加解密
加密介绍
密码的常用术语
明文:待加密的信息
密文:经过加密后的明文
加密:明文转为密文的过程
加密算法:明文转为密文的转换算法
加密密钥:通过加密算法进行加密操作用的密钥
解密:将密文转为明文的过程
解密算法:密文转为明文的算法
解密密钥:通过解密算法进行解密操作用的密钥
密码分析:截获密文者试图通过分析截获的密文从而推断出原来的明文或密钥的过程
主动攻击:攻击者非法入侵密码系统,采用伪造、修改、删除等手段向系统注入假消息进行欺骗(对密文具有破坏作用)
被动攻击:对一个保密系统采取截获密文并对其进行分析和攻击(对密文没有破坏作用)
密码体制:由明文空间、密文空间、密钥空间、加密算法和解密算法五部分构成
密码协议:也称安全协议,指以密码学为基础的消息交换的通信协议,目的是在网络环境中提供安全的服务
密码系统:指用于加密、解密的系统
柯克霍夫原则:数据的安全基于密钥而不是算法的保密。即系统的安全取决于密钥,对密钥保密,对算法公开。(现代密码学设计的基本原则)
密码分类(按密码体制分)
对称密码:别名单钥密码或私钥密码,加密密钥和解密密钥相同
非对称密码:别名双钥密码或公钥密码,加密密钥和解密密钥不同,密钥分公钥、私钥
密码分类
对称密码算法:别名单钥密码算法或私钥密码算法,应用于对称密码的加密、解密算法
非对称密码算法:别名双钥密码算法或公钥密码算法,非对称密码的加密、解密算法
摘要算法:
散列函数
散列函数,也称哈希函数或消息摘要函数或单向函数,用来验证数据的完整性
- 特点
长度不受限制
哈希值容易计算
散列运算过程不可逆 - 散列函数相关的算法
- 消息摘要算法 MD5 等
- SHA(安全散列算法)
- MAC(消息认证码算法)
数字签名
主要是针对以数字的形式存储的消息进行的处理
单向加密
- BASE64 : 严格说,属于编码格式,非加密算法
- MD5 :(Message Digest algorithm 5),信息摘要算法
- SHA :(Secure Hash Algorithm),安全散列算法
- HMAC :(Hash Message Authentication Code),散列消息鉴别码
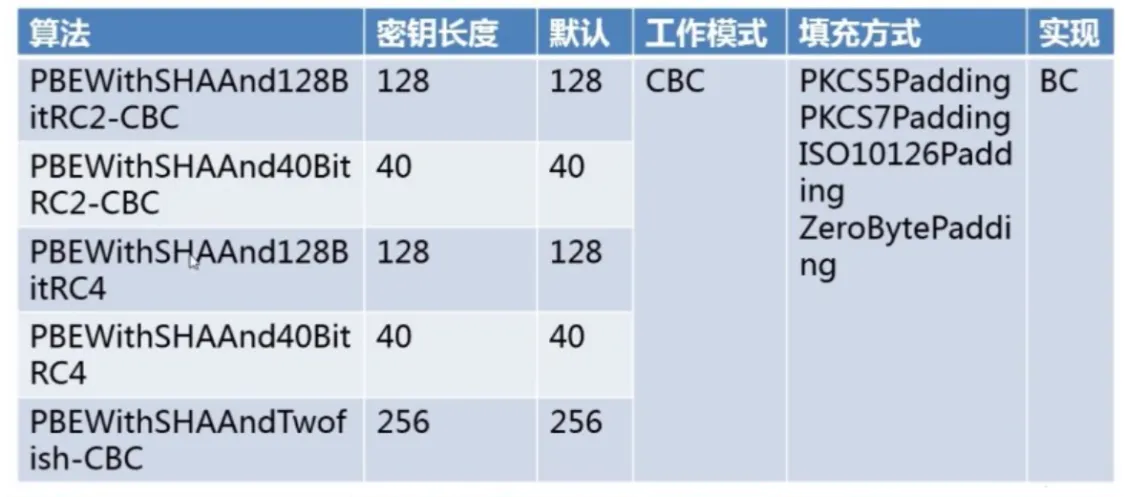
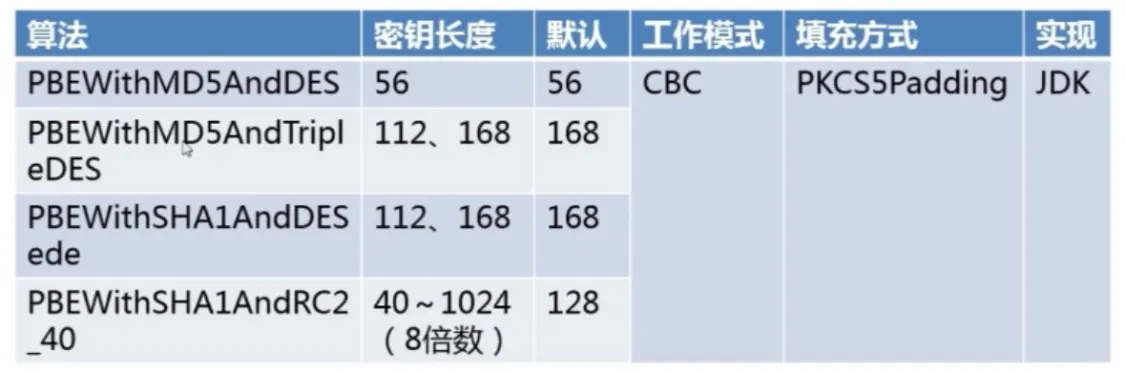
复杂的对称加密 (DES、PBE)、非对称加密
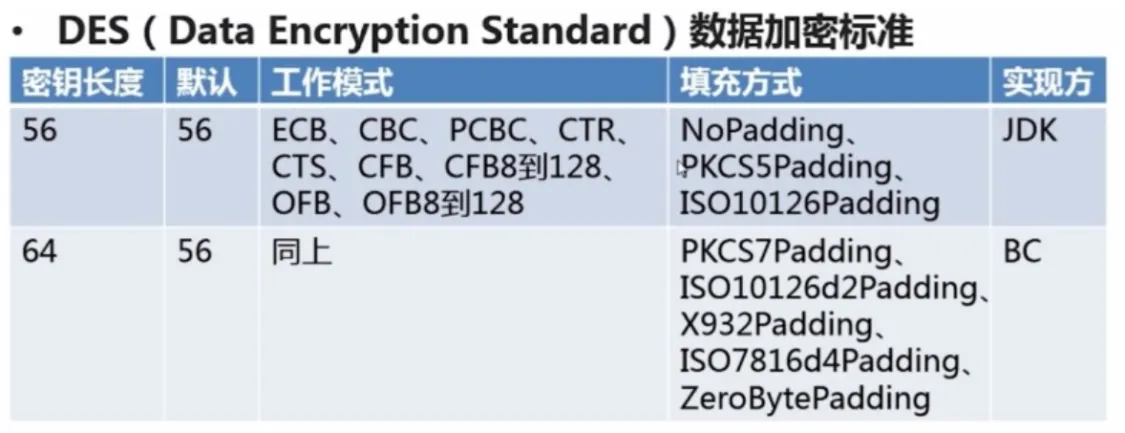
