Claude Agent Skill
Agent Skill Overviews
为什么用 Skills?
- 技能(Skills)定义:可复用、基于文件系统的资源,为 Claude 提供特定领域专业知识(含工作流程、背景信息、最佳实践),能将通用智能体转化为领域专家。
- 与提示词(Prompts)的区别:提示词是针对单次任务的对话级指令,而技能可按需加载,无需在多轮对话中重复提供相同指导。
Specialize Claude 相关要点总结:
- 定制化能力:针对特定领域任务,调整 Claude 的功能,使其适配专业场景需求。
- 减少重复性操作:只需创建一次内容或流程,后续可自动调用使用,提升效率。
- 功能组合:将 Claude 的各项技能进行整合,搭建能处理复杂任务的工作流程。
深入学习:Equipping agents for the real world with Agent Skills.
如何用 Skills?
Anthropic 提供用于常见文档任务(PowerPoint、Excel、Word、PDF)的 pre-built Agent Skills,您还可以创建自己的自定义技能。它们的工作方式相同。当与您的请求相关时,Claude 会自动使用它们。
Pre-built Agent Skills: 所有用户都可以在 claude.ai 上以及通过 Claude API 使用这些功能。完整的可用 skills: Agent Skills - Claude Docs 。
自定义 Skills 让你能够整合领域专业知识和组织知识。它们在 Claude 的各项产品中都可使用:你可以在 Claude Code 中创建它们,通过 API 上传它们,或者在 claude.ai 的设置中添加它们。
- For pre-built Agent Skills: See the quickstart tutorial to start using PowerPoint, Excel, Word, and PDF skills in the API
- For custom Skills: See the Agent Skills Cookbook to learn how to create your own Skills
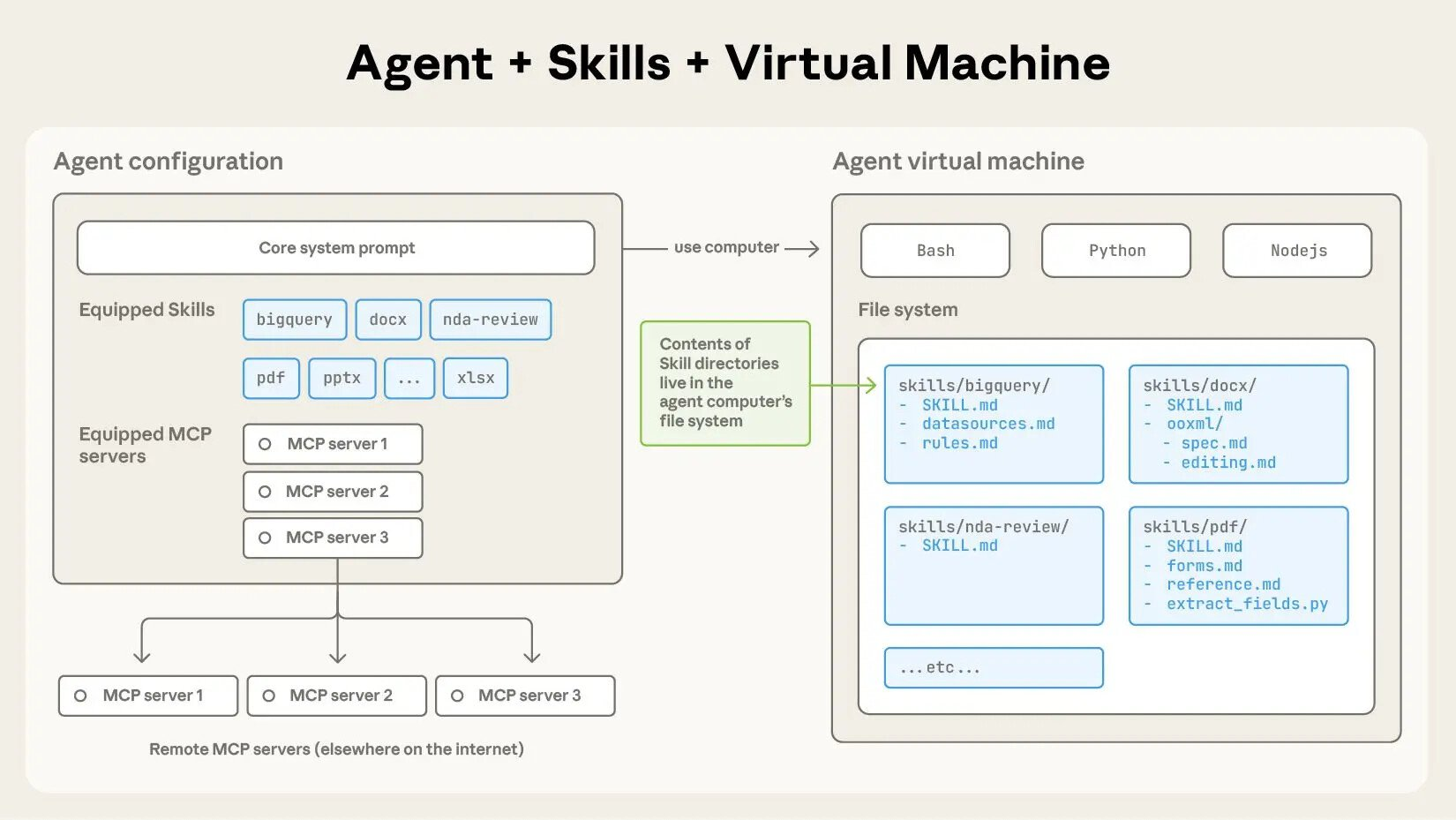
Skills 如何工作的
- 能力突破:Skills 借助 Claude 的虚拟机(VM)环境,实现了仅通过提示词(prompts)无法达成的功能。
- 运行基础:Claude 在具备文件系统访问权限的虚拟机中运行。
- Skills 形态:以目录形式存在,包含 instructions、executable code 及 reference materials,结构类似为新团队成员准备的入职指南。
该基于文件系统的架构支持progressive disclosure(渐进式信息披露):Claude 不会预先占用全部上下文,而是根据需求分阶段加载信息。
三种类型的 skill content,三种 loading 级别
技能可以包含三种类型的内容,每种内容在不同的时间加载:
Level 1: Metadata (always loaded)
Content type: Instructions。该技能的 YAML 前置信息提供了发现信息:
1
2
3
4
---
name: PDF Processing
description: Extract text and tables from PDF files, fill forms, merge documents. Use when working with PDF files or when the user mentions PDFs, forms, or document extraction.
---
- Claude 在启动时会加载相关 metadata 元数据,并将其纳入 system prompt 中。
- 该处理方式具有 “ 轻量 “ 特点。
- 优势:可安装多个 “ 技能(Skills)” 且无上下文惩罚。
- Claude 对各 “ 技能 “ 的认知范围:仅知晓其存在,以及何时该使用它们。
Level 2: Instructions (loaded when triggered)
Content type: Instructions。SKILL.md 的主体部分包含程序性知识:工作流程、最佳实践和指导:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# PDF Processing
## Quick start
Use pdfplumber to extract text from PDFs:
\`\`\`
import pdfplumber
with pdfplumber.open("document.pdf") as pdf:
text = pdf.pages[0].extract_text()
\`\`\`
For advanced form filling, see [FORMS.md](FORMS.md).
当你请求的内容与某项技能的描述相匹配时,Claude 会通过 bash 从文件系统中读取 SKILL.md。只有在此时,该内容才会进入上下文窗口。
Level 3: Resources and code (loaded as needed)
Content types: Instructions, code, and resources. 技能可以捆绑额外的材料:
1
2
3
4
5
6
pdf-skill/
├── SKILL.md (main instructions)
├── FORMS.md (form-filling guide)
