编解码
BASE64
Base64 是网络上最常见的用于传输 8Bit 字节代码的编码方式之一,大家可以查看 RFC2045~RFC2049,上面有 MIME 的详细规范。Base64 编码可用于在 HTTP 环境下传递较长的标识信息。例如,在 Java Persistence 系统 Hibernate 中,就采用了 Base64 来将一个较长的唯一 标识符 (一般为 128-bit 的 UUID)编码为一个字符串,用作 HTTP 表单和 HTTP GET URL 中的参数。在其他 应用程序 中,也常常需要把二进制数据编码为适合放在 URL(包括隐藏表单域)中的形式。此时,采用 Base64 编码不仅比较简短,同时也具有不可读性,即所编码的数据不会被人用肉眼所直接看到。
RFC2045 还规定每行位 76 个字符,每行末尾需添加一个回车换行符,即便是最后一行不够 76 个字符,也要加换行符。
实现原理
Base64 是一种用 64 个字符来表示任意二进制数据的方法。
- 每 3 个 8 位二进制码位一组,转换为 4 个 6 位二进制码为一组(不足 6 位时地位补 0)。3 个 8 位二进制码和 4 个 6 位二进制码长度都是 24 位。
- 对获得的 4 个 6 位二进制码补位,每个 6 位二进制码添加两位高位 0,组成 4 个 8 位二进制码。
- 将获得的 4 个 8 位二进制码转换为 4 个十进制码。
- 将获得的十进制码转换为 Base64 字符表中对应的字符。
案例1: 字符串 “A”,进行 Base64 编码,如下所示:
| 过程 | 数据 |
|---|---|
| 字符 | A |
| ASCII 码 | 65 |
| 二进制码 | 01000001 |
| 4 个 6 位二进制码 | 010000 010000 |
| 4 个 8 位二进制码 | 00010000 00010000 |
| 十进制码 | 16 16 |
| 字符表映射码 | Q Q = = |
字符串 A 经过 Base64 编码后得到字符串 QQ==。
结果出现了两个等号。很显然,当原文的二进制码长度不足 24 位,最终转换为十进制时也不足 4 项,这时就需要用等号补位。
将 Base64 编码后的字符串最多会有 2 个等号,这时因为:
余数 = 原文字节数 MOD 3。
案例2: 字符串 “ 密 “,对其使用 UTF-8 编码等到 Byte 数组{-27,-81,-122},
| 过程 | 数据 |
|---|---|
| 字符 | 密 |
| UTF-8 编码 | -27 -81 -122 |
| 二进制码 | 11100101 10101111 10000110 |
| 4 个 6 位二进制码 | 111001 011010 111110 000110 |
| 4 个 8 位二进制码 | 00111001 00011010 00111110 00000110 |
| 十进制码 | 57 26 62 6 |
| 字符表映射码 | 5 a + G |
| 字符串 “ 密 “ 经过 Base64 编码后得到字符串 | 5a+G |
案例3:
| 过程 | 数据 |
|---|---|
| 数字 1 查 ASCII 码表 | 49 |
| 1 的二进制分成 3 个 8bit: | 00110001 00000000 00000000 |
| 分成 4 个 bit: | 001100 010000 000000 000000 |
| 前面补 00: | 00001100 00010000 00000000 00000000 |
| 查 BASE64 表对应的十进制值: | 12 16 = = |
| 最终值 | MQ== |
案例4: 字符 Man
| 过程 |
|---|
| M a n |
| 77 97 110 |
| 01001101 01100001 01101110 |
| 010011 010110 000101 101110 |
| 19 22 5 46 |
| T W F u |
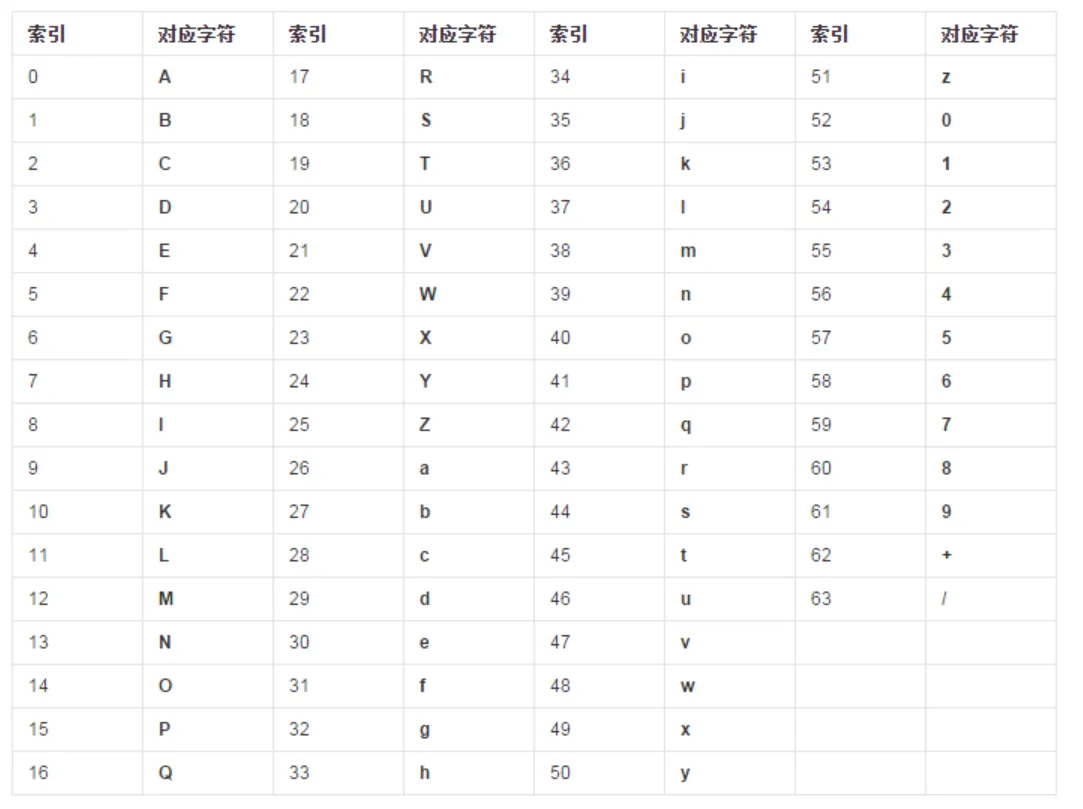
