.copyTo(output)
}
} }
}
| 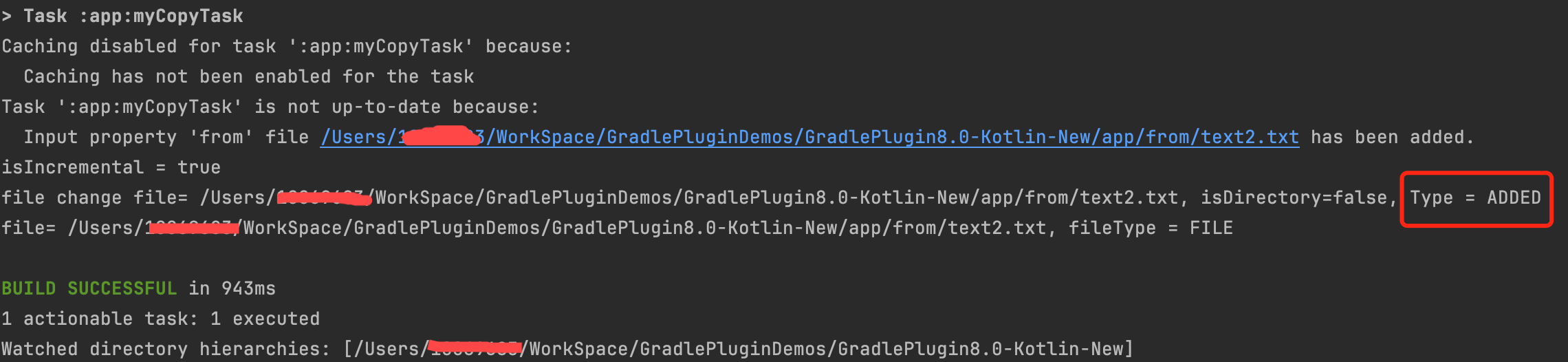 |
ChangeType 的几种类型:
- ADDED:表示文件是新增的;
- MODIFIED:表示文件是修改的;
- REMOVED:表示文件被删除;
全量编译的情况(增量编译失效的情况)
Task 并不是每次执行都是增量构建,我们可以通过 InputChanges 的 isIncremental 方法判断本次构建是否是增量构建,不过有以下几种情况会全量构建:
- 该 Task 是第一次执行;
- 该 Task 只有输入没有输出;
- 该 Task 的
upToDateWhen条件返回了 false; - 自上次构建以来,该 Task 的某个输出文件已更改;
- 自上次构建以来,该 Task 的某个属性输入发生了变化,例如一些基本类型的属性;
- 自上次构建以来,该 Task 的某个非增量文件输入发生了变化,非增量文件输入是指没有使用
@Incremental或@SkipWhenEmpty注解的文件输入.
当 Task 处于全量构建时,即 InputChanges 的 isIncremental 方法返回 false 时,通过 InputChanges 的 getFileChanges 方法能获取到所有的输入文件,并且每个文件的 ChangeType 都为 ADDED,当 Task 处于增量构建时,即 InputChanges 的 isIncremental 方法返回 true 时,通过 InputChanges 的 getFileChanges 方法能获取到只发生变化的输入文件。
常用的注解类型
Incremental build # Declaring inputs and outputs via annotations
| 注解 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| @Input | 任何 Serializable 类型或依赖性解析结果类型 | 一个简单的输入值或依赖关系解析结果 |
| @InputFile | File | 单个输入文件(不是目录) |
| @InputDirectory | File | 单个输入目录(不是文件) |
| @InputFiles | Iterable | 可迭代的输入文件和目录 |
| @OutputFile | File | 单个输出文件(不是目录) |
| @OutputDirectory | File | 单个输出目录(不是文件) |
| @OutputFiles | Map<String, File> 或 Iterable | 输出文件的可迭代或映射。使用文件树会关闭任务的缓存。 |
| @OutputDirectories | Map<String, File> 或 Iterable | 输出目录的可迭代。使用文件树会关闭任务的缓存。 |
| @Nested | 任何自定义类型 | 自定义类型,可能无法实现 Serializable,但至少有一个字段或属性标记了此表中的注释之一。它甚至可能是另一个@Nested。 |
| @Internal | 任何类型 | 表示该属性在内部使用,但既不是输入也不是输出。 |
