Bitmask
Bitmask
Android 中应用程序的状态表示
通过 int 值表示,通过 1 左移 n 位来表示不同的状态
int 值表示多种状态(最多 32 个状态)
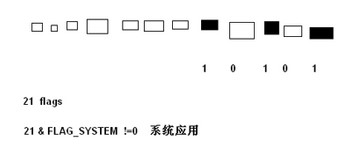
1、Android 中应用程序的状态表示:一个 int 值有 32 位,Android 中用前 28 位,每一位代表一个功能 (一总状态)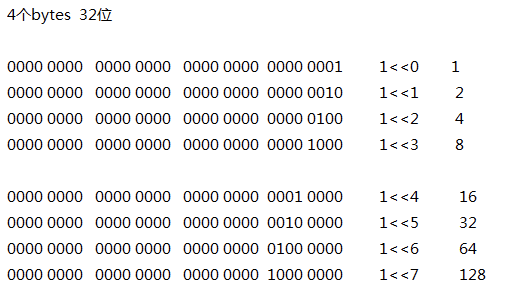
2、如:flags = 21
flags & FLAG_SYSTEM != 0 说明了第 0 位为 1,表示是系统应用,否则是非系统应用
3、再如
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
①int flags = applicationInfo.flags;
flags = 572998
转换成32位的二进制为:0000 0000 0000 1000 1011 1110 0100 0110
②分析:和定义好的常量进行&操作,如果不为0,表示该位为1
第0位为0,第17位为0,表示该应用不是系统应用,没有安装在sd卡(安装在内置存储空间)
③代码:
if ((flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_EXTERNAL_STORAGE)!=0) {
//表示应用安装在内部存储空间
}
if ((flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM)!=0) {
//表示应用是系统应用
}
ApplicationInfo 中常见的状态
1
2
public static final int FLAG_SYSTEM = 1<<0; //该位为1表示是系统应用
public static final int FLAG_EXTERNAL_STORAGE = 1<<18; //该位为1表示应用安装在外部存储设备
应用:如果应用的状态过多,可以这样定义,如:一个电视频道的状态,游戏的状态机(满足很多条件才能做某件事)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
ApplicationInfo中定义的常量,用一个int值来表示该应用的各种信息,
ApplicationInfo applicationInfo = packageInfo.applicationInfo;
public static final int FLAG_SYSTEM = 1<<0; //if set, this application is installed in the * device's system image.
public static final int FLAG_DEBUGGABLE = 1<<1;
public static final int FLAG_HAS_CODE = 1<<2;
......
public static final int FLAG_CANT_SAVE_STATE = 1<<28;
int flags = packageInfo.applicationInfo.flags; //Flags associated with the application.
flags是该应用程序信息的标识,一个int来表示,每一位代表一个信息,
所以,要想知道某一位是否设置了,只需要将该flags和某一位进行与操作,
如果为0,说明该位没有设置,否则,表示该位设置了。
(ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM & flags) != 0
应用:如上面的手机频道项目,一个频道有n多个属性,该频道是否免费,是否优惠,是否在套餐中,是否18岁以上才能看等10几个属性,可以这样定义,
private int isFree = 1<<0;
private int isFavorable 1<<1;
private int isInCombo 1<<2;
......