BASE64 码表
ACII编码表
BASE64 实现
1、com.sun.misc API
1、com.sun.misc 包是 Sun 公司提供给内部使用的专用 API,在 java API 文档中我们看不到任何有关 BASE64 影子,不建议使用。
2、Apache 的实现: (建议使用这种方式,当然,自己实现也可以)
参考 org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64
下载地址: http://commons.apache.org/codec/download_codec.cgi
Apache 还提供了,非标准的实现方式:
1.不再添加回车符。
2.Url Base64,也就是将 “+” 和 “" 换成了 “-“ 和 “_” 符号,且不适用补位。
3、Android 提供的 Base64
4、工具类,见下
Base64 工具类
Base64Util
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
package com.baidu.encryptdemo;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
/**
* A Base64 Encoder/Decoder.
* <p/>
* This class is used to encode and decode data in Base64 format as described in RFC 1521.
* <p/>
* This is "Open Source" software and released under the
* <a href="http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.html">GNU/LGPL </a>
* license. <br>
* It is provided "as is" without warranty of any kind. <br>
* Copyright 2003: Christian d'Heureuse, Inventec Informatik AG, Switzerland.
* <br>
* Home page: <a href="http://www.source-code.biz">www.source-code.biz </a> <br>
* <p/>
* Original name <b>Base64Coder.java </b>
* <p/>
* Version history: <br>
* 2003-07-22 Christian d'Heureuse (chdh): Module created. <br>
* 2005-08-11 chdh: Lincense changed from GPL to LGPL. <br>
* 2006-11-21 chdh: <br>
* Method encode(String) renamed to encodeString(String). <br>
* Method decode(String) renamed to decodeString(String). <br>
* New method encode(byte[],int) added. <br>
* New method decode(String) added. <br>
* 2007-04-30 francis.naoum: Added to sfp_lib. <br>
* byte[] encode(byte[]) changed to return a String. <br>
*
* @author Francis Naoum
* @since 1.0.0
*/
public final class Base64Util {
/**
* Mapping table from 6-bit nibbles to Base64 characters.
