ASM基础
ASM 基础
ASM 介绍
ASM 是什么?
ASM 是一种通用 Java 字节码操作和分析框架。它可以用于修改现有的 class 文件或动态生成 class 文件。
ASM 是在指令层次上操作字节码的,和 class 字节码更加接近。如果我们有些字节码操作的需求,ASM 一定可以实现的。只是使用起来比较麻烦一些。
ASM 帮我们解析 class 文件,修改 class 文件。
如何查看字节码?
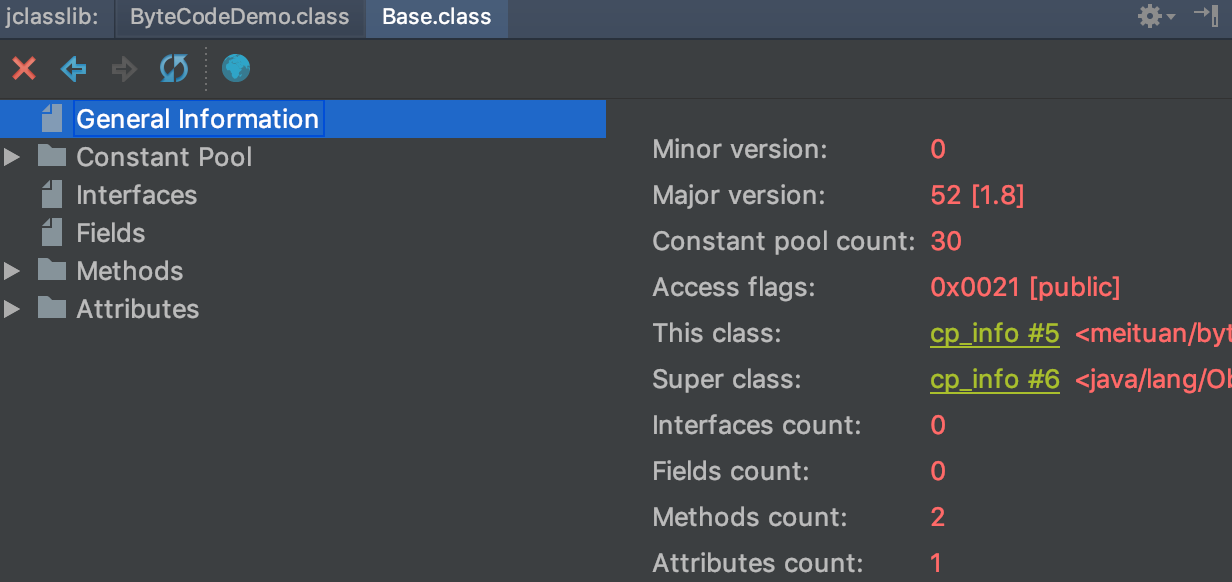
jclasslib 插件
如果每次查看反编译后的字节码都使用 javap 命令的话,好非常繁琐。这里推荐一个 Idea 插件:jclasslib。使用效果如图所示,代码编译后在菜单栏 View→Show Bytecode With jclasslib,可以很直观地看到当前字节码文件的类信息、常量池、方法区等信息。
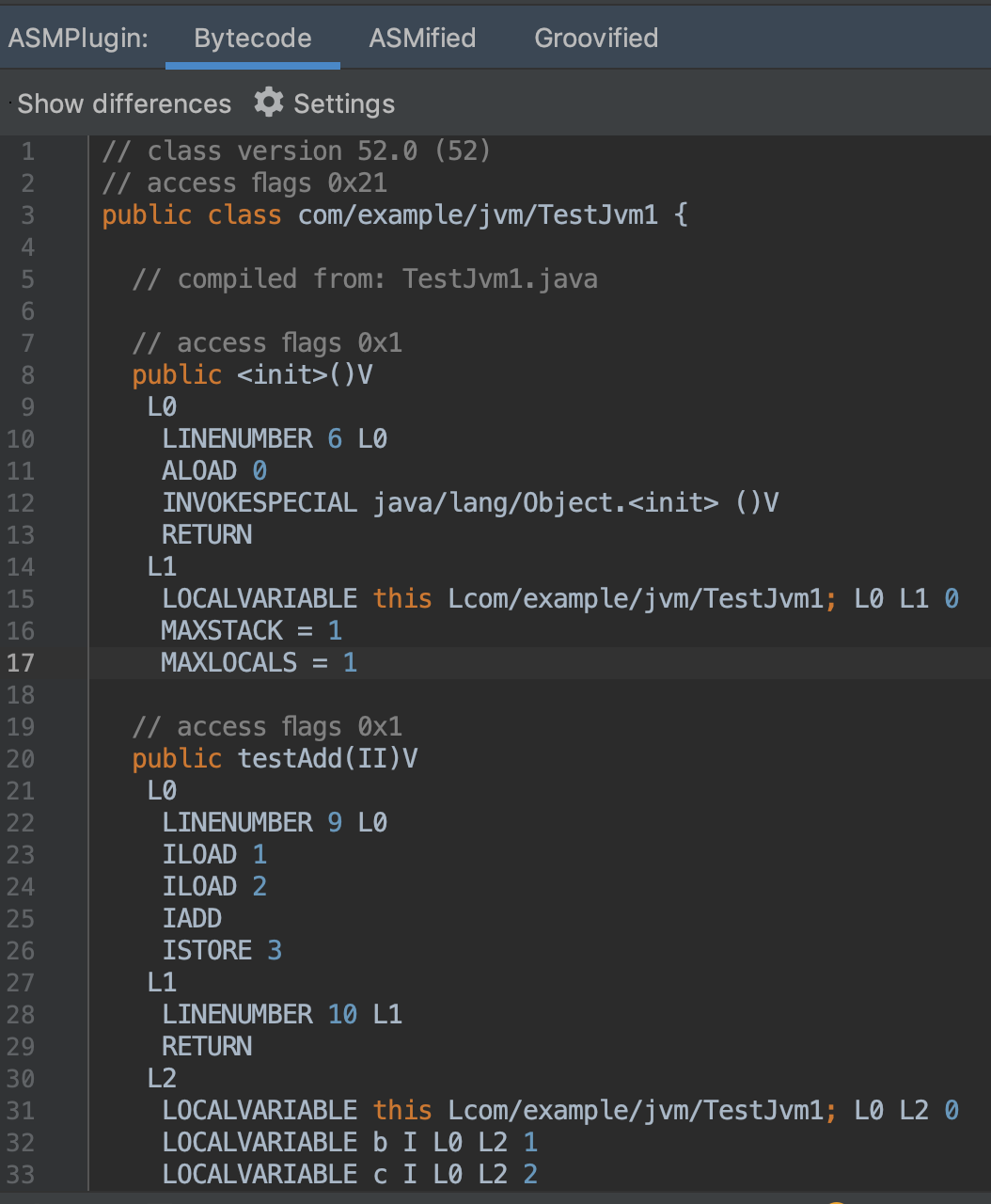
ASM Bytecode Viewer 插件
查看 class 文件对应的字节码
使用:找到目标.class 文件→右键→选择 ASM Bytecode Viewer
Show differences 可以展示前后 2 次的字节码对比
ASM Bytecode Outline (AS 已经装不上了,2015 年更新的了)
可以一键生成对应的 ASM API 代码
javap 命令
引入 ASM Gradle 依赖
1
2
implementation 'org.ow2.asm:asm:9.2'
implementation 'org.ow2.asm:asm-commons:9.2'
ASM API
ASM Tree API 对象模型
ASM Tree API 可以类比解析 XML 文件中的 DOM 方式,把整个类的结构读取到内存中,缺点是消耗内存多,但是编程比较简单。TreeApi 不同于 CoreAPI,TreeAPI 通过各种 Node 类来映射字节码的各个区域,类比 DOM 节点,就可以很好地理解这种编程方式。
- Tree API 优点
- 适宜处理简单类的修改
- 学习成本较低
- 代码量较少
- Tree API 缺点
- 处理大量信息会使代码变得复杂
- 代码难以复用
在对象模型 (Tree API) 下的 ASM 有 两类操作纬度:
- 获取节点:获取指定类、字段、方法节点。
- 操控操作码(针对方法节点):获取操作码位置、替换、删除、插入操作码、输出字节码
获取节点
1. 获取指定类的节点 ClassNode
模板代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
// 获取class字节码
ClassReader classReader = new ClassReader(xxx);
// class信息封装到ClassNode节点
ClassNode classNode = new ClassNode();
classReader.accept(classNode, 0);
// 一顿操作字节码
// 写回字节码的修改到目标位置
// 让 ClassWriter 自行计算最大栈深度和栈映射帧等信息
ClassWriter classWriter = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);
classNode.accept(classWriter);
byte[] data = classWriter.toByteArray();
File outputFile = new File("build", "Base3.class");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outputFile);
fos.write(data);
fos.close();
- 使用 ClassReader 来解析字节码
- ClassReader 在解析完字节码之后便可以通过 accept 方法来将结果写入到一个 ClassNode 对象之中
ClassNode 节点信息:
| 类型 | 名称 | 说明 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| int | version | class 文件的 major 版本(编译的 java 版本) | 52 |
| int | access | 访问级 | 33 |
| String | name | 类名,采用全地址,如 java/lang/String | me/hacket/asm/demo1/Base |