- DES :(Data Encryption Standard),数据加密算法
- PBE :(Password-based Encryption),基于密码验证
- RSA :(算法的名字以发明者的名字命名:Ron Rivest, AdiShamir 和 Leonard Adleman)
- DH :(Diffie-Hellman),密钥一致协议
- DSA :(Digital Signature Algorithm),数字签名
- ECC :(Elliptic Curves Cryptography),椭圆曲线密码编码学
MD5、SHA、HMAC这三种加密算法,可谓是非可逆加密,就是不可解密的加密方法。我们通常只把他们作为加密的基础。单纯的以上三种的加密并不可靠。
JDK 的加密与解密
Java 安全组成
- JCA(Java Cryptography Architecture)
提供基本的加密框架,如消息摘要,数字签名 - JCE(Java Cryptography Extension)
JCA 的扩展,提供了很多加密算法,如 DES、AES、RSA 算法都是通过 JCE 提供的 - JSSE(Java Secure Socket Extension)
提供基于 SSL 的加密功能,主要用于网络传输 - JAAS(Java Authentication and Authentication Service)
提供身份认证
cryptography 密码学
JDK 及其他扩展包引入
Java\jdk1.8.0_45\jre\lib\security\java.security
Java 相关包、类
- java.security
消息摘要 - javax.crypto
安全消息摘要,消息认证(鉴别)码 - java.net.ssl
安全套接字,和网络传输相关,如HttpsURLConnection、SSLContext
第三方扩展
- Bouncy Castle
- Commons Codec
Apache 提供
Base64、二进制、十六进制、字符集编码
Url 编码/解码
应用
- Base64 算法
- 消息摘要算法
- 对称加密算法
- 非对称加密算法
- 数字签名算法
- 数字证书
- 安全协议
消息摘要算法
作用
- 验证数据完整性
- 数字签名核心算法
MD(Message Digest) 消息摘要
MD5,128 位摘要信息
SHA(Secure Hash Algorithm) 安全散列