├── REFERENCE.md (detailed API reference)
└── scripts/
└── fill_form.py (utility script)
- Instructions: 包含专门指导和工作流程的其他 Markdown 文件(FORMS.md、REFERENCE.md)
- Code: 可执行脚本(fill_form.py、validate.py),Claude 通过 bash 运行这些脚本;脚本提供确定性操作,且不消耗上下文
- Resources: 像数据库模式、API 文档、模板或示例之类的参考资料
Claude 仅在被引用时才会访问这些文件。文件系统模型意味着每种内容类型都有不同的优势:指令用于灵活的指导,代码用于保证可靠性,资源用于事实查询。
| Level | When Loaded | Token Cost | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1: Metadata | Always (at startup) | ~100 tokens per Skill | name and description from YAML frontmatter |
| Level 2: Instructions | When Skill is triggered | Under 5k tokens | SKILL.md body with instructions and guidance |
| Level 3+: Resources | As needed | Effectively unlimited | Bundled files executed via bash without loading contents into context |
渐进式信息披露确保在任何特定时间,只有相关内容会占据上下文窗口。
The Skills architecture
- Skills 运行于特定代码执行环境,该环境中 Claude 具备文件系统访问权、执行 bash 命令及代码的能力。
- 可将 Skills 类比为虚拟机上的目录,Claude 通过常规 bash 命令(与本地电脑操作文件的命令一致)与这些 Skills 进行交互。
1、How Claude accesses Skill content:
- 当某一技能(Skill)被触发时,Claude 通过 bash 读取文件系统中的 SKILL.md,将其指令纳入上下文窗口。
- 若 SKILL.md 的指令提及其他文件(如 FORMS.md、数据库架构文件),Claude 会通过额外的 bash 命令读取这些文件。
- 若指令涉及可执行脚本,Claude 会通过 bash 运行脚本,但仅接收脚本输出,脚本代码本身不会进入上下文。
2、What this architecture enables:
- On-demand file access: Claude 只读取每项特定任务所需的文件。一项技能可能包含数十个参考文件,但如果你的任务只需要销售模式,Claude 就只会加载那个文件。其余文件仍留在文件系统中,不消耗任何令牌。
- Efficient script execution: 当 Claude 运行 validate_form.py 时,该脚本的代码从未加载到上下文窗口中。只有脚本的输出(如 “ 验证通过 “ 或特定的错误消息)会消耗令牌。这使得脚本比让 Claude 实时生成等效代码高效得多。
- No practical limit on bundled content: 由于文件在被访问前不会占用上下文,技能可以包含全面的 API 文档、大型数据集、丰富的示例或任何你需要的参考资料。对于未使用的捆绑内容,不会有上下文惩罚。
小结:
- 基于文件系统的模型是实现 “ 渐进式信息披露 “ 的核心。
- Claude(工具/系统)对 “ 技能(Skill)” 的操作方式,类似人类查阅入职指南中特定章节的逻辑。
- 其核心特点是:仅获取每项任务所需的精准信息,不冗余。
Example: Loading a PDF processing skill
以下是 Claude 加载和使用 PDF 处理技能的方式:
- Startup: System prompt includes:
PDF Processing - Extract text and tables from PDF files, fill forms, merge documents - User request: “Extract the text from this PDF and summarize it”
- Claude invokes:
bash: read pdf-skill/SKILL.md→ Instructions loaded into context - Claude determines: Form filling is not needed, so FORMS.md is not read
- Claude executes: Uses instructions from SKILL.md to complete the task
该图表展示了:
- Default state with system prompt and skill metadata pre-loaded
- Claude triggers the skill by reading SKILL.md via bash
- Claude optionally reads additional bundled files like FORMS.md as needed
- Claude proceeds with the task
这种动态加载确保只有相关的技能内容会占用上下文窗口。
Where Skills work
- Claude API