| String | signature | 签名,通常是 null | null |
| String | superName | 父类类名,采用全地址 | java/lang/Object |
List<String> | interfaces | 实现的接口,采用全地址 | [java/io/Serializable, me/hacket/asm/demo1/TestInterface] |
| String | sourceFile | 源文件,可能为 null | Base.java |
| String | sourceDebug | debug 源,可能为 null | null |
| String | outerClass | 外部类 | null |
| String | outerMethod | 外部方法 | null |
| String | outerMethodDesc | 外部方法描述(包括方法参数和返回值) | null |
List<AnnotationNode> | visibleAnnotations | 可见的注解 | null |
List<AnnotationNode> | invisibleAnnotations | 不可见的注解 | null |
List<Attribute> | attrs | 类的 Attribute | null |
List<InnerClassNode> | innerClasses | 类的内部类列表 | [org.objectweb.asm.tree.InnerClassNode@33c7353a] |
List<FieldNode> | fields | 类的字段列表 | [org.objectweb.asm.tree.FieldNode@681a9515] |
List<MethodNode> | methods | 类的方法列表 | 3 个 MethodNode 节点 |
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
// 被ASM操作的字节码
public class Base implements Serializable, TestInterface {
private int a;
public void process() {
System.out.println("process");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Base().process();
}
class TestInnerClass {
public void processInner() {
System.out.println("process inner");
}
}
}
// ASM代码
public class ASMTreeApiDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ClassReader classReader = new ClassReader("com/example/asm/demo1/Base");
ClassNode classNode = new ClassNode(Opcodes.ASM4);
classReader.accept(classNode, 0);
// 解析class节点
parseClassNode(classNode);
// 让 ClassWriter 自行计算最大栈深度和栈映射帧等信息
ClassWriter classWriter = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES);
classNode.accept(classWriter);
byte[] data = classWriter.toByteArray();
File outputFile = new File("build", "Base3.class");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outputFile);
fos.write(data);
fos.close();
System.out.println("ASMTreeApiDemo asm succeed!");
}
private static void parseClassNode(ClassNode node) {
int version = node.version;
int access = node.access;
String name = node.name;
String signature = node.signature;