| @SkipWhenEmpty | File 或 Iterable | 与@InputFiles 或@InputDirectory 一起使用,告诉 Gradle 在相应的文件或目录为空时跳过任务,以及使用此注释声明的所有其他输入文件。由于声明此注释为空的所有输入文件而跳过的任务将导致明显的 “ 无源 “ 结果。例如,NO-SOURCE 将在控制台输出中发出。暗示@Incremental。 |
| @Incremental | 任何类型 | 与@InputFiles 或@InputDirectory 一起使用,指示 Gradle 跟踪对带注释的文件属性的更改,因此可以通过 ` @InputChanges.getFileChanges() ` 查询更改。增量任务需要。 |
| @Optional | 任何类型 | 与可选 API 文档中列出的任何属性类型注释一起使用。此注释禁用对相应属性的验证检查。有关更多详细信息 , 请参阅 验证部分。 |
增量构建原理
在首次执行 Task 之前,Gradle 会获取输入的指纹,此指纹包含输入文件的路径和每个文件内容的散列。然后执行 Task,如果 Task 成功完成,Gradle 会获取输出的指纹,此指纹包含一组输出文件和每个文件内容的散列,Gradle 会在下次执行 Task 时保留两个指纹。
后续每次在执行 Task 之前,Gradle 都会对输入和输出进行新的指纹识别,如果新指纹与之前的指纹相同,Gradle 假设输出是最新的,并跳过 Task,如果它们不一样,Gradle 会执行 Task。Gradle 会在下次执行 Task 时保留两个指纹。
如果文件的统计信息(即 lastModified 和 size)没有改变,Gradle 将重复使用上次运行的文件指纹,即当文件的统计信息没有变化时,Gradle 不会检测到更改。
Gradle 还将 Task 的代码视为任务输入的一部分,当 Task、Action 或其依赖项在执行之间发生变化时,Gradle 认为该 Task 是过时的。
Gradle 了解文件属性(例如持有 Java 类路径的属性)是否对顺序敏感,当比较此类属性的指纹时,即使文件顺序发生变化,也会导致 Task 过时。
请注意,如果 Task 指定了输出目录,则自上次执行以来添加到该目录的任何文件都会被忽略,并且不会导致 Task 过时,如此不相关的 Task 可能会共享一个输出目录,而不会相互干扰,如果出于某种原因这不是你想要的行为,请考虑使用 TaskOutputs.upToDateWhen(groovy.lang.Closure)。
另请注意,更改不可用文件的可用性(例如,将损坏的符号链接的目标修改为有效文件,反之亦然),将通过最新检查进行检测和处理。
Task 的输入还用于计算启用时用于加载 Task 输出的构建缓存密钥。
Gradle Task Incremental 示例
上传 apk 到 pgyer
PgyUploadApkTask 功能:
- 输入为 build 成功后的 apk
- 输出为
build/output.txt,存储 apk 上传成功后 apk 文件的md5值 - 调用 pgyer upload
http v2接口上传 apk - 上传 apk 成功后,获取该文件的
md5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
// ...