要想判断一个频道是否具备某些属性,只需要将该频道的flag和某一个属性进行与操作,
如果结果不等于0,说明具备该属性。
重要:对于一些状态较多的,可以借鉴这种方式定义状态
BitMask 之 int 表示 32 状态或 byte 表示 8 种状态
Bitmask 位操作,bit mask int bit int bit mask
在 Android 中,也大量地使用了 BitMask,比如 android.view.View 这个类。
位操作
1、NOT
1
2
3
4
int a = 1;
int b = ~a;
NOT 0000 0001 = 1111 1110
2、OR
1
2
3
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = a | b;
3、AND
Bitmask
每一个 bit 可以有两种取值:0 或 1;
BitMask 采用一个数值来记录状态,使用这个数值的每一位来表达一个状态。 使用 BitMask 可用非常少的资源表达非常丰富的状态。更为重要的是,基于 BitMask 可 非常简单地进行组合状态查询。
byte
在 Java 中,一个 byte 类型,有 8 位(bit),可以表达 8 个不同的状态,并且这些状态是互不影响的。
- 设置状态
设置状态即和 mask 值进行逻辑『或』
1
status |= mask;
- 清除状态
清除状态与 mask 的反码进行逻辑『与』运算。 - 查询状态
与 mask 进行逻辑『与』运行,判断是否为零即可
一个诗人的状态在喝酒还是在写作:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
public final class Poet {
private byte mState;
/**
* 喝酒状态
*/
// 0000 0010
private static final byte STATE_BUSY_IN_WRITING = 0x01 << 1;
/**
* 写作状态
*/
// 0000 0100
private static final byte STATE_BUSY_IN_DRINKING = 0x01 << 2;
/**
* 边喝酒边写作状态
*/
private static final byte STATE_BUSY_MASK = STATE_BUSY_IN_WRITING | STATE_BUSY_IN_DRINKING;
/**
* 设置是否在喝酒
*/
public void setBusyInDrinking(boolean busy) {
if (busy) {
mState |= STATE_BUSY_IN_DRINKING;
} else {
mState &= ~STATE_BUSY_IN_DRINKING;
}
}
/**
* 设置是否在写作
*/
public void setBusyInWriting(boolean busy) {
if (busy) {
mState |= STATE_BUSY_IN_WRITING;
} else {
mState &= ~STATE_BUSY_IN_WRITING;
}
}
/**
* 查询是否在喝酒
*/
public boolean isBusyInDrinking() {
return (mState & STATE_BUSY_IN_DRINKING) != 0;
}
/**
* 查询是否在写作
*/
public boolean isBusyInWriting() {
return (mState & STATE_BUSY_IN_DRINKING) != 0;
}
/**
* 是否处于忙碌状态
*/
public boolean isBusy() {
return (mState & STATE_BUSY_MASK) != 0;
}
}
int
一个 int 类型,则有 32 位,可以表达 32 种状态。
一个 int 值 32 位,二进制数要转换为十六进制,就是以 4 位一段,分别转换为十六进制,如
0000 0000 , 1111 1101 , 1010 0101 , 1001 1011
0 0 , F D , A 5 , 9 B
十六进制表示就是:0x00FDA59B
Gson 中的 Modifier 大量用到
Reference
- 细谈 Android 中的 attributes 属性标志
http://www.jianshu.com/p/045c8529b9c6#> - BitMask 使用参考
http://www.jianshu.com/p/694979e1c252#> - 就算不去火星种土豆,也请务必掌握的 Android 状态管理最佳实践!
https://juejin.im/entry/5d1c2270e51d4576bc1a0e59
BitMask int 32 位
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
/**
* 64bit flag <br/>
* 1. 可根据按bit index add flag <br/>
* 2. 也可以自定义flag位 <br/>
*/
public abstract class BitMaskLong {
private static final long FLAG_UNKNOWN = 0x00;
private static final long FLAG_BASE = 0x01;
private long flags = FLAG_UNKNOWN;
public BitMaskLong() {
clearFlags();
}
public void addBitIndexFlag(@IntRange(from = 0, to = Long.SIZE - 1) int bitIndex) {
operateFlag(bitIndex, true);
}
public void clearBitIndexFlag(@IntRange(from = 0, to = Long.SIZE - 1) int bitIndex) {
operateFlag(bitIndex, false);
}
public boolean hasBitIndexFlag(@IntRange(from = 0, to = Long.SIZE - 1) int bitIndex) {
return hasFlag(FLAG_BASE << bitIndex);
}
// --------
public void addFlag(long flag) {
flags |= flag;
}
public boolean hasFlag(long flag) {
return (flags & flag) != FLAG_UNKNOWN;
}
public void clearFlag(long flag) {
flags &= ~flag;
}
// --------
public BitMaskLong addAllFlags() {
for (int i = 0; i < maxBitCount(); i++) {
addBitIndexFlag(i);
}
return this;
}
public void clearFlags() {
flags = FLAG_UNKNOWN;
}
public long getFlags() {
return flags;
}
/**
* set index位 flag
*
* @param bitIndex index bit位
* @param isAdd true设置flag,false清除flag
*/
private void operateFlag(@IntRange(from = 0, to = Long.SIZE - 1) int bitIndex, boolean isAdd) {
if (bitIndex < 0 || bitIndex > maxBitCount() - 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index must range 0~" + (maxBitCount() - 1) + " , current bitIndex is " + bitIndex);
}
if (isAdd) {
addFlag(FLAG_BASE << bitIndex);
} else {
clearFlag(FLAG_BASE << bitIndex);
}
}
// --------
public int maxBitCount() {
return Long.SIZE;
}