String superName = node.superName;
List<String> interfaces = node.interfaces;
String sourceFile = node.sourceFile;
String sourceDebug = node.sourceDebug;
String outerClass = node.outerClass;
String outerMethod = node.outerMethod;
String outerMethodDesc = node.outerMethodDesc;
List<AnnotationNode> visibleAnnotations = node.visibleAnnotations;
List<AnnotationNode> invisibleAnnotations = node.invisibleAnnotations;
List<Attribute> attrs = node.attrs;
List<InnerClassNode> innerClasses = node.innerClasses;
List<FieldNode> fields = node.fields;
List<MethodNode> methods = node.methods;
System.out.println("version=" + version);
System.out.println("access=" + access);
System.out.println("name=" + name);
System.out.println("signature=" + signature);
System.out.println("superName=" + superName);
System.out.println("interfaces=" + interfaces);
System.out.println("sourceFile=" + sourceFile);
System.out.println("sourceDebug=" + sourceDebug);
System.out.println("outerClass=" + outerClass);
System.out.println("outerMethod=" + outerMethod);
System.out.println("outerMethodDesc=" + outerMethodDesc);
System.out.println("visibleAnnotations=" + visibleAnnotations);
System.out.println("invisibleAnnotations=" + invisibleAnnotations);
System.out.println("attrs=" + attrs);
System.out.println("innerClasses=" + innerClasses);
System.out.println("fields=" + fields);
System.out.println("methods=" + methods);
}
}
输出:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
version=52
access=33
name=me/hacket/asm/demo1/Base
signature=null
superName=java/lang/Object
interfaces=[java/io/Serializable, me/hacket/asm/demo1/TestInterface]
sourceFile=Base.java
sourceDebug=null
outerClass=null
outerMethod=null
outerMethodDesc=null
visibleAnnotations=null
invisibleAnnotations=null
attrs=null
innerClasses=[org.objectweb.asm.tree.InnerClassNode@33c7353a]
fields=[org.objectweb.asm.tree.FieldNode@681a9515]
methods=[org.objectweb.asm.tree.MethodNode@3af49f1c, org.objectweb.asm.tree.MethodNode@19469ea2, org.objectweb.asm.tree.MethodNode@13221655]
ASMTreeApiDemo asm succeed!