import org.gradle.api.DefaultTask
import org.gradle.api.file.RegularFileProperty
import org.gradle.api.tasks.InputFile
import org.gradle.api.tasks.OutputFile
import org.gradle.api.tasks.TaskAction
import java.io.File
abstract class PgyUploadApkTask : DefaultTask() {
@get:InputFile
abstract val apkFileProperty: RegularFileProperty
@get:OutputFile
abstract val outputFilProperty: RegularFileProperty
init {
group = Constants.GROUP
description = "上传apk到蒲公英"
}
@Suppress("CheckResult")
@TaskAction
fun doTaskAction() {
val apkFile = apkFileProperty.get().asFile
println("PgyUploadApkTask doTaskAction apkFile=$apkFile")
if (apkFile == null) {
println("apkFile is null")
throw IllegalArgumentException("apkFile is null")
}
if (!apkFile.exists()) {
println("apkFile($apkFile) not exists")
throw IllegalArgumentException("apkFile not exists")
}
// 上传apk到蒲公英
val extension = Extension.getExtension(project)
println("pgyerApiKey=${extension?.pgyerApiKey}")
val apiKey = extension?.pgyerApiKey
val changeLog = extension?.changeLog
// 上传成功后,将返回的下载地址写入output文件
val req1 = COSTokenRequest1(apiKey ?: "")
val output = outputFilProperty.get().asFile
if (!output.exists()) {
output.createNewFile()
}
val apkFileMd5Hash = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5")
.digest(Files.readAllBytes(apkFile.toPath()))
.joinToString("") { hash -%3E "%02x".format(hash) }
println("uploadApk apkFile=${apkFile}, apkFileMd5Hash=$apkFileMd5Hash")
UploadApkToPgyerHelper.uploadApk(req1, apkFile)
.subscribe({
val s1 = System.currentTimeMillis()
val md5Hash = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5")
.digest(Files.readAllBytes(apkFile.toPath()))
.joinToString("") { hash -> "%02x".format(hash) }
val cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - s1
println(
"uploadApk success it=$it\noutput=$output(${output.exists()})\n" +
"MD5 hash of ${output.name} is $md5Hash\ncost=${cost}ms"
)
output.writeText(md5Hash)
}, {
println("uploadApk error e=$it, output=$output")
it.printStackTrace()
output.writeText("error: $it")
throw it
})
Utils.log(" ${this.name} task end. ")
}
}
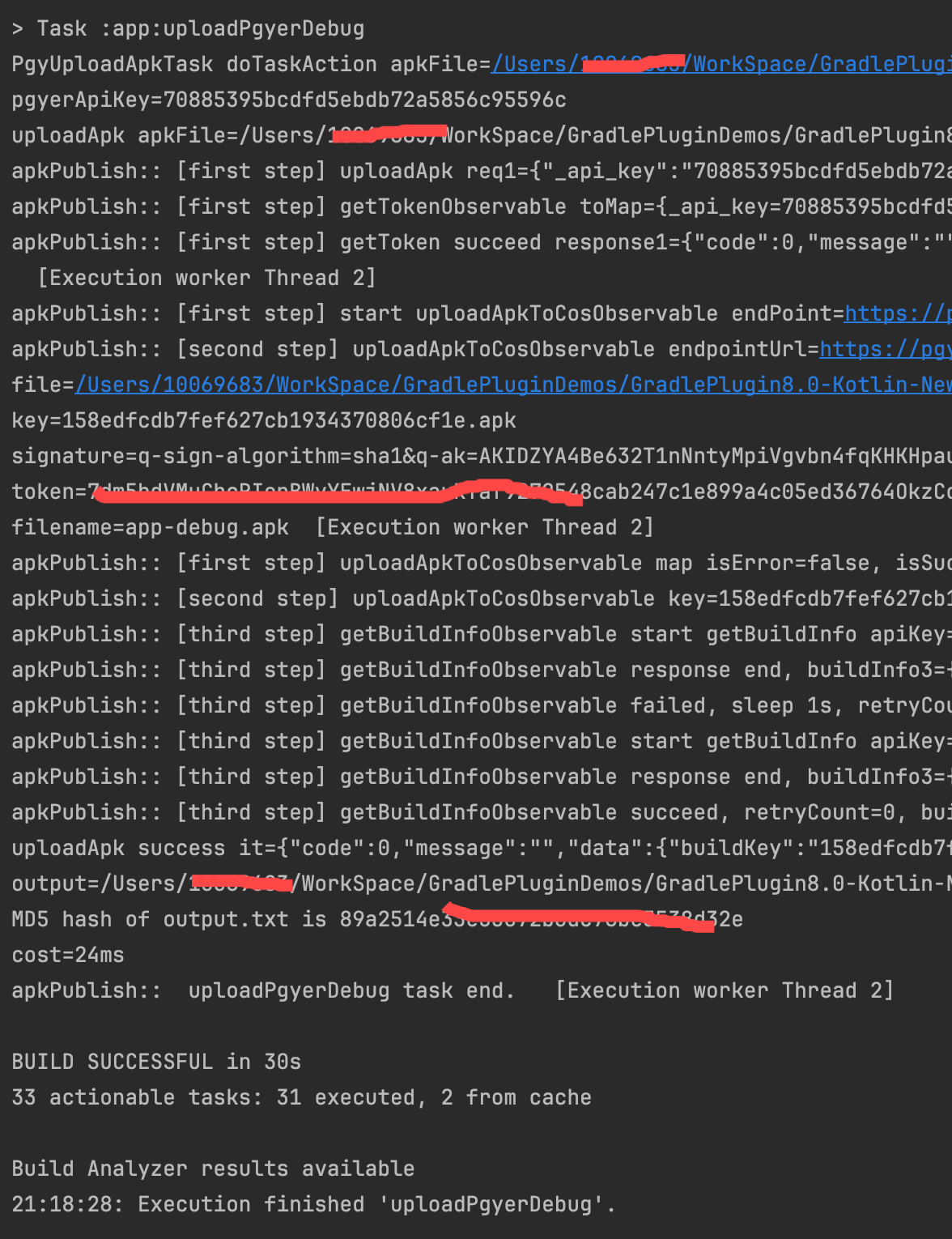
- 首次运行:
./gradlew :app:uploadPgyerDebug,成功上传 apk 后
|  |
- 二次运行
| 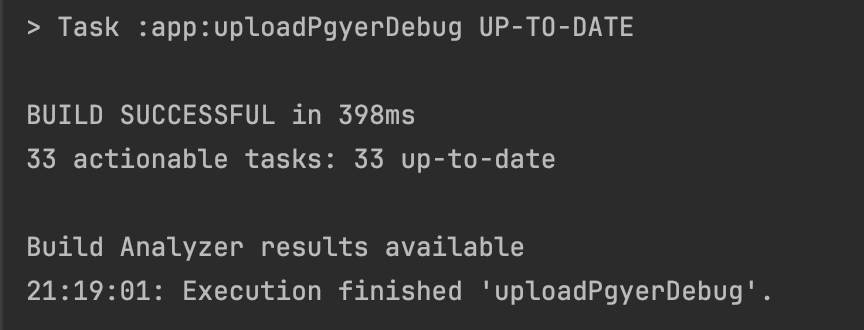 |
Lazy Task Configuration(8.x)
| 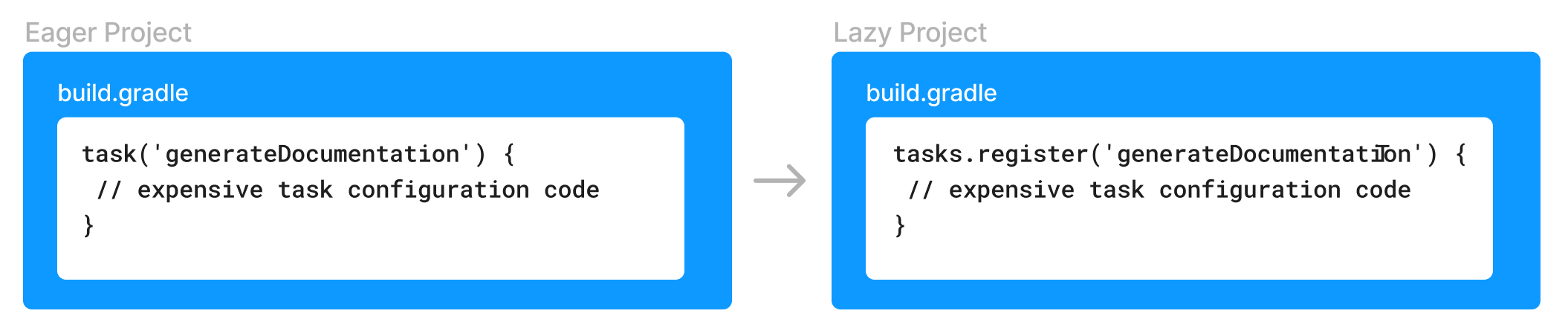 |
Gradle 提供了 lazy 属性,属性值的计算延迟到需要的才计算,Configuration 不会计算,到 Execute 阶段才去计算。