*/
private static final char[] MAP1 = new char[64];
static {
int i = 0;
for (char c = 'A'; c <= 'Z'; c++) {
MAP1[i++] = c;
}
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {
MAP1[i++] = c;
}
for (char c = '0'; c <= '9'; c++) {
MAP1[i++] = c;
}
MAP1[i++] = '+';
MAP1[i++] = '/';
}
/**
* Mapping table from Base64 characters to 6-bit nibbles.
*/
private static final byte[] MAP2 = new byte[128];
static {
for (int i = 0; i < MAP2.length; i++) {
MAP2[i] = -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
MAP2[MAP1[i]] = (byte) i;
}
}
/**
* Encodes a string into Base64 format. No blanks or line breaks are inserted.
*
* @param string a String to be encoded.
* @return A String with the Base64 encoded data.
*/
public static String encodeString(final String string) {
String encodedString = null;
try {
encodedString = encodeString(string, "UTF-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uue) {
// Should never happen, java has to support "UTF-8".
}
return encodedString;
}
/**
* Encodes a string into Base64 format. No blanks or line breaks are inserted.
*
* @param string a String to be encoded.
* @param encoding The character encoding of the string.
* @return A String with the Base64 encoded data.
* @throws UnsupportedEncodingException if the java runtime does not support <code>encoding</code>.
*/
public static String encodeString(final String string, final String encoding) throws
UnsupportedEncodingException {
byte[] stringBytes = string.getBytes(encoding);
return encode(stringBytes);
}
/**
* Encodes a byte array into Base64 format. No blanks or line breaks are inserted.
* <p/>
* This method has been modified to return a string not a char[].
*
* @param input an array containing the data bytes to be encoded.
* @return A character array with the Base64 encoded data.
*/
public static String encode(final byte[] input) {
char[] chars = encode(input, input.length);
return new String(chars);
}
/**
* Encodes a byte array into Base64 format. No blanks or line breaks are inserted.
*
* @param input an array containing the data bytes to be encoded.
* @param iLen number of bytes to process in <code>in</code>.
* @return A character array with the Base64 encoded data.
*/
public static char[] encode(final byte[] input, final int iLen) {
int oDataLen = (iLen * 4 + 2) / 3; // output length without padding
int oLen = ((iLen + 2) / 3) * 4; // output length including padding
char[] out = new char[oLen];
int ip = 0;
int op = 0;
while (ip < iLen) {
int i0 = input[ip++] & 0xff;
int i1 = ip < iLen ? input[ip++] & 0xff : 0;
int i2 = ip < iLen ? input[ip++] & 0xff : 0;
int o0 = i0 >>> 2;
int o1 = ((i0 & 3) << 4) | (i1 >>> 4);
int o2 = ((i1 & 0xf) << 2) | (i2 >>> 6);
int o3 = i2 & 0x3F;
out[op++] = MAP1[o0];
out[op++] = MAP1[o1];
out[op] = op < oDataLen ? MAP1[o2] : '=';
op++;
out[op] = op < oDataLen ? MAP1[o3] : '=';
op++;
}
return out;
}
/**
* Decodes a string from Base64 format.
*
* @param string a Base64 String to be decoded.
* @return A String containing the decoded data.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the input is not valid Base64 encoded data.
*/
public static String decodeString(final String string) {
String decodedString = null;
try {
byte[] decodedBytes = decode(string);
decodedString = new String(decodedBytes, "UTF-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uue) {
// Should never happen, java has to support "UTF-8".
}
return decodedString;
}
/**
* Decodes a byte array from Base64 format.
*
* @param string a Base64 String to be decoded.
* @return An array containing the decoded data bytes.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the input is not valid Base64 encoded data.
*/
public static byte[] decode(final String string) {
return decode(string.toCharArray());
}
/**
* Decodes a byte array from Base64 format. No blanks or line breaks are allowed within the Base64 encoded data.
*
* @param input a character array containing the Base64 encoded data.
* @return An array containing the decoded data bytes.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the input is not valid Base64 encoded data.