2. 获取指定字段的节点 FieldNode
字段节点列表 fields 是一个 List<FieldNode>,它储存着类节点的所有字段。
FieldNode 节点信息:
| 类型 | 名称 | 说明 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| int | access | 访问级 | 2 |
| String | name | 字段名 | a |
| String | signature | 签名,通常是 null | null |
| String | desc | 类型描述,例如 Ljava/lang/String、D(double)、F(float) | I |
| Object | value | 初始值,通常为 null | null |
List<AnnotationNode> | visibleAnnotations | 可见的注解 | null |
List<AnnotationNode> | invisibleAnnotations | 不可见的注解 | null |
List<Attribute> | attrs | 字段的 Attribute | null |
为类添加需要的字段 public static int sField = 100:
1
2
FieldNode newFieldNode = new FieldNode(Opcodes.ACC_PUBLIC | Opcodes.ACC_STATIC, "sField", "I", null, 100);
classNode.fields.add(0, newFieldNode);
3. 获取指定的方法节点
方法节点包含的信息:
| 类型 | 名称 | 说明 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| int | access | 访问级 | 9 |
| String | name | 方法名 | main |
| String | signature | 签名,通常是 null | null |
| String | desc | 方法描述,其包含方法的返回值和参数 | ([Ljava/lang/String;)V |
List<String> | exceptions | 可能返回的异常列表 | [] |
List<AnnotationNode> | visibleAnnotations | 可见的注解 | null |
List<AnnotationNode> | invisibleAnnotations | 不可见的注解 | null |
List<Attribute> | attrs | 方法的 Attribute 列表 | null |
| Object | annotationDefault | 默认的注解 | null |
List<AnnotationNode>[] | visibleParameterAnnotations | 可见的参数注解列表 | null |
List<AnnotationNode>[] | invisibleParameterAnnotations | 不可见的参数注解列表 | null |
| InsnList | instructions | 操作码列表 | org.objectweb.asm.tree.InsnList@816f27d |
List<TryCatchBlockNode> | tryCatchBlocks | try-catch 块列表 | [] |
| int | maxStack | 最大操作栈的深度 | 2 |
| int | maxLocals | 最大局部变量区的大小 | 1 |
List<LocalVariableNode> | localVariables | 本地(局部)变量节点列表 | [org.objectweb.asm.tree.LocalVariableNode@87aac27] |
操控操作码
instructions,操作码列表,它是 方法节点中用于存储操作码的地方,其中 每一个元素都代表一行操作码。
ASM 将一行字节码封装为一个 xxxInsnNode(Insn 表示的是 Instruction 的缩写,即指令/操作码),例如 ALOAD/ARestore 指令被封装入变量操作码节点 VarInsnNode,INVOKEVIRTUAL 指令则会被封入方法操作码节点 MethodInsnNode 之中。
所有的指令节点都继承自抽象操作码节点 AbstractInsnNode。
所有的指令码节点说明:
| 名称 | 说明 | 参数 |
|---|---|---|
| FieldInsnNode | 用于 GETFIELD 和 PUTFIELD 之类的字段操作的字节码 | 1. String owner 字段所在的类 2. String name 字段的名称 3. String desc 字段的类型 |
| FrameNode | 栈映射帧的对应的帧节点 | |
| IincInsnNode | 用于 IINC 变量自加操作的字节码 | int var:目标局部变量的位置 int incr:要增加的数 |
| InsnNode | 一切无参数值操作的字节码,例如 ALOAD_0,DUP(注意不包含 POP) | 无 |
| IntInsnNode | 用于 BIPUSH、SIPUSH 和 NEWARRAY 这三个直接操作整数的操作 | int operand:操作的整数值 |