Provider 和 Property
Gradle 提供了 2 种 lazy 属性
- Provider:代表一个可读不可写的属性
- 该属性只可读
Provider.get()返回当前属性值- 一个 Provider 能从另外一个 Provider 创建,通过
Provider.map(Transformer)方法 - 其他类型可以继承 Provider
- Property:代表一个可读可写的属性
- 属性可读可写
- Property 继承 Provider
- Property.set(T) 方法为属性指定一个值
- Property.set(Provider) 方法为属性指定一个 Provider;在属性值配置前,允许将 Provider 和 Property 连接到一起
- 可用工厂方法 ObjectFactory.property(Class) 创建一个 Property
示例:
Property 和 Provider 的属性,不会在 Configuration 阶段执行,在 execute 需要时才执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
abstract class Greeting : DefaultTask() {
@Input
val fileText = getFileTextStr() // Configruation阶段就执行
@get:Input
abstract val greeting: Property<String> // Configruation阶段不执行,Execute阶段执行
private fun getFileTextStr(): String {
println("===================>>> HELLO FROM MY TASK, I AM HACKET")
return "===================>>> HELLO FROM MY TASK, I AM HACKET"
}
@Internal
val message: Provider<String> = greeting.map { // Configruation阶段不执行,Execute阶段执行
println("===================>>> message map $it")
"===================>>> $it from Gradle" }
@TaskAction
fun printMessage() {
logger.quiet(message.get())
}
}
tasks.register<Greeting>("greeting") {
group = "custom"
// 可读可写的属性
greeting.set("Hi")
greeting = "Hi"
// 报错:Provider属性只读,不可更改
// message = "message"
}
//> Configure project :app
//===================>>> HELLO FROM MY TASK, I AM HACKET
//> Task :app:greeting
//===================>>> message map Hi
//===================>>> Hi from Gradle
创建 Property or Provider 实例:
- ` Project.getObjects().property(Class) `
- Provider.map (Transformer) 创建 Provider 从
Provider和Property
属性相连,一个属性引用另外一个属性:message 通过 Property.map{} 引用 greeting 属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
// A project extension
interface MessageExtension {
// A configurable greeting
abstract val greeting: Property<String>
}
// A task that displays a greeting
abstract class Greeting : DefaultTask() {
// Configurable by the user
@get:Input
abstract val greeting: Property<String>
// Read-only property calculated from the greeting
@Internal
val message: Provider<String> = greeting.map { it + " from Gradle" }
@TaskAction
fun printMessage() {
logger.quiet(message.get())
}
}
// Create the project extension
val messages = project.extensions.create<MessageExtension>("messages")
// Create the greeting task