*/
public static byte[] decode(final char[] input) {
int iLen = input.length;
if (iLen % 4 != 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Length of Base64 encoded input string is not a multiple of 4.");
}
while (iLen > 0 && input[iLen - 1] == '=') {
iLen--;
}
int oLen = (iLen * 3) / 4;
byte[] out = new byte[oLen];
int ip = 0;
int op = 0;
while (ip < iLen) {
int i0 = input[ip++];
int i1 = input[ip++];
int i2 = ip < iLen ? input[ip++] : 'A';
int i3 = ip < iLen ? input[ip++] : 'A';
if (i0 > 127 || i1 > 127 || i2 > 127 || i3 > 127) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal character in Base64 encoded data.");
}
int b0 = MAP2[i0];
int b1 = MAP2[i1];
int b2 = MAP2[i2];
int b3 = MAP2[i3];
if (b0 < 0 || b1 < 0 || b2 < 0 || b3 < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal character in Base64 encoded data.");
}
int o0 = (b0 << 2) | (b1 >>> 4);
int o1 = ((b1 & 0xf) << 4) | (b2 >>> 2);
int o2 = ((b2 & 3) << 6) | b3;
out[op++] = (byte) o0;
if (op < oLen) {
out[op++] = (byte) o1;
}
if (op < oLen) {
out[op++] = (byte) o2;
}
}
return out;
}
/**
* Dummy constructor.
*/
private Base64Util() {
}
}
BdBase64Util
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
452
453
454
455
456
457
458
459
460
461
462
463
464
465
466
467
468
469
470
471
472
473
474
475
476
477
478
479
480
481
482
483
484
485
486
487
488
489
490
491
492
493
494
495
496
497
498
499
500
501
502
503
504
505
506
507
508
509
510
511
512
513
514
515
516
517
518
519
520
521
522
523
524
525
526
527
528
529
530
531
532
533
534
535
536
537
538
539
540
541
542
543
544
545
546
547
548
549
550
551
552
553
554
555
556
557
558
559
560
561
562
563
564
565
566
567
568
569
570
571
572
573
574
575
576
577
578
579
580
581
582
583
584
585
586
587
588
589
590
591
592
593
594
595
596
597
598
599
600
601
602
603
604
605
606
607
608
609
610
611
612
613
614
615
616
617
618
619
620
621
622
623
624
625
626
627
628
629
630
631
632
633
634
635
636
637
638
639
640
641
642
643
644
645
646
647
648
649
650
651
652
653
654
655
656
657
658
659
660
661
662
663
664
665
666
667
668
669
670
671
672
673
674
675
676
677
678
679
680
681
682
683
684
685
686
687
688
689
690
691
692
693
694
695
696
697
698
699
700
701
702
703
704
705
706
707
708
709
710
package com.baidu.encryptdemo;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
/***
* Utilities for encoding and decoding the Base64 representation of binary data. See RFCs <a
* href="http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2045.txt">2045</a> and <a href="http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3548.txt">3548</a>.
*/
public class BdBase64Util {
/***
* Default values for encoder/decoder flags.
*/
public static final int DEFAULT = 0;
/***
* Encoder flag bit to omit the padding '=' characters at the end of the output (if any).
*/
public static final int NO_PADDING = 1;
/***
* Encoder flag bit to omit all line terminators (i.e., the output will be on one long line).
*/
public static final int NO_WRAP = 2;
/***
* Encoder flag bit to indicate lines should be terminated with a CRLF pair instead of just an LF. Has no effect if
* {@code NO_WRAP} is specified as well.
*/
public static final int CRLF = 4;
/***
* Encoder/decoder flag bit to indicate using the "URL and filename safe" variant of Base64 (see RFC 3548 section 4)
* where {@code -} and {@code _} are used in place of {@code +} and {@code /}.
*/
public static final int URL_SAFE = 8;
/***
* Flag to pass to {@link Base64OutputStream} to indicate that it should not close the output stream it is wrapping
* when it itself is closed.
*/
public static final int NO_CLOSE = 16;
static abstract class Coder {
public byte[] output;
public int op;
/***
* Encode/decode another block of input data. this.output is provided by the caller, and must be big enough to
* hold all the coded data. On exit, this.opwill be set to the length of the coded data.
*
* @param finish true if this is the final call to process for this object. Will finalize the coder state and
* include any final bytes in the output.
* @return true if the input so far is good; false if some error has been detected in the input stream..
*/
public abstract boolean process(byte[] input, int offset, int len, boolean finish);
/***
* @return the maximum number of bytes a call to process() could produce for the given number of input bytes.
* This may be an overestimate.
*/
public abstract int maxOutputSize(int len);
}
/***
* Decode the Base64-encoded data in input and return the data in a new byte array.
