堆
堆
堆基础
堆定义
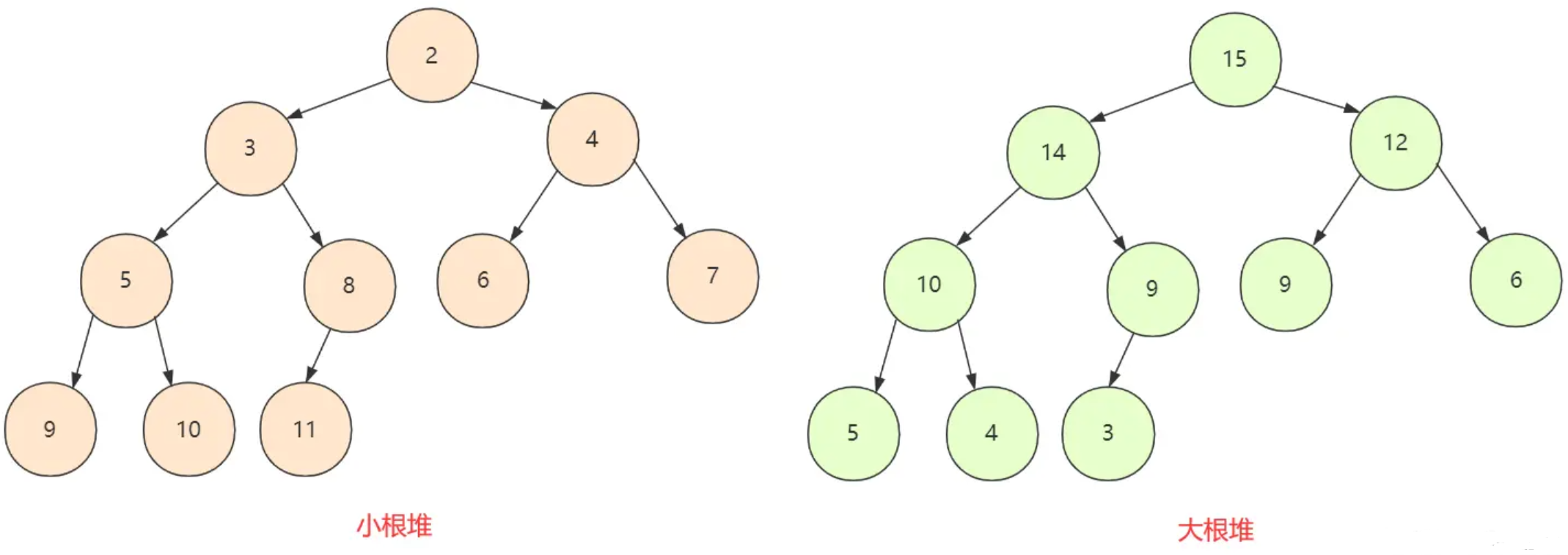
- 堆是一颗完全二叉树
- 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于(小根堆)或不小于其父节点(大根堆)的值
- 用数组来实现
大根堆、小根堆
- 大根堆 每个节点的值都大于等于子节点的值;最大值在根节点
- 小根堆 每个节点的值都小于等于子节点的值;最小值在根节点
堆排序
- 构建堆,取堆顶为最小 (最大)
- 将剩下的元素重新构建一个堆,取堆顶,一直到元素取完为止
构建堆
堆相关面试题
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素 medium
题目
给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 k 个最大的元素。 请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。 你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。 输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4], k = 2 输出: 5
考察点
- 能否实现算法的优化
- 能否了解快速选择排序算法
- 能否说明堆算法和快速排序算法的适用场景
解法 1:先排序,后遍历
思路
第 K 个最大元素:先按升序排序,然后找到 nums.length-k 就是第 K 个最大元素
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public static int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length-k];
}
时间复杂度不止 O(n),默认的排序算法为快速排序,复杂度为 O(nlogn)
解法 2-1:最小堆 PriorityQueue
思路
- 最小堆,堆顶是最小的元素;
- 最小堆类似于一个漏斗,把大的数会往下沉,只保留 k 个数;超过 k 个数时,看堆顶的元素是否小于遍历的值,如果小于将堆顶给删除,这样能保证堆中的元素总是为数组中最大的 K 个数
这里最合适的操作其实是 replace(),即直接把新读进来的元素放在堆顶,然后执行下沉(siftDown())操作。Java 当中的 PriorityQueue 没有提供这个操作,只好先 poll() 再 offer()。
- 遍历整个数组,最后返回堆顶就行
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public static int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
// 构建一个小根堆,堆顶元素最小,最大的值会往下沉
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int num : nums) {
pq.offer(num);
// 元素超过k了,删除堆顶最小的值
if (pq.size() > k) {
if (pq.peek() < num) { // 堆顶的元素小于num才删除
pq.poll();
}
}
}
// 遍历完毕,pq堆顶就是第k个最大值
return pq.peek();
}
复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(nlogk),调整一个数的时间复杂度为 O(logk),有 n 个数需要调整
- 空间复杂度:O(k),容量为 k 个数组
解法 2-2:最小堆手写堆
思路
- 参考最小堆的构建写法
- 堆的个数大于 k 时,剩下的元素每次和堆顶元素比较,如果大于堆顶元素,就需要将堆顶元素替换掉
- 这样就能保证堆中元素就是最大的 k 个数,堆顶就是第 K 个最大元素(N-K 处元素)
解法 3:快速选择,递归(最优解)
思路
- 参考快速排序的的过程,快速排序每次会将一个元素排好序
- 我们要找第 K 个最大元素,对于升序数组来说,就是找 n-k 索引处的元素
- 在快速排序每排序完一个元素后,得到一个排序后元素的索引 pivotIndex 后,比较该索引和 n-k 索引
- pivotIndex 等于 n-k,那么该索引就是我们要找的元素,直接返回
- n-k>pivotIndex,说明目标值在右侧,递归范围 [pivotIndex+1, high]
- n-k<pivotIndex,说明目标值在左侧,递归范围 [low, pivotIndex-1]
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
public static int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
return quickSelect(nums, 0, nums.length - 1, k);
}
private static int quickSelect(int[] nums, int low, int high, int k) {
if (low >= high) {
return nums[low];
}
int targetIndex = nums.length - k;
int partitionIndex = partition(nums, low, high);
if (targetIndex == partitionIndex) { // 等于
return nums[targetIndex];
} else if (targetIndex > partitionIndex) { // 大于
return quickSelect(nums, partitionIndex + 1, high, k);
} else { // 小于
return quickSelect(nums, low, partitionIndex - 1, k);
}
}
private static int partition(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
// 随机pivot,防止递归树倾斜
int pivotIndex = left + new Random().nextInt(right - left) + 1;
// 交换pivot和left
swap(nums, left, pivotIndex);
pivotIndex = left;
// 默认选择最左边的作为pivot
int pivot = nums[pivotIndex];
while (left < right) {
// 从右遍历
while (left < right && nums[right] >= pivot) {
right--;
}
// 从左遍历
while (left < right && nums[left] <= pivot) {
left++;
}
swap(nums, left, right);
}
// 最后将基准值索引处的值和left交换位置