| InvokeDynamicInsnNode | 用于 Java7 新增的 INVOKEDYNAMIC 操作的字节码 | String name:方法名称 String desc:方法描述 Handle bsm:句柄 Object[] bsmArgs:参数常量 |
| JumpInsnNode | 用于 IFEQ 或 GOTO 等跳转操作字节码 | LabelNode label:目标 label |
| LabelNode | 一个用于表示跳转点的 Label 节点 | 无 |
| LdcInsnNode | 使用 LDC 加载常量池中的引用值并进行插入的字节码 | Object cst:引用值 |
| LineNumberNode | 表示行号的节点 | int line:行号 LabelNode start:对应的第一个 Label |
| LookupSwitchInsnNode | 用于实现 LOOKUPSWITCH 操作的字节码 | LabelNode dflt:default 块对应的 Label List keys 键列表 List labels:对应的 Label 节点列表 |
| MethodInsnNode | 用于 INVOKEVIRTUAL 等传统方法调用操作的字节码,不适用于 Java7 新增的 INVOKEDYNAMIC | String owner :方法所在的类 String name :方法名称 String desc:方法描述 |
| MultiANewArrayInsnNode | 用于 MULTIANEWARRAY 操作的字节码 | String desc:类型描述 int dims:维数 |
| TableSwitchInsnNode | 用于实现 TABLESWITCH 操作的字节码 | int min:键的最小值 int max:键的最大值 LabelNode dflt:default 块对应的 Label List labels:对应的 Label 节点列表 |
| TypeInsnNode | 用于实现 NEW、ANEWARRAY 和 CHECKCAST 等类型相关操作的字节码 | String desc:类型 |
| VarInsnNode | 用于实现 ALOAD、ASTORE 等局部变量操作的字节码 | int var:局部变量 |
获取操作码的位置
1
2
3
4
5
for(AbstractInsnNode ainNode : methodNode.instructions.toArray()) {
if(ainNode.getOpcode() == Opcodes.SIPUSH && ((IntInsnNode)ainNode).operand == 16) {
// ... 进行操作
}
}
由于一般情况下我们都无法确定操作码在列表中的具体位置,因此通常会通过遍历的方式去判断其关键特征,以此来定位指定的操作码。
有时一个方法中会有多个相同的指令,这是我们需要靠判断前后字节码识别其特征来定位,也可以记下其命中次数然后设定在某一次进行操作,一般情况下我们都是使用的第二种。
替换指定的操作码
1
2
3
4
5
for(AbstractInsnNode ainNode : methodNode.instructions.toArray()) {
if(ainNode.getOpcode() == Opcodes.BIPUSH && ((IntInsnNode)ainNode).operand == 16) {
methodNode.instructions.set(ainNode, new VarInsnNode(Opcodes.ALOAD, 1));
}
}
InsnList 的 set 方法就能替换指定的操作码对象。
删除指定的操作码
1
methodNode.instructions.remove(xxx);
xxx 表示的是要删除的操作码实例,我们直接调用用 InsnList 的 remove 方法将它移除掉即可
插入指定的操作码
InsnList 主要提供了 四类 方法用于插入字节码:
- add(AbstractInsnNode insn): 将一个操作码添加到 InsnList 的末尾
- insert(AbstractInsnNode insn): 将一个操作码插入到这个 InsnList 的开头
- insert(AbstractInsnNode insnNode,AbstractInsnNode insn): 将一个操作码插入到另一个操作码的下面
- insertBefore(AbstractInsnNode insnNode,AbstractInsnNode insn) 将一个操作码插入到另一个操作码的上面
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
for(AbstractInsnNode ainNode : methodNode.instructions.toArray()) {
if(ainNode.getOpcode() == Opcodes.BIPUSH && ((IntInsnNode)ainNode).operand == 16) {
methodNode.instructions.insert(ainNode, new MethodInsnNode(Opcodes.INVOKEVIRTUAL, "java/awt/image/BufferedImage", "getWidth", "(Ljava/awt/image/ImageObserver;)I"));
methodNode.instructions.insert(ainNode, new InsnNode(Opcodes.ACONSTNULL));