tasks.register<Greeting>("greeting") {
// Attach the greeting from the project extension
// Note that the values of the project extension have not been configured yet
greeting = messages.greeting
}
messages.apply {
// Configure the greeting on the extension
// Note that there is no need to reconfigure the task's `greeting` property. This is automatically updated as the extension property changes
greeting = "Hi"
}
处理文件目录的 Lazy property
处理文件和目录的 Property:
- RegularFileProperty 单个 File
- DirectoryProperty 目录
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
// A task that generates a source file and writes the result to an output directory
abstract class GenerateSource : DefaultTask() {
// The configuration file to use to generate the source file
@get:InputFile
abstract val configFile: RegularFileProperty
// The directory to write source files to
@get:OutputDirectory
abstract val outputDir: DirectoryProperty
@TaskAction
fun compile() {
val inFile = configFile.get().asFile
logger.quiet("configuration file = $inFile")
val dir = outputDir.get().asFile
logger.quiet("output dir = $dir")
val className = inFile.readText().trim()
val srcFile = File(dir, "${className}.java")
srcFile.writeText("public class ${className} { }")
}
}
// Create the source generation task
tasks.register<GenerateSource>("generate") {
// Configure the locations, relative to the project and build directories
configFile = layout.projectDirectory.file("src/config.txt")
outputDir = layout.buildDirectory.dir("generated-source")
}
// Change the build directory
// Don't need to reconfigure the task properties. These are automatically updated as the build directory changes
layout.buildDirectory = layout.projectDirectory.dir("output")
其他 Task 的 output 作为另一个 Task 的 input
示例:Producer 的 output 做为 Consumer 的 input
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
abstract class Producer : DefaultTask() {
@get:OutputFile
abstract val outputFile: RegularFileProperty
@TaskAction
fun produce() {
val message = "Hello, World 1!"
val output = outputFile.get().asFile
output.writeText(message)
logger.quiet("Producer Wrote '${message}' to $output")
}
}
abstract class Consumer : DefaultTask() {
@get:InputFile
abstract val inputFile: RegularFileProperty
@TaskAction
fun consume() {
val input = inputFile.get().asFile
val message = input.readText()