swap(nums, pivotIndex, left);
return left;
}
private static void swap(int[] nums, int m, int n) {
int temp = nums[m];
nums[m] = nums[n];
nums[n] = temp;
}
复杂度
- 时间复杂度 O(n)
- 空间复杂度 O(logn),递归栈空间开销
解法 4:快速选择,迭代(最优解)
和快速选择递归不同,我们也可以用迭代来实现,只需要控制好 low 和 high 的边界即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
public static int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int targetIndex = nums.length - k;
int low = 0;
int high = nums.length - 1;
while (low <= high) { // 条件一定要是<=,否则会返回-1
int partitionIndex = partition(nums, low, high);
System.out.println("partitionIndex=" + partitionIndex + ",targetIndex=" + targetIndex + ",low=" + low + ",high=" + high);
if (targetIndex == partitionIndex) {
return nums[targetIndex];
} else if (targetIndex > partitionIndex) { // 在右侧
low = partitionIndex + 1;
} else { // 在左侧
high = partitionIndex - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
private static int partition(int[] nums, int low, int high) {
// 随机pivot
int pivotIndex = low + new Random().nextInt(high - low + 1);
int pivot = nums[pivotIndex];
// 交换pivotIndex和low
swap(nums, pivotIndex, low);
int left = low;
int right = high;
while (left < right) {
while (left < right && nums[right] >= pivot) {
right--;
}
while (left < right && nums[left] <= pivot) {
left++;
}
swap(nums, left, right);
}
swap(nums, left, low);
return left;
}
private static void swap(int[] nums, int m, int n) {
int temp = nums[m];
nums[m] = nums[n];
nums[n] = temp;
}
最小的 k 个数(需返回数组)
1. 排序法
对 n 个数排序,然后迭代前 k 个数即可,时间复杂度以 快排为准 是 O(nlogn)
2. 局部替换法
假设前 k 个数就是整个数组中最小的,找出最大的数和 k+1 比较,如果比 k+1 大就和 K=1 互换位置,然后再将 k 数组中的最大数找出,在进行比较,知道数组末尾.时间复杂度 O(nk)
3. 最大堆
对思路二中找最大数的优化,用前 K 个数建立最大堆,每次用堆顶元素和 n-k 中各个元素比较,如果堆顶元素较大,则互换位置,然后调整堆,使之重新成为最大堆。时间复杂度 O(n*logk)
思路
- 利用大根堆来做 PriorityQueue pq
- 前 k 个元素直接入堆
- k 个元素后,堆顶和要待插入的元素比较,如果堆顶大于待插入元素,将堆顶移除,将新元素插入到堆
- 遍历 pq 所有元素,大根堆 k 个元素就是最小的 k 个数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public static ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] input, int k) {
if (k <= 0) return new ArrayList<>();
// 默认小根堆,这里需要一个大根堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer i1, Integer i2) {
return i2 - i1;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
pq.offer(input[i]);
}
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = k; i < input.length; i++) {
Integer peek = pq.peek();
if (peek != null && peek > input[i]) {
pq.poll();
pq.offer(input[i]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result.add(pq.poll());
}
return result;
}
最大的 k 个数(需返回数组)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public static ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution10(int[] input, int k) {
if (k <= 0) return new ArrayList<>();
// 默认小根堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(k);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
pq.offer(input[i]);
}
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = k; i < input.length; i++) {
Integer peek = pq.peek();
if (peek != null && peek < input[i]) {
pq.poll();
pq.offer(input[i]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result.add(pq.poll());
}
return result;
}
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权