固定长度摘要信息
SHA1:160 位
SHA2(SHA-224、SHA-256、SHA-384、SHA-512)
MAC(Message Authentication Code) 消息认证码
HMAC(keyed-Hash Message Authentication Code) 含有密钥的散列函数算法
融合了 MD 和 SHA 两种算法
- MD 系列:HmacMD2、HmacMD4、HmacMD5
- SHA 系列:HmacSHA1、HmacSHA224、HmacSHA256、HmacSHA384、HmacSHA512
应用如 SecureCRT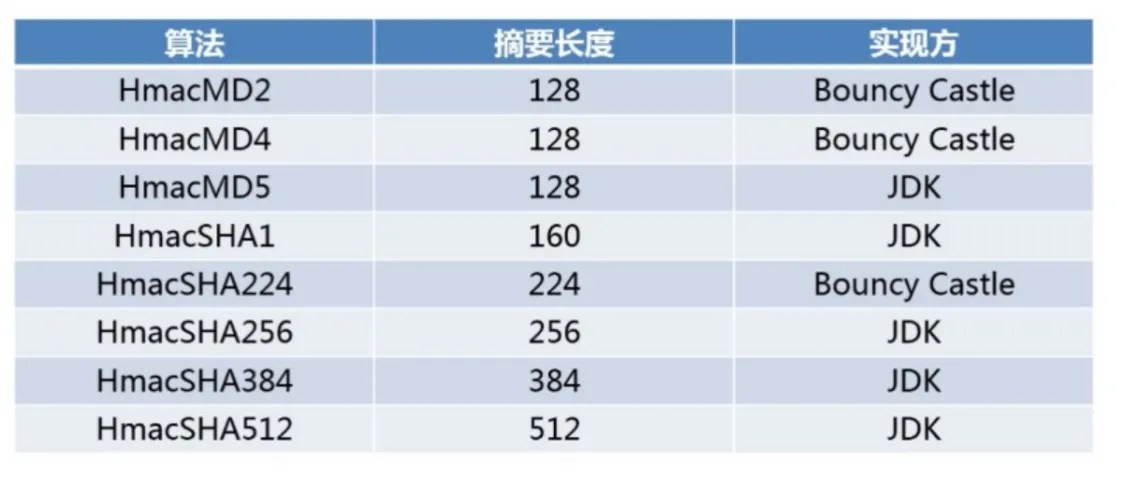
消息摘要封装
MessageDigestUtil.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
public class MessageDigestUtil {
/**
* Used to build output as Hex
*/
private static final char[] DIGITS_LOWER = { '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd',
'e', 'f' };
/**
* Used to build output as Hex
*/
private static final char[] DIGITS_UPPER = { '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D',
'E', 'F' };
/**
* 输出16进制bytes数组表示
*
* @param data
* @return String
*/
public static String toHexString(final byte[] data) {
return new String(encodeHex(data, DIGITS_LOWER));
}
private static char[] encodeHex(final byte[] data, final char[] toDigits) {
final int l = data.length;
final char[] out = new char[l << 1];
// two characters form the hex value.