- Claude Code
- Claude.ai
Skill structure
每项 Skill 都需要一个带有 YAML 前置信息的 SKILL.md 文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
---
name: Your Skill Name
description: Brief description of what this Skill does and when to use it
---
# Your Skill Name
## Instructions
[Clear, step-by-step guidance for Claude to follow]
## Examples
[Concrete examples of using this Skill]
Required fields: name and description 这是 YAML 前置元数据中仅支持的两个字段。 Frontmatter limits:
name: 64 characters maximumdescription: 1024 characters maximum
该 description 应既包含这项技能的作用,也说明 Claude 应在何时使用它。For complete authoring guidance, see the best practices guide.
Available Skills
Pre-built Agent Skills
以下 pre-built 的代理技能可立即使用:
- PowerPoint (pptx): Create presentations, edit slides, analyze presentation content
- Excel (xlsx): Create spreadsheets, analyze data, generate reports with charts
- Word (docx): Create documents, edit content, format text
- PDF (pdf): Generate formatted PDF documents and reports
这些技能在 Claude API 和 claude.ai 上均可使用。参见 quickstart tutorial,了解如何在 API 中开始使用它们。
Custom Skills examples
关于自定义技能的完整示例,见 Skills cookbook。
Get started with Agent Skills in the API
Get started with Agent Skills in the API - Claude Docs
了解如何在 10 分钟内使用 Agent Skills 通过 Claude API 创建文档。
Claude Code Agent Skills
Claude Code Skill 基础
Claude Skill 介绍
Skills 是包含了 SKILL.md 、脚本及其他资源的一组文件夹。大模型可以通过使用 Skills 提升处理特别任务的能力。Claude 可在需要时加载这些内容。
Agent Skills 目前支持在
Claude.ai、Claude Code、Claude Agent SDK和Claude 开发平台使用。
不像 slash commands 是用户主动调用,skills 是 LLM 调用的(根据你的 request 和 skill 描述)。
更多见:Agent Skills - Claude Docs
Skills 的工作原理
在执行任务时,Claude 会扫描可用的技能,以寻找相关匹配。一旦找到匹配项,它只会加载所需的最少信息和文件——确保 Claude 在快速访问专业技能的同时保持高效。
技能具备以下特点:
- 可组合性 :技能可以相互叠加。Claude 会自动识别所需技能,并协调它们的使用。
- 便携性 :技能采用统一的格式,适用于任何场景。只需构建一次,即可在 Claude 应用、Claude Code 及 API 中通用。
- 高效 :仅在需要时加载所需内容。
- 强大 :技能可包含用于执行任务的可运行代码,尤其在传统编程比生成令牌更可靠的情况下。
将技能视为定制化的入职培训材料,帮助您整合专业知识,使 Claude 成为您最关注领域的专家。如需深入了解 Agent Skills 设计模式、架构及开发最佳实践。
Claude Code 中使用
- 在 ~/.claude/ 文件夹下创建技能文件夹和 SKILL.md,比如
~/.claude/pdf/SKILL.md - SKILL.md 以 ymal 格式的元数据开头,定义技能名字与简介
name和description 一级: 这些元数据会常驻上下文,以极少的 token 占用让大模型始终知道什么时候可以用什么技能二级: SKILL.md 内容教 AI 大概怎么搞,不要太冗长,保持 5K 以内;三级: 把具体的操作拆分成更细节的 md 文件在 SKILL.md 加以描述,在需要的时候才去读取- 可以写好一些脚本放在文件夹里
- 支持项目级:
项目文件夹/.claude/skills/
Skill 的理解
本质上是为了提升能力并节省 context window 设计的一套 渐进式展开 的机制。
这套机制并不陌生,有点类似 Cursor 之前的 .mdc 配置。
- 比纯 MCP 好用一些
- 这个功能非常有价值,以往只能在
AGENTS.md里罗里吧嗦想教会 AI 一切,又抠抠搜搜想节省上下文,主打一个 200K 焦虑。 现在可以充分利用这个渐进式展开的机制,为我们的大模型多装备一些技能卡,提升开发效率,增加刷 L 站的摸鱼时间。
创建一个 Skill