* <p/>
* <p/>
* The padding '=' characters at the end are considered optional, but if any are present, there must be the correct
* number of them.
*
* @param str the input String to decode, which is converted to bytes using the default charset
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the input contains incorrect padding
*/
public static byte[] decode(String str) {
return decode(str.getBytes(), DEFAULT);
}
/***
* Decode the Base64-encoded data in input and return the data in a new byte array.
* <p/>
* <p/>
* The padding '=' characters at the end are considered optional, but if any are present, there must be the correct
* number of them.
*
* @param str the input String to decode, which is converted to bytes using the default charset
* @param flags controls certain features of the decoded output. Pass {@code DEFAULT} to decode standard Base64.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the input contains incorrect padding
*/
public static byte[] decode(String str, int flags) {
return decode(str.getBytes(), flags);
}
/***
* Decode the Base64-encoded data in input and return the data in a new byte array.
* <p/>
* <p/>
* The padding '=' characters at the end are considered optional, but if any are present, there must be the correct
* number of them.
*
* @param input the input array to decode
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the input contains incorrect padding
*/
public static byte[] decode(byte[] input) {
return decode(input, 0, input.length, DEFAULT);
}
/***
* Decode the Base64-encoded data in input and return the data in a new byte array.
* <p/>
* <p/>
* The padding '=' characters at the end are considered optional, but if any are present, there must be the correct
* number of them.
*
* @param input the input array to decode
* @param flags controls certain features of the decoded output. Pass {@code DEFAULT} to decode standard Base64.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the input contains incorrect padding
*/
public static byte[] decode(byte[] input, int flags) {
return decode(input, 0, input.length, flags);
}
/***
* Decode the Base64-encoded data in input and return the data in a new byte array.
* <p/>
* <p/>
* The padding '=' characters at the end are considered optional, but if any are present, there must be the correct
* number of them.
*
* @param input the data to decode
* @param offset the position within the input array at which to start
* @param len the number of bytes of input to decode
* @param flags controls certain features of the decoded output. Pass {@code DEFAULT} to decode standard Base64.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the input contains incorrect padding
*/
public static byte[] decode(byte[] input, int offset, int len, int flags) {
// Allocate space for the most data the input could represent.
// (It could contain less if it contains whitespace, etc.)
Decoder decoder = new Decoder(flags, new byte[len * 3 / 4]);
if (!decoder.process(input, offset, len, true)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("bad base-64");
}
// Maybe we got lucky and allocated exactly enough output space.
if (decoder.op == decoder.output.length) {
return decoder.output;
}
// Need to shorten the array, so allocate a new one of the
// right size and copy.
byte[] temp = new byte[decoder.op];
System.arraycopy(decoder.output, 0, temp, 0, decoder.op);
return temp;
}
static class Decoder extends Coder {
/***
* Lookup table for turning bytes into their position in the Base64 alphabet.
*/
private static final int DECODE[] = {-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 62,
-1, -1, -1, 63, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, -1, -1, -1, -2, -1, -1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 26,
27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1,};
/***
* Decode lookup table for the "web safe" variant (RFC 3548 sec. 4) where - and _ replace + and /.
*/
private static final int DECODE_WEBSAFE[] = {-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, 62, -1, -1, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, -1, -1, -1, -2, -1, -1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, -1, -1, -1, -1, 63,
-1, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50,
51, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1,};
/***
* Non-data values in the DECODE arrays.
*/
private static final int SKIP = -1;
private static final int EQUALS = -2;
/***
* States 0-3 are reading through the next input tuple. State 4 is having read one '=' and expecting exactly one
* more. State 5 is expecting no more data or padding characters in the input. State 6 is the error state; an
* error has been detected in the input and no future input can "fix" it.
*/
private int state; // state number (0 to 6)
private int value;
final private int[] alphabet;
public Decoder(int flags, byte[] output) {
this.output = output;
alphabet = ((flags & URL_SAFE) == 0) ? DECODE : DECODE_WEBSAFE;
state = 0;
value = 0;
}
/***
* @return an overestimate for the number of bytes {@code len} bytes could decode to.
*/
public int maxOutputSize(int len) {
return len * 3 / 4 + 10;
}
/***
* Decode another block of input data.
*
* @return true if the state machine is still healthy. false if bad base-64 data has been detected in the input
* stream.