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < l; i++) {
out[j++] = toDigits[(0xF0 & data[i]) >>> 4];
out[j++] = toDigits[0x0F & data[i]];
}
return out;
}
/**
* md5摘要算法输出
*
* @param input
* @return String
*/
public static String md5(String input) {
try {
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance(MessageDigestAlgorithms.MD5);
byte[] result = md.digest(input.getBytes());
return toHexString(result);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static String sha1ToHex(String input) {
return shaToHex(input, MessageDigestAlgorithms.SHA_1);
}
public static String sha256ToHex(String input) {
return shaToHex(input, MessageDigestAlgorithms.SHA_256);
}
public static String sha384ToHex(String input) {
return shaToHex(input, MessageDigestAlgorithms.SHA_384);
}
public static String sha512ToHex(String input) {
return shaToHex(input, MessageDigestAlgorithms.SHA_512);
}
/**
* sha算法输出
*
* @param input
* @param algorithm
* sha算法类型
* @return String
*/
private static String shaToHex(String input, String algorithm) {
try {
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);
md.update(input.getBytes());
return toHexString(md.digest());
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
MessageDigestAlgorithms.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
public class MessageDigestAlgorithms {
private MessageDigestAlgorithms() {
// cannot be instantiated.
}
/**
* The MD2 message digest algorithm defined in RFC 1319.
*/
public static final String MD2 = "MD2";
/**
* The MD5 message digest algorithm defined in RFC 1321.
*/
public static final String MD5 = "MD5";
/**
* The SHA-1 hash algorithm defined in the FIPS PUB 180-2.
*/
public static final String SHA_1 = "SHA-1";
/**
* The SHA-256 hash algorithm defined in the FIPS PUB 180-2.
*/
public static final String SHA_256 = "SHA-256";
/**
* The SHA-384 hash algorithm defined in the FIPS PUB 180-2.
*/
public static final String SHA_384 = "SHA-384";
/**
* The SHA-512 hash algorithm defined in the FIPS PUB 180-2.
*/