技能以包含 SKILL.md 文件的目录形式存储。
Skill 分类
个人 skills: 作用于所有项目,存储在 ~/.claude/skills/
1
mkdir -p ~/.claude/skills/my-skill-name
将个人技能用于:
- 你的个人工作流程和偏好
- 你正在培养的实验性技能
- 个人生产力工具
项目 skills: 项目技能会与你的团队共享。将它们存储在项目内的 .claude/skills/ 目录中:
1
mkdir -p .claude/skills/my-skill-name
将项目技能用于:
- 团队工作流程和惯例
- 特定项目的专业知识
- 共享工具和脚本 项目的 skills 需要提交到 git 仓库,团队所有成员共享
Pluin skills: 也可以来自 claude code plugin,可分为个人和项目 skillss。
Write SKILL.md
创建 SKILL.md 文件,以 yaml 格式开头的 md 文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
---
name: Your Skill Name
description: Brief description of what this Skill does and when to use it
---
# Your Skill Name
## Instructions
Provide clear, step-by-step guidance for Claude.
## Examples
Show concrete examples of using this Skill.
description字段对于 Claude 发现何时使用你的技能至关重要。它既应包含该技能的功能,也应说明 Claude 应该在何时使用它。
See the best practices guide for complete authoring guidance.
Add supporting files
创建一些额外的文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
my-skill/
├── SKILL.md (required)
├── reference.md (optional documentation)
├── examples.md (optional examples)
├── scripts/
│ └── helper.py (optional utility)
└── templates/
└── template.txt (optional template)
在 SKILL.md 中引用这些文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
For advanced usage, see [reference.md](reference.md).
Run the helper script:
\```bash
python scripts/helper.py input.txt
\```
Claude 仅在需要时读取这些文件,并通过渐进式信息披露来高效管理 context 。
Restrict tool access with allowed-tools
使用 allowed-tools 前置信息字段来限制 Claude 在 skill 激活时可以使用的工具:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
---
name: Safe File Reader
description: Read files without making changes. Use when you need read-only file access.
allowed-tools: Read, Grep, Glob
---
# Safe File Reader
This Skill provides read-only file access.
## Instructions
1. Use Read to view file contents
2. Use Grep to search within files
3. Use Glob to find files by pattern
当此 skill 激活时,Claude 只能使用指定工具(Read、Grep、Glob),无需请求许可。这在以下场景中很有用:
- 不应修改文件的 read-only skill
- 范围有限的 skill(例如,仅进行数据分析,不进行文件写入)
- 需要限制功能的安全敏感工作流
如果未指定 allowed-tools,Claude 将按照标准权限模型,像往常一样请求使用工具的许可。
allowed-tools仅支持 Claude Code 中的技能。
View available Skills
技能由 Claude 从三个来源自动发现:
- Personal Skills:
~/.claude/skills/ - Project Skills:
.claude/skills/ - Plugin Skills: bundled with installed plugins
要查看所有可用技能,请直接询问 Claude:
1
2
3
What Skills are available?
# 或
List all available Skills
这将显示所有来源的所有技能,包括插件技能。
Test a Skill 测试技能
创建 skill 后,通过提出与你的描述相符的问题来测试它。
示例:如果您的描述中提到 “PDF 文件 “:
1
Can you help me extract text from this PDF?