*/
public boolean process(byte[] input, int offset, int len, boolean finish) {
if (this.state == 6)
return false;
int p = offset;
len += offset;
// Using local variables makes the decoder about 12%
// faster than if we manipulate the member variables in
// the loop. (Even alphabet makes a measurable
// difference, which is somewhat surprising to me since
// the member variable is final.)
int state = this.state;
int value = this.value;
int op = 0;
final byte[] output = this.output;
final int[] alphabet = this.alphabet;
while (p < len) {
// Try the fast path: we're starting a new tuple and the
// next four bytes of the input stream are all data
// bytes. This corresponds to going through states
// 0-1-2-3-0. We expect to use this method for most of
// the data.
//
// If any of the next four bytes of input are non-data
// (whitespace, etc.), value will end up negative. (All
// the non-data values in decode are small negative
// numbers, so shifting any of them up and or'ing them
// together will result in a value with its top bit set.)
//
// You can remove this whole block and the output should
// be the same, just slower.
if (state == 0) {
while (p + 4 <= len
&& (value =
((alphabet[input[p] & 0xff] << 18) | (alphabet[input[p + 1] & 0xff] << 12)
| (alphabet[input[p + 2] & 0xff] << 6) | (alphabet[input[p + 3] & 0xff]))) >= 0) {
output[op + 2] = (byte) value;
output[op + 1] = (byte) (value >> 8);
output[op] = (byte) (value >> 16);
op += 3;
p += 4;
}
if (p >= len)
break;
}
// The fast path isn't available -- either we've read a
// partial tuple, or the next four input bytes aren't all
// data, or whatever. Fall back to the slower state
// machine implementation.
int d = alphabet[input[p++] & 0xff];
switch (state) {
case 0:
if (d >= 0) {
value = d;
++state;
} else if (d != SKIP) {
this.state = 6;
return false;
}
break;
case 1:
if (d >= 0) {
value = (value << 6) | d;
++state;
} else if (d != SKIP) {
this.state = 6;
return false;
}
break;
case 2:
if (d >= 0) {
value = (value << 6) | d;
++state;
} else if (d == EQUALS) {
// Emit the last (partial) output tuple;
// expect exactly one more padding character.
output[op++] = (byte) (value >> 4);
state = 4;
} else if (d != SKIP) {
this.state = 6;
return false;
}
break;
case 3:
if (d >= 0) {
// Emit the output triple and return to state 0.
value = (value << 6) | d;
output[op + 2] = (byte) value;
output[op + 1] = (byte) (value >> 8);
output[op] = (byte) (value >> 16);
op += 3;
state = 0;
} else if (d == EQUALS) {
// Emit the last (partial) output tuple;
// expect no further data or padding characters.
output[op + 1] = (byte) (value >> 2);
output[op] = (byte) (value >> 10);
op += 2;
state = 5;
} else if (d != SKIP) {
this.state = 6;
return false;
}
break;
case 4:
if (d == EQUALS) {
++state;
} else if (d != SKIP) {
this.state = 6;
return false;
}
break;
case 5:
if (d != SKIP) {
this.state = 6;
return false;
}
break;
}
}
if (!finish) {
// We're out of input, but a future call could provide
// more.
this.state = state;
this.value = value;
this.op = op;
return true;
}
// Done reading input. Now figure out where we are left in
// the state machine and finish up.
switch (state) {
case 0:
// Output length is a multiple of three. Fine.
break;
case 1:
// Read one extra input byte, which isn't enough to
// make another output byte. Illegal.
this.state = 6;
return false;
case 2:
// Read two extra input bytes, enough to emit 1 more
// output byte. Fine.
output[op++] = (byte) (value >> 4);
break;
case 3:
// Read three extra input bytes, enough to emit 2 more
// output bytes. Fine.
output[op++] = (byte) (value >> 10);
output[op++] = (byte) (value >> 2);
break;
case 4:
// Read one padding '=' when we expected 2. Illegal.
this.state = 6;
return false;
case 5:
// Read all the padding '='s we expected and no more.
// Fine.
break;
}
this.state = state;
this.op = op;
return true;
}
}
/***
* Base64-encode the given data and return a newly allocated String with the result.