public static final String SHA_512 = "SHA-512";
}
对称加密
对称加密概念
对称加密算法是较传统的加密体制,即通信双方在加/解密过程中使用他们共享的单一密钥,鉴于其算法简单和加密速度快的优点,目前仍然在使用,但是安全性方面就差一点可能。最常用的对称密码算法是 DES 算法,而 DES 密钥长度较短,已经不适合当今分布式开放网络对数据加密安全性的要求。一种新的基于 Rijndael 算法的对称高级数据加密标准 AES 取代了数据加密标准 DES,弥补了 DES 的缺陷,目前使用比较多一点
分类
- DES 密钥长度不够,出现了 3DES
- AES 替代 DES
- PBE
- IDEA
DES(Data Encryption Standard) 数据加密标准
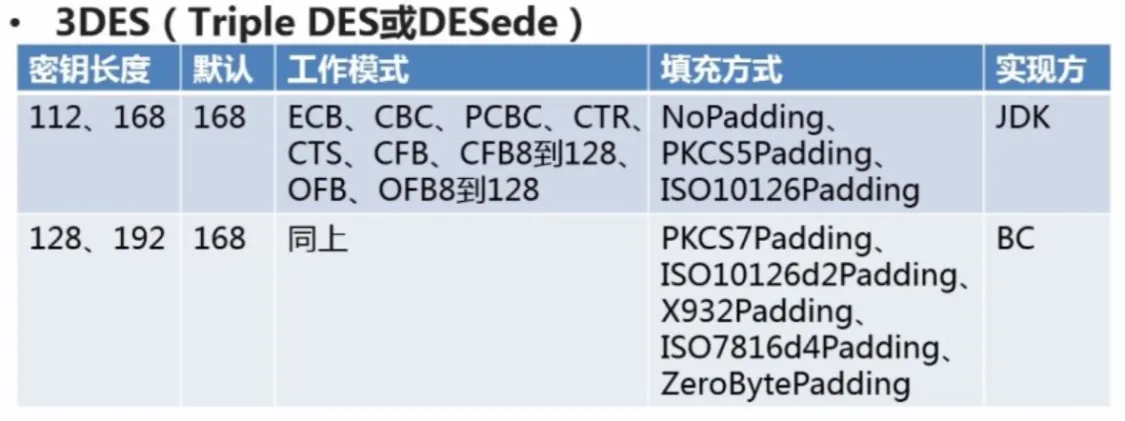
3DES(Triple DES 或 DESede)
相比较与 DES:
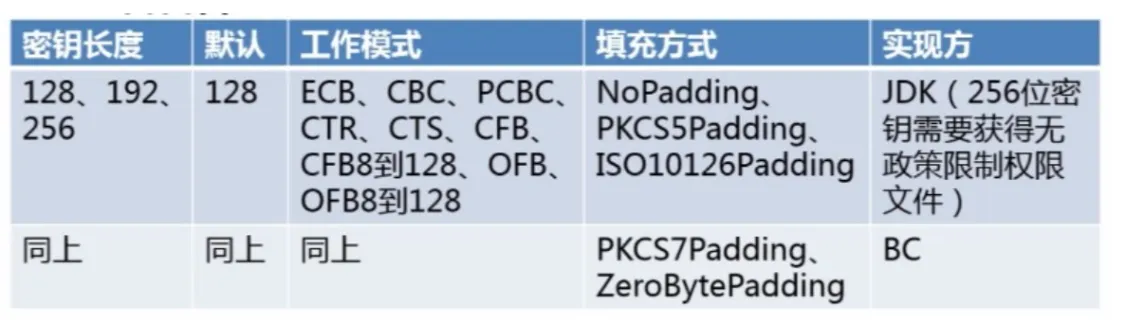
AES
AES 是目前使用最多的对称加密算法,AES 还未被破解;AES 通常用于移动通信系统加密以及基于 SSH 协议的软件
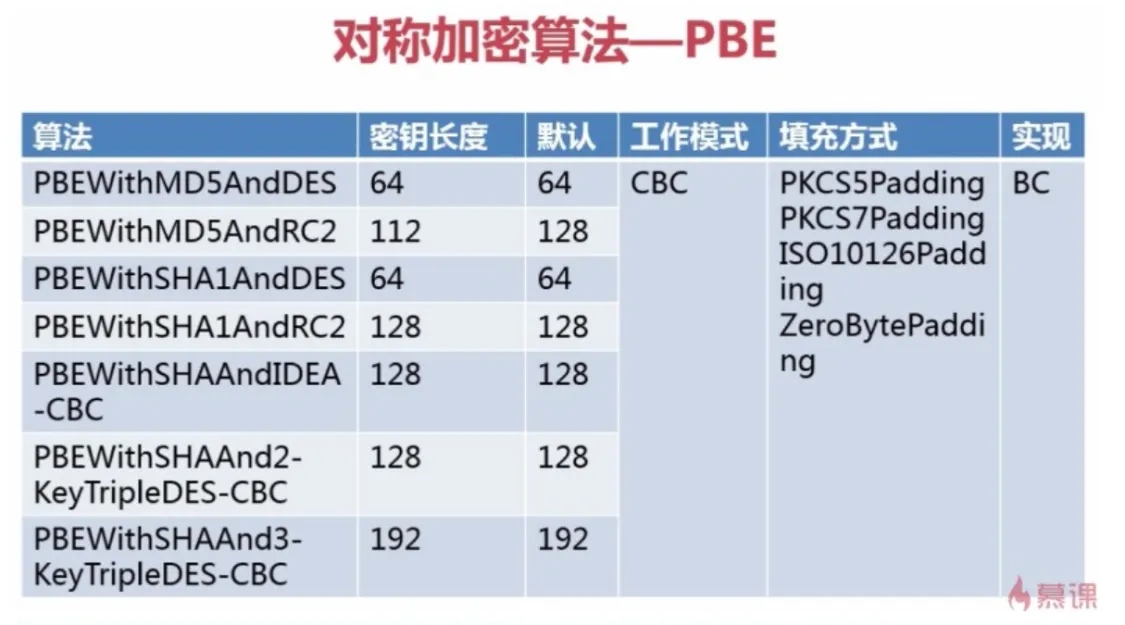
PBE(Password Based Encryption) 基于口令加密
PBE 算法结合了消息摘要算法和对称加密算法的优点
只是对已有算法的包装(MD5、AES)
AES(Rijndael)
高级加密标准(英语:Advanced Encryption Standard,缩写:AES),在密码学中又称 Rijndael加密法,是美国联邦政府采用的一种区块加密标准。这个标准用来替代原先的 DES,已经被多方分析且广为全世界所使用。经过五年的甄选流程,高级加密标准由美国国家标准与技术研究院(NIST)于 2001 年 11 月 26 日发布于 FIPS PUB 197,并在 2002 年 5 月 26 日成为有效的标准。2006 年,高级加密标准已然成为对称密钥加密中最流行的算法之一。
AES 基本概念
AES(Rijndael) 三个基本概念:密钥,填充,模式
1、密钥 (SecretKey)
密钥是 AES 算法实现加密和解密的根本。对称加密算法之所以对称,是因为这类算法对明文的加密和解密需要使用同一个密钥。
AES 支持三种长度的密钥:128位,192位,256位
平时大家所说的 AES128,AES192,AES256,实际上就是指的 AES 算法对不同长度密钥的使用。
从安全性来看,AES256 安全性最高,
从性能来看,AES 性能最高,
本质原因是它们的加密处理轮数不同。
AES 中 128 位密钥版本有 10 个加密循环,192 比特密钥版本有 12 个加密循环,256 比特密钥版本则有 14 个加密循环。
2、填充 (Padding)
Padding 是用来填充最后一块使得变成一整块
要想了解填充的概念,我们先要了解 AES 的 分组加密 特性
AES 算法在对明文加密的时候,并不是把整个明文一股脑加密成一整段密文,而是把明文拆分成一个个独立的明文块,每一个明文块长度 128bit。
这些明文块经过 AES 加密器的复杂处理,生成一个个独立的密文块,这些密文块拼接在一起,就是最终的 AES 加密结果。
但是这里涉及到一个问题:
假如一段明文长度是 192bit,如果按每 128bit 一个明文块来拆分的话,第二个明文块只有 64bit,不足 128bit。这时候怎么办呢?就需要对明文块进行填充(Padding)。
不同的语言有不同的填充方式
1. NoPadding
不做任何填充,但是要求明文必须是 16 字节的整数倍。
2. PKCS5Padding(默认)
如果明文块少于 16 个字节(128bit),在明文块末尾补足相应数量的字符,且每个字节的值等于缺少的字符数。 比如明文:{1,2,3,4,5,a,b,c,d,e},缺少 6 个字节,则补全为{1,2,3,4,5,a,b,c,d,e,6,6,6,6,6,6}
3. ISO10126Padding
如果明文块少于 16 个字节(128bit),在明文块末尾补足相应数量的字节,最后一个字符值等于缺少的字符数,其他字符填充随机数。
比如明文:{1,2,3,4,5,a,b,c,d,e},缺少 6 个字节,则可能补全为{1,2,3,4,5,a,b,c,d,e,5,c,3,G,$,6}
3、模式 (Mode)
AES 的工作模式,体现在把明文块加密成密文块的处理过程中。AES 加密算法提供了五种不同的工作模式:
ECB、CBC、CTR、CFB、OFB
模式之间的主题思想是近似的,在处理细节上有一些差别。我们这一期只介绍各个模式的基本定义。