如果 Claude 判断你的请求与该技能匹配,它会自主决定使用该技能——你无需明确调用。该技能会根据你的问题语境自动激活。
Debug a Skill 调试技能
如果 Claude 没有使用你的技能,请检查以下常见问题:
1、Make description specific 使描述具体化 在描述中既包含该技能的功能,也说明何时使用它。
1
2
3
4
5
## too vague
description: Helps with documents
## Specific
description: Extract text and tables from PDF files, fill forms, merge documents. Use when working with PDF files or when the user mentions PDFs, forms, or document extraction.
2、Verify file path 验证文件路径,检查文件是否存在
- Personal Skills:
~/.claude/skills/skill-name/SKILL.md - Project Skills:
.claude/skills/skill-name/SKILL.md
3、Check YAML syntax 检查 YAML 语法 无效的 YAML 会阻止技能加载。请验证前置内容:
1
cat SKILL.md | head -n 10
确保:
- Opening
---on line 1 第 1 行的开头为--- - Closing
---before Markdown content Markdown 内容前的闭合--- - Valid YAML syntax (no tabs, correct indentation) 有效的 YAML 语法(无制表符,正确缩进)
4、View errors 查看错误 以调试模式运行 Claude Code,查看技能加载错误:
1
claude --debug
Share Skills with your team
推荐方法:通过 插件 分发技能。 通过插件分享技能:
- 在
skills/目录中创建一个带有技能的插件 - 将插件添加到市场
- 团队成员安装该插件 完整说明请参见 为你的插件添加技能。
也可以通过项目仓库直接分享技能:
- Step 1: Add Skill to your project
1
2
mkdir -p .claude/skills/team-skill
# Create SKILL.md
- Step 2: Commit to git
1
2
3
git add .claude/skills/
git commit -m "Add team Skill for PDF processing"
git push
- Step 3: Team members get Skills automatically 当团队成员拉取最新更改时,技能会立即可用:
1
2
git pull
claude # Skills are now available
Update a Skill
1
2
3
4
5
# Personal Skill
code ~/.claude/skills/my-skill/SKILL.md
# Project Skill
code .claude/skills/my-skill/SKILL.md
更改将在您下次启动 Claude Code 时生效。如果 Claude Code 已在运行,请重启它以加载更新。
Remove a Skill
删除技能目录:
1
2
3
4
5
6
# Personal
rm -rf ~/.claude/skills/my-skill
# Project
rm -rf .claude/skills/my-skill
git commit -m "Remove unused Skill"
Best practices
Keep Skills focused 保持技能专注
一项技能应对应一项能力。
Focused:
- “PDF form filling” ”PDF 表单填写 “
- “Excel data analysis” ”Excel 数据分析 “
- “Git commit messages” ”Git 提交消息 “
Too broad:
- “Document processing” (split into separate Skills)” 文档处理 “(拆分为单独的技能)
- “Data tools” (split by data type or operation)” 数据工具 “(按数据类型或操作拆分)
Write clear descriptions 撰写清晰的描述
在描述中加入特定触发条件,帮助 Claude 了解何时使用技能:
Clear:
1
description: Analyze Excel spreadsheets, create pivot tables, and generate charts. Use when working with Excel files, spreadsheets, or analyzing tabular data in .xlsx format.
Vague:
1
description: For files
Test with your team 与团队一起测试
让团队成员使用技能并提供反馈:
- 该技能是否在预期时激活?
- 说明清晰吗?
- 是否有缺失的示例或边缘情况?
Document Skill versions 记录技能版本
你可以在 SKILL.md 内容中记录技能版本,以跟踪随时间的变化。添加一个版本历史部分:
1
2
3
4
5
6
# My Skill
## Version History
- v2.0.0 (2025-10-01): Breaking changes to API
- v1.1.0 (2025-09-15): Added new features
- v1.0.0 (2025-09-01): Initial release
这有助于团队成员了解不同版本之间的变化。
Skill Troubleshooting
参考: Troubleshooting- Agent Skills - Claude Docs
Skill authoring best practices
Skill authoring best practices - Claude Docs
了解如何编写有效的技能,以便 Claude 能够发现并成功运用这些技能。
优秀的技能(Skills)应当简洁明了、结构清晰,并且经过实际使用的检验。本指南提供了实用的编写建议,以帮助你写出 Claude 能够发现并有效使用的技能(Skills)。
Core principles
Concise is key 简洁是关键
context window 是一种公共资源。你的技能与 Claude 需要了解的其他所有信息共享这个上下文窗口,包括:
- The system prompt
- Conversation history
- Other Skills’ metadata
- Your actual request
- 并非技能(Skill)中的所有令牌(token)都有即时成本。
- 启动时,仅预加载所有技能的元数据(name 和 description)。
- Claude 仅在技能相关时才读取 SKILL.md,且仅按需读取额外文件。
- SKILL.md 保持简洁仍很重要:一旦 Claude 加载它,其每一个令牌都会与对话历史及其他上下文资源竞争。
Default assumption: Claude 已经非常聪明了,只添加 Claude 没有的 context info
好的示例是简洁,不用过多的描述。
设定适当的自由度
让技能的 “ 具体程度 “ 与任务本身的 “ 风险敏感度 “ 和 “ 可变空间 “ 相匹配,避免过度约束或指导不足。
Test with all models you plan to use
技能是对模型的补充,因此其效果取决于底层模型。请用你计划使用该技能的所有模型对其进行测试。
按模型划分的测试注意事项:
- Claude Haiku(快速、经济实惠):该技能是否提供了足够的指导?