*
* @param input the data to encode
*/
public static String encodeToString(byte[] input) {
try {
return new String(encode(input, DEFAULT), "US-ASCII");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// US-ASCII is guaranteed to be available.
throw new AssertionError(e);
}
}
/***
* Base64-encode the given data and return a newly allocated String with the result.
*
* @param input the data to encode
* @param flags controls certain features of the encoded output. Passing {@code DEFAULT} results in output that
* adheres to RFC 2045.
*/
public static String encodeToString(byte[] input, int flags) {
try {
return new String(encode(input, flags), "US-ASCII");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// US-ASCII is guaranteed to be available.
throw new AssertionError(e);
}
}
/***
* Base64-encode the given data and return a newly allocated String with the result.
*
* @param input the data to encode
* @param offset the position within the input array at which to start
* @param len the number of bytes of input to encode
* @param flags controls certain features of the encoded output. Passing {@code DEFAULT} results in output that
* adheres to RFC 2045.
*/
public static String encodeToString(byte[] input, int offset, int len, int flags) {
try {
return new String(encode(input, offset, len, flags), "US-ASCII");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// US-ASCII is guaranteed to be available.
throw new AssertionError(e);
}
}
/***
* Base64-encode the given data and return a newly allocated byte[] with the result.
*
* @param input the data to encode
*/
public static byte[] encode(byte[] input) {
return encode(input, 0, input.length, DEFAULT);
}
/***
* Base64-encode the given data and return a newly allocated byte[] with the result.
*
* @param input the data to encode
* @param flags controls certain features of the encoded output. Passing {@code DEFAULT} results in output that
* adheres to RFC 2045.
*/
public static byte[] encode(byte[] input, int flags) {
return encode(input, 0, input.length, flags);
}
/***
* Base64-encode the given data and return a newly allocated byte[] with the result.
*
* @param input the data to encode
* @param offset the position within the input array at which to start
* @param len the number of bytes of input to encode
* @param flags controls certain features of the encoded output. Passing {@code DEFAULT} results in output that
* adheres to RFC 2045.
*/
public static byte[] encode(byte[] input, int offset, int len, int flags) {
Encoder encoder = new Encoder(flags, null);
// Compute the exact length of the array we will produce.
int output_len = len / 3 * 4;
// Account for the tail of the data and the padding bytes, if any.
if (encoder.do_padding) {
if (len % 3 > 0) {
output_len += 4;
}
} else {
switch (len % 3) {
case 0:
break;
case 1:
output_len += 2;
break;
case 2:
output_len += 3;
break;
}
}
// Account for the newlines, if any.
if (encoder.do_newline && len > 0) {
output_len += (((len - 1) / (3 * Encoder.LINE_GROUPS)) + 1) * (encoder.do_cr ? 2 : 1);
}
encoder.output = new byte[output_len];
encoder.process(input, offset, len, true);
assert encoder.op == output_len;
return encoder.output;
}
static class Encoder extends Coder {
/***
* Emit a new line every this many output tuples. Corresponds to a 76-character line length (the maximum
* allowable according to <a href="http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2045.txt">RFC 2045</a>).
*/
public static final int LINE_GROUPS = 19;
/***
* Lookup table for turning Base64 alphabet positions (6 bits) into output bytes.
*/
private static final byte ENCODE[] = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N',
'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h',
'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', '0', '1',
'2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '+', '/',};
/***
* Lookup table for turning Base64 alphabet positions (6 bits) into output bytes.
*/
private static final byte ENCODE_WEBSAFE[] = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M',
'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g',
'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', '0',
'1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '-', '_',};
final private byte[] tail;
int tailLen;
private int count;
final public boolean do_padding;
final public boolean do_newline;
final public boolean do_cr;
final private byte[] alphabet;
public Encoder(int flags, byte[] output) {
this.output = output;
do_padding = (flags & NO_PADDING) == 0;
do_newline = (flags & NO_WRAP) == 0;
do_cr = (flags & CRLF) != 0;
alphabet = ((flags & URL_SAFE) == 0) ? ENCODE : ENCODE_WEBSAFE;
tail = new byte[2];
tailLen = 0;
count = do_newline ? LINE_GROUPS : -1;
}
/***
* @return an overestimate for the number of bytes {@code len} bytes could encode to.