- ECB 模式(默认):
电码本模式 Electronic Codebook Book - CBC 模式:
密码分组链接模式 Cipher Block Chaining - CTR 模式:
计算器模式 Counter - CFB 模式:
密码反馈模式 Cipher FeedBack - OFB 模式:
输出反馈模式 Output FeedBack
ECB
ECB 模式(Electronic Codebook Book)是最简单的工作模式,在该模式下,每一个明文块的加密都是完全独立,互不干涉的。
优点:
- 简单
- 有利于并行计算
缺点:
- 相同的明文块经过加密会变成相同的密文块,因此安全性较差。
CBC
CBC 模式(Cipher Block Chaining)引入了一个新的概念:初始向量IV(Initialization Vector)。
IV 是做什么用的呢?它的作用和 MD5 的 “ 加盐 “ 有些类似,目的是防止同样的明文块始终加密成同样的密文块。
IV称为 初始向量,不同的 IV 加密后的字符串是不同的,加密和解密需要相同的 IV,既然 IV 看起来和 key 一样,却还要多一个 IV 的目的,对于每个块来说,key 是不变的,但是只有第一个块的 IV 是用户提供的,其他块 IV 都是自动生成。
IV 的长度为 16 字节。超过或者不足,可能实现的库都会进行补齐或截断。但是由于块的长度是 16 字节,所以一般可以认为需要的 IV 是 16 字节。
从图中可以看出,CBC 模式在每一个明文块加密前会让明文块和一个值先做异或操作。IV 作为初始化变量,参与第一个明文块的异或,后续的每一个明文块和它前一个明文块所加密出的密文块相异或。
这样以来,相同的明文块加密出的密文块显然是不一样的。
优点:
- 安全性更高
缺点:
- 无法并行计算,性能上不如 ECB
- 引入初始化向量 IV,增加复杂度。
javax.crypto 代码
- kgen.init 传入的第一个参数 128 决定了密钥的长度是 128bit。
- Cipher.getInstance(“AES/CBC/NoPadding”) 决定了 AES 选择的填充方式是 NoPadding,工作模式是 CBC 模式。
几点补充:
- 我们在调用封装好的 AES 算法时,表面上使用的 Key 并不是真正用于 AES 加密解密的密钥,而是用于生成真正密钥的 “ 种子 “。
- 填充明文时,如果明文长度原本就是 16 字节的整数倍,那么除了 NoPadding 以外,其他的填充方式都会填充一组额外的 16 字节明文块。
AES 注意
- 加解密密钥 SecretKey 要一致
- 加解密填充 Padding 要一致
- 加解密模式 Mode 要一致
- 加解密初始化向量 IV 要一致
AES 常见错误
java.security.InvalidKeyException: Invalid AES key length: 26 bytes
AES 的秘钥长度不对,只能是 16,24,32,对应 128bit,192bit,256bit
1
2
3
4
interface AESConstants {
int AES_BLOCK_SIZE = 16;
int[] AES_KEYSIZES = new int[]{16, 24, 32};
}
java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException: class configured for SecureRandom (provider: Crypto) cannot be found
javax.crypto.BadPaddingException: Given final block not properly padded
貌似是需要 Base64
其实就是 SecureRandom 创建的方式不同而引起的错误
Caused by: java.security.NoSuchProviderException: no such provider: Crypto
AndroidN(7.0) 移除了 Crypto
AES 代码实现
自己总结 AES(推荐 3 星)
- 提供 SHA-256 生成 key 和 KeyGenerator 生成 key,可以自己选择
- 加密后 Base64 编码
- 解密前先 Base64 解密
- 这个需要自己将 iv 给后端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
public final class AESUtil {
private static final String DEFAULT_CHATSET = "UTF-8";