- Claude Sonnet(平衡型):该技能是否清晰且高效?
- Claude Opus(强大推理能力):该技能是否避免了过度解释?
对 Opus 来说效果极佳的内容,可能需要为 Haiku 补充更多细节。如果你计划在多个模型中使用你的技能,目标应该是制定出对所有模型都适用的指令。
Skill structure
Naming conventions (命名规范)
使用一致的命名模式可以让技能(Skills)更易于引用和讨论。我们建议技能名称采用动名词形式(动词 + -ing),因为这能清晰地描述该技能所提供的活动或能力。
Good naming examples (gerund form )(动名词形式):
- “Processing PDFs”
- “Analyzing spreadsheets”
- “Managing databases”
- “Testing code”
- “Writing documentation”
Acceptable alternatives(可接受的替代方案:):
- Noun phrases(名词短语): “PDF Processing”, “Spreadsheet Analysis”
- Action-oriented(面向行动的): “Process PDFs”, “Analyze Spreadsheets”
Avoid(避免):
- Vague names(不明确的 name): “Helper”, “Utils”, “Tools”
- Overly generic(过于宽泛): “Documents”, “Data”, “Files”
- Inconsistent patterns within your skill collection 您的技能集合中存在不一致的模式
一致的命名有助于:
- 在文档和对话中引用技能
- 一眼了解技能的作用
- 对多个技能进行整理和搜索
- 维护专业、统一的技能库
Writing effective descriptions (撰写有效的描述)
description 字段有助于技能的发现,它应当既包含该技能的功能,也说明何时使用该技能。
始终使用第三人称写作。该描述会被注入到系统提示中,不一致的视角可能会导致识别问题。
- Good: ”Processes Excel files and generates reports”
- Avoid: ”I can help you process Excel files”
- Avoid: ”You can use this to process Excel files”
要具体,并包含关键术语: 既包含该技能的功能,也包含使用它的具体触发条件/场景
每个技能都有且仅有一个 description 字段。该描述对于技能选择至关重要:Claude 会利用它从可能超过 100 个的可用技能中挑选出合适的技能。你的描述必须提供足够的细节,让 Claude 知道何时选择该技能,而 SKILL.md 的其余部分则提供实现细节。
Effective examples:
PDF Processing skill:
1
description: Extract text and tables from PDF files, fill forms, merge documents. Use when working with PDF files or when the user mentions PDFs, forms, or document extraction.
Excel Analysis skill:
1
description: Analyze Excel spreadsheets, create pivot tables, generate charts. Use when analyzing Excel files, spreadsheets, tabular data, or .xlsx files.
Git Commit Helper skill:
1
description: Generate descriptive commit messages by analyzing git diffs. Use when the user asks for help writing commit messages or reviewing staged changes.
避免像这样模糊的描述:
1
2
3
4
5
6
description: Helps with documents
description: Processes data
description: Does stuff with files
Progressive disclosure 渐进式信息披露模式
SKILL.md 起到概述的作用,会在需要时指引 Claude 查看详细材料,就像入职指南中的目录一样。关于渐进式披露如何运作的解释, see How Skills work。
实用指南:
- 为获得最佳性能,请将 SKILL.md 的主体内容控制在 500 行以内
- 当接近此限制时,将内容拆分到单独的文件中
- 使用以下模式有效地组织说明、代码和资源
视觉概览:从简单到复杂
一个基础的技能只需从一个包含 metadata 和 instructions 的 SKILL.md 文件开始:
随着你的技能不断提升,你可以捆绑额外的内容,Claude 只会在需要时加载这些内容:
完整的技能目录结构可能如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
pdf/
├── SKILL.md # Main instructions (loaded when triggered)
├── FORMS.md # Form-filling guide (loaded as needed)
├── reference.md # API reference (loaded as needed)
├── examples.md # Usage examples (loaded as needed)
└── scripts/
├── analyze_form.py # Utility script (executed, not loaded)
├── fill_form.py # Form filling script
└── validate.py # Validation script
Pattern 1: High-level guide with references 带参考资料的高级指南
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
---
name: PDF Processing
description: Extracts text and tables from PDF files, fills forms, and merges documents. Use when working with PDF files or when the user mentions PDFs, forms, or document extraction.