methodNode.instructions.set(ainNode, new VarInsnNode(Opcodes.ALOAD, 1));
}
}
ASM Core API 事件模型
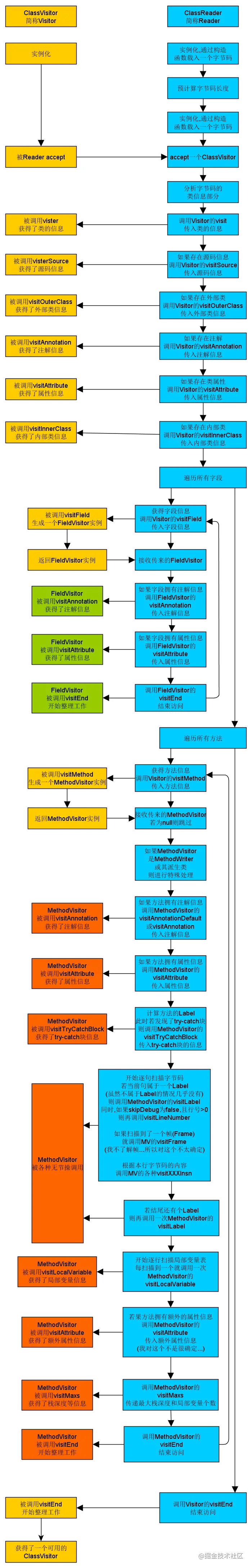
ASM Core API 可以类比解析 XML 文件中的 SAX 方式,不需要把这个类的整个结构读取进来,就可以用流式的方法来处理字节码文件。好处是非常节约内存,但是编程难度较大。然而出于性能考虑,一般情况下编程都使用 Core API。
- ClassReader
用于读取已经编译好的 .class 文件
- ClassWriter
用于重新构建编译后的类,如修改类名、属性以及方法,也可以生成新的类的字节码文件。
- 各种 Visitor 类
Core API 根据字节码从上到下依次处理,对于字节码文件中不同的区域有不同的 Visitor,比如用于访问方法的 MethodVisitor、用于访问类变量的 FieldVisitor、用于访问注解的 AnnotationVisitor 等等。为了实现 AOP,其重点是要灵活运用 MethodVisitor。
- 模板代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(classFile);
// 1
ClassReader classReader = new ClassReader(is);
// 2
ClassWriter classWriter = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_MAXS);
// 3
ClassVisitor classVisitor = new TraceClassAdapter(Opcodes.ASM5, classWriter);
// 4
classReader.accept(classVisitor, ClassReader.EXPAND_FRAMES);
1
2
3
4
1. 将目标文件转换为流的形式,并将它融入类读取器 ClassReader 之中
2. 构建了一个类写入器 ClassWriter,其参数 `COMPUTE_MAXS` 的作用是将自动计算本地变量表最大值和操作数栈最大值的任务托付给了ASM(EXPAND_FRAMES,旨在说明在读取 class 的时候需要同时展开栈映射帧(StackMap Frame),如果我们需要使用自定义的 MethodVisitor 去修改方法中的指令时必须要指定这个参数)
3. 新建了一个自定义的类访问器,这个自定义的 ClassVisitor 的作用是为了在每一个方法的开始和结尾处插入相应的记时代码,以便统计出每一个方法的耗时
4. 类读取器 ClassReader 实例这个被访问者调用了自身的 accept 方法接收了一个 classVisitor 实例
ClassReader 类读取(解析)者
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class ClassReader {
public void accept(final ClassVisitor classVisitor, final int parsingOptions) {
accept(classVisitor, new Attribute[0], parsingOptions);
}
public void accept(final ClassVisitor classVisitor, final Attribute[] attributePrototypes, final int parsingOptions) {}
}
ClassVisitor 被定义为了一个能接收并解析 ClassReader 传入信息的类。当在 accept 方法中 ClassVisitor 访问 ClassReader 时,ClassReader 便会先开始字节码的解析工作,并将保存在内存中的结果源源不断地通过调用各种 visitxxx 方法传入到 ClassVisitor 之中。
需要注意的是,其中 只有 visit 这个方法一定会被调用一次,因为它获取了类头部的描述信息,显然易见,它必不可少,而对于其它的 visitxxx 方法来说都不能确定。
例如其中的 visitMethod 方法,只有当 ClassReader 解析出一个方法的字节码时,才会调用一次 visitMethod 方法,并由此生成一个方法访问者 MethodVisitor 的实例。
Visitor
ClassVisitor 类访问者
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
public class ClassReader {
public void accept(final ClassVisitor classVisitor, final Attribute[] attributePrototypes, final int parsingOptions) {
// ...
// 1. Read the access_flags, this_class, super_class, interface_count and interfaces fields.(读取类的描述信息,例如 access、name 等等)
// ...
// 2. 读取类的属性信息,例如签名 signature、sourceFile 等等
// ...