*/
public int maxOutputSize(int len) {
return len * 8 / 5 + 10;
}
public boolean process(byte[] input, int offset, int len, boolean finish) {
// Using local variables makes the encoder about 9% faster.
final byte[] alphabet = this.alphabet;
final byte[] output = this.output;
int op = 0;
int count = this.count;
int p = offset;
len += offset;
int v = -1;
// First we need to concatenate the tail of the previous call
// with any input bytes available now and see if we can empty
// the tail.
switch (tailLen) {
case 0:
// There was no tail.
break;
case 1:
if (p + 2 <= len) {
// A 1-byte tail with at least 2 bytes of
// input available now.
v = ((tail[0] & 0xff) << 16) | ((input[p++] & 0xff) << 8) | (input[p++] & 0xff);
tailLen = 0;
}
;
break;
case 2:
if (p + 1 <= len) {
// A 2-byte tail with at least 1 byte of input.
v = ((tail[0] & 0xff) << 16) | ((tail[1] & 0xff) << 8) | (input[p++] & 0xff);
tailLen = 0;
}
break;
}
if (v != -1) {
output[op++] = alphabet[(v >> 18) & 0x3f];
output[op++] = alphabet[(v >> 12) & 0x3f];
output[op++] = alphabet[(v >> 6) & 0x3f];
output[op++] = alphabet[v & 0x3f];
if (--count == 0) {
if (do_cr)
output[op++] = '\r';
output[op++] = '\n';
count = LINE_GROUPS;
}
}
// At this point either there is no tail, or there are fewer
// than 3 bytes of input available.
// The main loop, turning 3 input bytes into 4 output bytes on
// each iteration.
while (p + 3 <= len) {
v = ((input[p] & 0xff) << 16) | ((input[p + 1] & 0xff) << 8) | (input[p + 2] & 0xff);
output[op] = alphabet[(v >> 18) & 0x3f];
output[op + 1] = alphabet[(v >> 12) & 0x3f];
output[op + 2] = alphabet[(v >> 6) & 0x3f];
output[op + 3] = alphabet[v & 0x3f];
p += 3;
op += 4;
if (--count == 0) {
if (do_cr)
output[op++] = '\r';
output[op++] = '\n';
count = LINE_GROUPS;
}
}
if (finish) {
// Finish up the tail of the input. Note that we need to
// consume any bytes in tail before any bytes
// remaining in input; there should be at most two bytes
// total.
if (p - tailLen == len - 1) {
int t = 0;
v = ((tailLen > 0 ? tail[t++] : input[p++]) & 0xff) << 4;
tailLen -= t;
output[op++] = alphabet[(v >> 6) & 0x3f];
output[op++] = alphabet[v & 0x3f];
if (do_padding) {
output[op++] = '=';
output[op++] = '=';
}
if (do_newline) {
if (do_cr)
output[op++] = '\r';
output[op++] = '\n';
}
} else if (p - tailLen == len - 2) {
int t = 0;
v =
(((tailLen > 1 ? tail[t++] : input[p++]) & 0xff) << 10)
| (((tailLen > 0 ? tail[t++] : input[p++]) & 0xff) << 2);
tailLen -= t;
output[op++] = alphabet[(v >> 12) & 0x3f];
output[op++] = alphabet[(v >> 6) & 0x3f];
output[op++] = alphabet[v & 0x3f];
if (do_padding) {
output[op++] = '=';
}
if (do_newline) {
if (do_cr)
output[op++] = '\r';
output[op++] = '\n';
}
} else if (do_newline && op > 0 && count != LINE_GROUPS) {
if (do_cr)
output[op++] = '\r';
output[op++] = '\n';
}
assert tailLen == 0;
assert p == len;
} else {
// Save the leftovers in tail to be consumed on the next
// call to encodeInternal.
if (p == len - 1) {
tail[tailLen++] = input[p];
} else if (p == len - 2) {
tail[tailLen++] = input[p];
tail[tailLen++] = input[p + 1];
}
}
this.op = op;
this.count = count;
return true;
}
}
private BdBase64Util() {
} // don't instantiate
}
JDK8.x 和 common codec 中对 Base64 算法的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class Base64Util {
public static String jdkBase64Encode(String src) {
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(src.getBytes());
}
public static String jdkBase64Decode(String src) {
return new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode(src));
}
public static String codecBase64Encode(String src) {
return org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64.encodeBase64String(src.getBytes());
}
public static String codecBase64Decode(String src) {
return new String(org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64.decodeBase64(src));
}
}