logger.quiet("Consumer Read '${message}' from $input")
}
}
val producer = tasks.register<Producer>("producer")
val consumer = tasks.register<Consumer>("consumer")
consumer {
group = "custom"
// Connect the producer task output to the consumer task input
// Don't need to add a task dependency to the consumer task. This is automatically added
inputFile = producer.flatMap { it.outputFile }
}
producer {
group = "custom"
// Set values for the producer lazily
// Don't need to update the consumer.inputFile property. This is automatically updated as producer.outputFile changes
outputFile = layout.buildDirectory.file("file.txt")
}
// Change the build directory.
// Don't need to update producer.outputFile and consumer.inputFile. These are automatically updated as the build directory changes
layout.buildDirectory = layout.projectDirectory.dir("output")
//> Task :app:producer
//Producer Wrote 'Hello, World 1!' to /Users/xxx/WorkSpace/GradlePluginDemos/GradlePlugin8.0-Kotlin-New/app/output/file.txt
//
//> Task :app:consumer
//Consumer Read 'Hello, World 1!' from /Users/xxx/WorkSpace/GradlePluginDemos/GradlePlugin8.0-Kotlin-New/app/output/file.txt
上面会自动将 Consumer Task 依赖 Producer Task,隐式的依赖关系也可以不用 File
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
abstract class Producer : DefaultTask() {
@get:OutputFile
abstract val outputFile: RegularFileProperty
@TaskAction
fun produce() {
val message = "Hello, World!"
val output = outputFile.get().asFile
output.writeText( message)
logger.quiet("Wrote '${message}' to ${output}")
}
}
abstract class Consumer : DefaultTask() {
@get:Input
abstract val message: Property<String>
@TaskAction
fun consume() {
logger.quiet(message.get())
}
}
val producer = tasks.register<Producer>("producer") {
// Set values for the producer lazily
// Don't need to update the consumer.inputFile property. This is automatically updated as producer.outputFile changes
outputFile = layout.buildDirectory.file("file.txt")
}
tasks.register<Consumer>("consumer") {
// Connect the producer task output to the consumer task input
// Don't need to add a task dependency to the consumer task. This is automatically added
message = producer.flatMap { it.outputFile }.map { it.asFile.readText() }
}
//$ gradle consumer
//> Task :producer
//Wrote 'Hello, World!' to /home/user/gradle/samples/kotlin/build/file.txt
//
//> Task :consumer
//Hello, World!