// 3. Visit the class declaration. The minor_version and major_version fields start 6 bytes before the first constant pool entry, which itself starts at cpInfoOffsets[1] - 1 (by definition). (访问类的描述信息)
classVisitor.visit(readInt(cpInfoOffsets[1] - 7), accessFlags, thisClass, signature, superClass, interfaces);
// 4. Visit the SourceFile and SourceDebugExtenstion attributes. (访问源码和 debug 信息)
if ((parsingOptions & SKIP_DEBUG) == 0 && (sourceFile != null || sourceDebugExtension != null)) {
classVisitor.visitSource(sourceFile, sourceDebugExtension);
}
// 5. Visit the Module, ModulePackages and ModuleMainClass attributes.
if (moduleOffset != 0) {
readModuleAttributes(classVisitor, context, moduleOffset, modulePackagesOffset, moduleMainClass);
}
// 6. Visit the NestHost attribute.
if (nestHostClass != null) {
classVisitor.visitNestHost(nestHostClass);
}
// 7. Visit the EnclosingMethod attribute.(访问外部类)
if (enclosingMethodOffset != 0) {
String className = readClass(enclosingMethodOffset, charBuffer);
int methodIndex = readUnsignedShort(enclosingMethodOffset + 2);
String name = methodIndex == 0 ? null : readUTF8(cpInfoOffsets[methodIndex], charBuffer);
String type = methodIndex == 0 ? null : readUTF8(cpInfoOffsets[methodIndex] + 2, charBuffer);
classVisitor.visitOuterClass(className, name, type);
}
// 8. Visit the RuntimeVisibleAnnotations attribute. (访问类注解和类型注解)
classVisitor.visitAnnotation(annotationDescriptor, /* visible = */ true),
classVisitor.visitAnnotation(annotationDescriptor, /* visible = */ false),
classVisitor.visitTypeAnnotation(context.currentTypeAnnotationTarget,context.currentTypeAnnotationTargetPath,annotationDescriptor,/* visible = */ true)
classVisitor.visitTypeAnnotation(
context.currentTypeAnnotationTarget,
context.currentTypeAnnotationTargetPath,
annotationDescriptor,
/* visible = */ false)
// 9. Visit the non standard attributes.(访问类的属性)
while (attributes != null) {
// Copy and reset the nextAttribute field so that it can also be used in ClassWriter.
Attribute nextAttribute = attributes.nextAttribute;
attributes.nextAttribute = null;
classVisitor.visitAttribute(attributes);
attributes = nextAttribute;
}
// 10. Visit the NestedMembers attribute.
if (nestMembersOffset != 0) {
int numberOfNestMembers = readUnsignedShort(nestMembersOffset);
int currentNestMemberOffset = nestMembersOffset + 2;
while (numberOfNestMembers-- > 0) {
classVisitor.visitNestMember(readClass(currentNestMemberOffset, charBuffer));
currentNestMemberOffset += 2;
}
}
// 11. Visit the PermittedSubclasses attribute.
// 12. Visit the InnerClasses attribute.(访问内部类)
classVisitor.visitInnerClass(
readClass(currentClassesOffset, charBuffer),
readClass(currentClassesOffset + 2, charBuffer),
readUTF8(currentClassesOffset + 4, charBuffer),
readUnsignedShort(currentClassesOffset + 6));
// 13. Visit Record components.
// 14. Visit the fields and methods. (访问字段和方法)
int fieldsCount = readUnsignedShort(currentOffset);
currentOffset += 2;
while (fieldsCount-- > 0) {
currentOffset = readField(classVisitor, context, currentOffset);
}
int methodsCount = readUnsignedShort(currentOffset);
currentOffset += 2;
while (methodsCount-- > 0) {
currentOffset = readMethod(classVisitor, context, currentOffset);
}
// 15. Visit the end of the class. (访问当前类结束时调用)
classVisitor.visitEnd();
}
}
参数:
- classVisitor 类访问者
- attributePrototypes
- parsingOptions 解析 class 的参数,
SKIP_CODE、SKIP_DEBUG、SKIP_FRAMES和EXPAND_FRAMES中的一个。
FieldVisitor 字段访问者(类内字段的解析)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
private int readField(final ClassVisitor classVisitor, final Context context, final int fieldInfoOffset) {
// 1、读取字段的描述信息
// 2、读取字段的属性
// 3、访问字段的声明
FieldVisitor fieldVisitor = classVisitor.visitField(accessFlags, name, descriptor, signature, constantValue);
if (fieldVisitor == null) {
return currentOffset;
}
// 4、访问字段的注解和类型注解
fieldVisitor.visitAnnotation(...)
fieldVisitor.visitTypeAnnotation(...)
// 5、访问字段的属性
while (attributes != null) {
// Copy and reset the nextAttribute field so that it can also be used in FieldWriter.