public String toBinaryString() {
String binaryString = Long.toBinaryString(flags);
while (maxBitCount() - binaryString.length() > 0) {
binaryString = 0 + binaryString;
}
return binaryString;
}
public String toString() {
int i = Long.bitCount(flags);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[二进制位]");
sb.append(toBinaryString());
sb.append("[位数]");
sb.append(i);
return sb.toString();
}
}
案例:控制新闻列表页的自动刷新逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
public final class ListRefreshStateInt {
public static class ArticleRefreshBitMaskInt extends BitMaskInt {
private ArticleRefreshBitMaskInt() {
}
public static BitMaskInt newFlag() {
return new ArticleRefreshBitMaskInt();
}
private static final int FLAG_BASE = 0x01;
private static final int FLAG_SUBSCRIBE = FLAG_BASE << 0;
private static final int FLAG_VIDEO = FLAG_BASE << 1;
private static final int FLAG_TEXT = FLAG_BASE << 3;
private static final int FLAG_IMAGE = FLAG_BASE << 5;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1();
// test2();
}
// 自定义flag
private static void test2() {
BitMaskInt flags = ArticleRefreshBitMaskInt.newFlag();
flags.addFlag(ArticleRefreshBitMaskInt.FLAG_TEXT | ArticleRefreshBitMaskInt.FLAG_VIDEO);
System.out.println(flags.toString());
flags.addFlag(ArticleRefreshBitMaskInt.FLAG_SUBSCRIBE | ArticleRefreshBitMaskInt.FLAG_IMAGE);
System.out.println(flags.toString());
}
// 通过bit index
private static void test1() {
BitMaskInt flags = ArticleRefreshBitMaskInt.newFlag();
// .addFlags();
flags.addBitIndexFlag(31);
System.out.println(flags.toString());
}
}
BitMask 应用
BitMask(long 64 bit) 实现列表各个列表刷新状态的控制
Long 版,支持最多 64 位
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
/**
* 64bit flag <br/>
* 1. 可根据按bit index add flag <br/>
* 2. 也可以自定义flag位 <br/>
*/
public abstract class BitMaskLong {
private static final long FLAG_UNKNOWN = 0x00;
private static final long FLAG_BASE = 0x01;
private long flags = FLAG_UNKNOWN;
public BitMaskLong() {
clearFlags();
}
public void addBitIndexFlag(@IntRange(from = 0, to = Long.SIZE - 1) int bitIndex) {
operateFlag(bitIndex, true);
}
public void clearBitIndexFlag(@IntRange(from = 0, to = Long.SIZE - 1) int bitIndex) {
operateFlag(bitIndex, false);
}
public boolean hasBitIndexFlag(@IntRange(from = 0, to = Long.SIZE - 1) int bitIndex) {
return hasFlag(FLAG_BASE << bitIndex);
}
// --------
public void addFlag(long flag) {
flags |= flag;
}
public boolean hasFlag(long flag) {
return (flags & flag) != FLAG_UNKNOWN;
}
public void clearFlag(long flag) {
flags &= ~flag;
}
// --------
public BitMaskLong addAllFlags() {
for (int i = 0; i < maxBitCount(); i++) {
addBitIndexFlag(i);
}
return this;
}
public void clearFlags() {
flags = FLAG_UNKNOWN;
}
public long getFlags() {
return flags;
}
/**
* set index位 flag
*
* @param bitIndex index bit位
* @param isAdd true设置flag,false清除flag
*/
private void operateFlag(@IntRange(from = 0, to = Long.SIZE - 1) int bitIndex, boolean isAdd) {
if (bitIndex < 0 || bitIndex > maxBitCount() - 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index must range 0~" + (maxBitCount() - 1) + " , current bitIndex is " + bitIndex);
}
if (isAdd) {
addFlag(FLAG_BASE << bitIndex);
} else {
clearFlag(FLAG_BASE << bitIndex);
}
}
// --------
public int maxBitCount() {
return Long.SIZE;
}
public String toBinaryString() {
String binaryString = Long.toBinaryString(flags);
while (maxBitCount() - binaryString.length() > 0) {
binaryString = 0 + binaryString;
}
return binaryString;
}
public String toString() {
int i = Long.bitCount(flags);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[二进制位]");
sb.append(toBinaryString());
sb.append("[位数]");
sb.append(i);
return sb.toString();
}
}
参考
- Android 中 BitMask 的使用
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权