处理 Collection 的 Lazy property
Gradle 提供了 2 种方式:
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
abstract class Producer1 : DefaultTask() {
@get:OutputFile
abstract val outputFile: RegularFileProperty
@TaskAction
fun produce() {
val message = "Hello, World!"
val output = outputFile.get().asFile
output.writeText(message)
logger.quiet("Producer1 Wrote '${message}' to ${output}")
}
}
abstract class Consumer1 : DefaultTask() {
@get:InputFiles
abstract val inputFiles: ListProperty<RegularFile>
@TaskAction
fun consume() {
inputFiles.get().forEach { inputFile ->
val input = inputFile.asFile
val message = input.readText()
logger.quiet("Consumer1 Read '${message}' from ${input}")
}
}
}
val producerOne = tasks.register<Producer1>("producerOne")
val producerTwo = tasks.register<Producer1>("producerTwo")
tasks.register<Consumer1>("consumer1") {
group = "custom"
// Connect the producer task outputs to the consumer task input
// Don't need to add task dependencies to the consumer task. These are automatically added inputFiles.add(producerOne.get().outputFile)
inputFiles.add(producerTwo.get().outputFile)
}
// Set values for the producer tasks lazily
// Don't need to update the consumer.inputFiles property. This is automatically updated as producer.outputFile changes
producerOne {
group = "custom"
outputFile = layout.buildDirectory.file("one.txt")
}
producerTwo {
group = "custom"
outputFile = layout.buildDirectory.file("two.txt")
}
// Change the build directory.
// Don't need to update the task properties. These are automatically updated as the build directory changes
layout.buildDirectory = layout.projectDirectory.dir("output")
// 首次运行./gradlew consumer1
//> Task :app:producerOne
//Producer1 Wrote 'Hello, World!' to /Users/xxx/WorkSpace/GradlePluginDemos/GradlePlugin8.0-Kotlin-New/app/output/one.txt
//
//> Task :app:producerTwo
//Producer1 Wrote 'Hello, World!' to /Users/xxx/WorkSpace/GradlePluginDemos/GradlePlugin8.0-Kotlin-New/app/output/two.txt
//
//> Task :app:consumer1
//Consumer1 Read 'Hello, World!' from /Users/xxx/WorkSpace/GradlePluginDemos/GradlePlugin8.0-Kotlin-New/app/output/one.txt
//Consumer1 Read 'Hello, World!' from /Users/xxx/WorkSpace/GradlePluginDemos/GradlePlugin8.0-Kotlin-New/app/output/two.txt
处理 map 的 lazy property
Gradle 提供了 MapProperty