Attribute nextAttribute = attributes.nextAttribute;
attributes.nextAttribute = null;
fieldVisitor.visitAttribute(attributes);
attributes = nextAttribute;
}
// 6、访问字段结束时调用
fieldVisitor.visitEnd();
}
MethodVisitor 方法访问者 (类内方法的解析)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
private int readMethod(final ClassVisitor classVisitor, final Context context, final int methodInfoOffset) {
// 1、读取方法描述信息
// 2、读取方法属性信息
// 3、访问方法描述信息
MethodVisitor methodVisitor = classVisitor.visitMethod(
context.currentMethodAccessFlags,
context.currentMethodName,
context.currentMethodDescriptor,
signatureIndex == 0 ? null : readUtf(signatureIndex, charBuffer),
exceptions);
// 4、访问方法参数信息
if (methodParametersOffset != 0 && (context.parsingOptions & SKIP_DEBUG) == 0) {
int parametersCount = readByte(methodParametersOffset);
int currentParameterOffset = methodParametersOffset + 1;
while (parametersCount-- > 0) {
// Read the name_index and access_flags fields and visit them.
methodVisitor.visitParameter(
readUTF8(currentParameterOffset, charBuffer),
readUnsignedShort(currentParameterOffset + 2));
currentParameterOffset += 4;
}
}
// 5、访问方法的注解信息
methodVisitor.visitAnnotationDefault()
methodVisitor.visitAnnotation(...)
methodVisitor.visitTypeAnnotation(...)
// 6、访问方法的属性信息
while (attributes != null) {
// Copy and reset the nextAttribute field so that it can also be used in MethodWriter.
Attribute nextAttribute = attributes.nextAttribute;
attributes.nextAttribute = null;
methodVisitor.visitAttribute(attributes);
attributes = nextAttribute;
}
// 7、访问方法代码对应的字节码信息
if (codeOffset != 0) {
methodVisitor.visitCode();
readCode(methodVisitor, context, codeOffset);
}
// 8、访问方法结束
methodVisitor.visitEnd();
}
ClassWriter
ClassWriter 也是 ClassVisitor 的一个子类,但是,它并不会储存信息,而是马上会将传入的信息转译成字节码,并在之后随时输出它们。对于 ClassReader 这个被访问者来说,它负责读取我们传入的类文件中的字节流数据,并提供解析流中包含的一切类属性信息的操作。
一张图总结
Ref
- 字节码增强技术探索(美团) https://tech.meituan.com/2019/09/05/java-bytecode-enhancement.html
- 深入探索编译插桩技术(四、ASM 探秘)(jsonchao)
https://juejin.cn/post/6844904118700474375 - Android 中看似高大上的字节码修改,这样学就对了! https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/dQjsxduUiNrMYH2xhhpmQA
hongyang
ASM 相关开源库学习
ARouter AutoRegister
- ARouter 的 AutoRegister 路由自动注册 https://github.com/alibaba/ARouter/tree/develop/arouter-gradle-plugin
ASM 扫描所有符合条件的 class 自动收集需要注册的 class,ASM 写到 ARouter 预留的方法中去。
Hunter
什么是 Hunter?
Hunter 是这么一个框架,帮你快速开发插件,在编译过程中修改字节码,它底层基于 ASM 和 Gradle Transform API 实现。在这个框架基础上,我尝试开发了几款实用的插件。你也可以用 Hunter 开发自己的插件,诸如实现 App 性能监控(UI,网络等等),加强或修改第三方库以满足你的需求,甚至可以加强、修改 Android framework 的接口。Hunter 本身支持 Transform 增量、并发编译,所以不用担心使用这一系列插件会增加编译时间。
基于 Hunter 的插件
OkHttp-Plugin
通过修改字节码的方式 hack 掉 okhttp,为你的应用所有的 OkhttpClient 设置全局 Interceptor / Eventlistener (包括第三方依赖里的 OkhttpClient)
Timing-Plugin
帮你监控所有 UI 线程的执行耗时,并且提供了算法,帮你打印出一个带有每步耗时的堆栈,统计卡顿方法分布,并且提供接口让你选择自己的方式来处理卡顿信息。
Debug-Plugin
只要为指定方法加上某个 annotation,就可以帮你打印出这个方法所有输入参数的值,以及返回值,执行时间。这个插件相比 JakeWharton 的 hugo 有很多优点:支持 koltin,支持自定义 logger,不影响断点调试,支持打印对象 toString 内容,编译速度更快
Booster
ByteX
- 神策数据官方 Android 埋点插件,用于 Android 端的数据采集 https://github.com/sensorsdata/sa-sdk-android-plugin2
- 字节跳动抖音 Android 团队 ByteX 项目
ASM 应用
无痕慢点
耗时方法统计
三方库 bug 修复
点击防抖
组件化路由库注册路由表
线程收敛?
##