---
# PDF Processing
## Quick start
Extract text with pdfplumber:
``python
import pdfplumber
with pdfplumber.open("file.pdf") as pdf:
text = pdf.pages[0].extract_text()
``
## Advanced features
**Form filling**: See [FORMS.md](FORMS.md) for complete guide
**API reference**: See [REFERENCE.md](REFERENCE.md) for all methods
**Examples**: See [EXAMPLES.md](EXAMPLES.md) for common patterns
Claude 仅在需要时才加载 FORMS.md、REFERENCE.md 或 EXAMPLES.md。
Pattern 2: Domain-specific organization 特定领域组织
对于包含多个领域的技能,应按领域组织内容,以避免加载不相关的上下文。当用户询问销售指标时,Claude 只需读取与销售相关的模式,无需读取财务或营销数据。这样可以降低令牌使用量,并使上下文更加集中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
bigquery-skill/
├── SKILL.md (overview and navigation)
└── reference/
├── finance.md (revenue, billing metrics)
├── sales.md (opportunities, pipeline)
├── product.md (API usage, features)
└── marketing.md (campaigns, attribution)
Skill.md
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# BigQuery Data Analysis
## Available datasets
**Finance**: Revenue, ARR, billing → See [reference/finance.md](reference/finance.md)
**Sales**: Opportunities, pipeline, accounts → See [reference/sales.md](reference/sales.md)
**Product**: API usage, features, adoption → See [reference/product.md](reference/product.md)
**Marketing**: Campaigns, attribution, email → See [reference/marketing.md](reference/marketing.md)
## Quick search
Find specific metrics using grep:
``bash
grep -i "revenue" reference/finance.md
grep -i "pipeline" reference/sales.md
grep -i "api usage" reference/product.md
``
Pattern 3: Conditional details 条件详情
展示基本内容,链接到高级内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# DOCX Processing
## Creating documents
Use docx-js for new documents. See [DOCX-JS.md](DOCX-JS.md).
## Editing documents
For simple edits, modify the XML directly.
**For tracked changes**: See [REDLINING.md](REDLINING.md)
**For OOXML details**: See [OOXML.md](OOXML.md)
只有当用户需要那些功能时,Claude 才会读取 REDLINING.md 或 OOXML.md。
Avoid deeply nested references(避免深度嵌套的引用)
当文件从其他被引用的文件中被引用时,Claude 可能会部分读取这些文件。遇到嵌套引用时,Claude 可能会使用诸如 head -100 之类的命令来预览内容,而不是读取整个文件,这会导致信息不完整。
Keep references one level deep from SKILL.md(保持从 SKILL.md 出发的引用层级为一级)。所有参考文件都应直接从 SKILL.md 链接,以确保 Claude 在需要时能读取完整的文件。
Bad example: Too deep:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# SKILL.md
See [advanced.md](advanced.md)...
# advanced.md
See [details.md](details.md)...
# details.md
Here's the actual information...
Good example: One level deep:
1
2
3
4
5
6
# SKILL.md
**Basic usage**: [instructions in SKILL.md]
**Advanced features**: See [advanced.md](advanced.md)
**API reference**: See [reference.md](reference.md)
**Examples**: See [examples.md](examples.md)
用目录来组织较长的参考文件
对于超过 100 行的参考文件,要在顶部包含一个目录。这样即使 Claude 在进行部分读取预览时,也能了解到可用信息的完整范围。
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# API Reference
## Contents
- Authentication and setup
- Core methods (create, read, update, delete)
- Advanced features (batch operations, webhooks)
- Error handling patterns
- Code examples
## Authentication and setup
...
## Core methods
...
Claude 随后可以阅读完整文件,或根据需要跳转到特定部分。
有关这种基于文件系统的架构如何实现渐进式信息披露的详细信息,请参见下面 Runtime environment 部分中的运行时环境部分。
Workflows and feedback loops(工作流程和反馈循环)
Use workflows for complex tasks
对复杂任务使用工作流:将复杂操作分解为清晰的、按顺序排列的步骤。对于特别复杂的工作流程,提供一个清单,让 Claude 可以复制到其回复中,并在进展过程中逐一勾选。
示例 1: 研究综合工作流程(适用于无代码技能):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
## Research synthesis workflow
Copy this checklist and track your progress:
\```
Research Progress:
- [ ] Step 1: Read all source documents
- [ ] Step 2: Identify key themes
- [ ] Step 3: Cross-reference claims
- [ ] Step 4: Create structured summary
- [ ] Step 5: Verify citations
\```
**Step 1: Read all source documents**
Review each document in the `sources/` directory. Note the main arguments and supporting evidence.