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
// Map Configuration for Task Properties
abstract class Generator: DefaultTask() {
@get:Input
abstract val properties: MapProperty<String, Int>
@TaskAction
fun generate() {
properties.get().forEach { entry ->
logger.quiet("${entry.key} = ${entry.value}")
}
}
}
// Some values to be configured later
var b = 0
var c = 0
tasks.register<Generator>("generate") {
group = "custom"
properties.put("a", 1)
// Values have not been configured yet
properties.put("b", providers.provider { b })
properties.putAll(providers.provider { mapOf("c" to c, "d" to c + 1) })
}
conversion
默认值,如果显示设置了值,conversion 再设置就无效了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
tasks.register("show") {
group = "test"
val property = objects.property (String::class)
// Set a convention
property.convention("convention 1")
println("value = " + property.get())
// Can replace the convention
property.convention("convention 2")
println("value = " + property.get())
property.set("explicit value")
// Once a value is set, the convention is ignored
property.convention("ignored convention")
doLast {
println("value = " + property.get())
}
}
//> Configure project :app
//value = convention 1
//value = convention 2
//> Task :app:show
//value = explicit value
Provider 使用指南
- 需要配置的属性,暴露 Property 的 getter;不需要配置的属性,暴露 Provider 的 getter
- 避免在代码中简单调用
obj.getProperty().get()和obj.getProperty().set(T)新增 getter 和 setter - 升级你的插件用 Providers,遵照以下指南:
- 如果是新的属性,暴露一个 Property 或 Provider 的 getter
- 如果还在开发中,更改为 Property 或 Provider 的 getter
- 如果已经是稳定的了,添加新的 Property 或 Provider 的 getter 属性,deprecate 旧的;将旧的 getter/setter 连接到新的属性
Provider Files API
Provider<RegularFile>
Provider < RegularFile > File on disk
Factories
Provider<Directory>
Directory on disk
Factories
FileCollection
Unstructured collection of files
Factories
FileTree
Hierarchy of files
Factories
- Project.fileTree(Object) will produce a ConfigurableFileTree, or you can use Project.zipTree(Object) and Project.tarTree(Object)
- DirectoryProperty.getAsFileTree()
Property Files API
- RegularFileProperty
- DirectoryProperty
- ConfigurableFileCollection
- ConfigurableFileTree
- SourceDirectorySet
Lazy Collections API Reference
ListProperty<T>ListProperty<T>
Lazy Objects API Reference
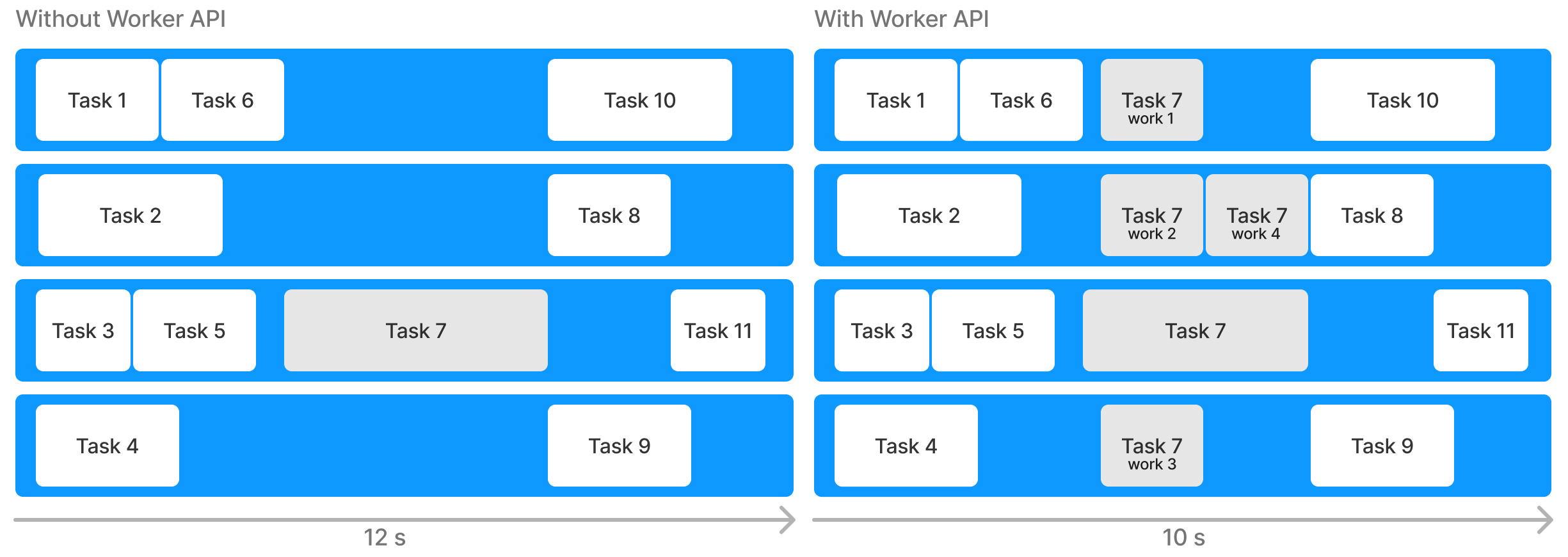
Parallel Tasks
|  |