**Step 2: Identify key themes**
Look for patterns across sources. What themes appear repeatedly? Where do sources agree or disagree?
**Step 3: Cross-reference claims**
For each major claim, verify it appears in the source material. Note which source supports each point.
**Step 4: Create structured summary**
Organize findings by theme. Include:
- Main claim
- Supporting evidence from sources
- Conflicting viewpoints (if any)
**Step 5: Verify citations**
Check that every claim references the correct source document. If citations are incomplete, return to Step 3.
这个例子展示了工作流如何应用于不需要代码的分析任务。清单模式适用于任何复杂的、多步骤的流程。
示例 2: PDF 表单填写工作流程(适用于带代码的技能):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
## PDF form filling workflow
Copy this checklist and check off items as you complete them:
\```
Task Progress:
- [ ] Step 1: Analyze the form (run analyze_form.py)
- [ ] Step 2: Create field mapping (edit fields.json)
- [ ] Step 3: Validate mapping (run validate_fields.py)
- [ ] Step 4: Fill the form (run fill_form.py)
- [ ] Step 5: Verify output (run verify_output.py)
\```
**Step 1: Analyze the form**
Run: `python scripts/analyze_form.py input.pdf`
This extracts form fields and their locations, saving to `fields.json`.
**Step 2: Create field mapping**
Edit `fields.json` to add values for each field.
**Step 3: Validate mapping**
Run: `python scripts/validate_fields.py fields.json`
Fix any validation errors before continuing.
**Step 4: Fill the form**
Run: `python scripts/fill_form.py input.pdf fields.json output.pdf`
**Step 5: Verify output**
Run: `python scripts/verify_output.py output.pdf`
If verification fails, return to Step 2.
清晰的步骤可防止 Claude 跳过关键的验证环节。这份清单能帮助 Claude 和你追踪多步骤工作流程中的进度。
Implement feedback loops
实施反馈循环
常见模式: 运行验证程序→修复错误→重复
这种模式极大地提高了输出质量。
示例 1: 符合风格指南(适用于无代码技能):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
## Content review process
1. Draft your content following the guidelines in STYLE_GUIDE.md
2. Review against the checklist:
- Check terminology consistency
- Verify examples follow the standard format
- Confirm all required sections are present
3. If issues found:
- Note each issue with specific section reference
- Revise the content
- Review the checklist again
4. Only proceed when all requirements are met
5. Finalize and save the document
这展示了使用参考文档而非脚本的验证循环模式。” 验证器 “ 是 STYLE_GUIDE.md,Claude 通过读取和比较来执行检查。
示例 2: 文档编辑流程(适用于带代码的技能):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
## Document editing process
1. Make your edits to `word/document.xml`
2. **Validate immediately**: `python ooxml/scripts/validate.py unpacked_dir/`
3. If validation fails:
- Review the error message carefully
- Fix the issues in the XML
- Run validation again
4. **Only proceed when validation passes**
5. Rebuild: `python ooxml/scripts/pack.py unpacked_dir/ output.docx`
6. Test the output document
验证循环可及早发现错误。
Content guidelines
避免包含时效性强的信息
不要包含会过时的信息:
反面示例:具有时间敏感性(将会变得不正确):
1
2
If you're doing this before August 2025, use the old API.
After August 2025, use the new API.
好例子(使用 “ 旧模式 “ 部分):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
## Current method
Use the v2 API endpoint: `api.example.com/v2/messages`
## Old patterns
<details>
<summary>Legacy v1 API (deprecated 2025-08)</summary>
The v1 API used: `api.example.com/v1/messages`
This endpoint is no longer supported.
</details>
” 旧模式 “ 部分提供了历史背景,同时又不会使主要内容显得杂乱。
使用一致的术语
选择一个术语,并在整个技能中使用它:
Good - Consistent
- Always “API endpoint”
- Always “field”
- Always “extract”
Bad - Inconsistent
- Mix “API endpoint”, “URL”, “API route”, “path”
- Mix “field”, “box”, “element”, “control”
- Mix “extract”, “pull”, “get”, “retrieve”
一致性有助于 Claude 理解并遵循指令。
Common patterns
Skill authoring best practices - Claude Docs
Evaluation and iteration
Skill authoring best practices - Claude Docs
Advanced: Skills with executable code
Equipping agents for the real world with Agent Skills
Skill authoring best practices - Claude Docs
Ref
- simon: Claude Skills are awesome, maybe a bigger deal than MCP
- engineering blog:Equipping agents for the real world with Agent Skills
- Claude Code Skills: Agent Skills - Claude Docs
- Claude Skills Developer: Agent Skills - Claude Docs
- GitHub - anthropics/skills: Public repository for Skills