// AESCrypt-ObjC uses SHA-256 (and so a 256-bit key)
private static final String HASH_ALGORITHM = "SHA-256";
private static final int DEFAULT_IV_BYTES_SIZE = 16;
// AES 加密
private static final String AES = "AES";// 或者Rijndael
// AES是加密方式 CBC是工作模式 PKCS5Padding是填充模式
private static final String DEFAULT_CIPHER_TRANSFORMATION = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
// SHA1PRNG 强随机种子算法, 要区别4.2以上版本的调用方法
private static final String SHA1PRNG = "SHA1PRNG";
// 对密钥进行处理,Android中使用
// private static SecretKeySpec getRawKey(byte[] seed) throws Exception {
// KeyGenerator kgen = KeyGenerator.getInstance(AES);
// //for android
// SecureRandom sr = null;
// // 在4.2以上版本中,SecureRandom获取方式发生了改变
// if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 17) {
// sr = SecureRandom.getInstance(SHA1PRNG, "Crypto");
// } else {
// sr = SecureRandom.getInstance(SHA1PRNG);
// }
// // for Java
// // secureRandom = SecureRandom.getInstance(SHA1PRNG);
// sr.setSeed(seed);
// kgen.init(256, sr); //256 bits or 128 bits,192bits
// //AES中128位密钥版本有10个加密循环,192比特密钥版本有12个加密循环,256比特密钥版本则有14个加密循环。
// SecretKey skey = kgen.generateKey();
// byte[] raw = skey.getEncoded();
// SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(raw, AES);
// return secretKeySpec;
// }
/**
* Generates SHA256 hash of the password which is used as key
*
* @param password used to generated key
* @return SHA256 of the password
*/
private static SecretKeySpec generateKey(final String password) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
final MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance(HASH_ALGORITHM);
byte[] bytes = password.getBytes("UTF-8");
digest.update(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
byte[] key = digest.digest();
log("[generateKey] SHA-256 key:" + bytesToHex(key));
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key, AES);
return secretKeySpec;
}
public static byte[] createIV() {
SecureRandom secureRandom = new SecureRandom();
secureRandom.setSeed(SecureRandom.getSeed(DEFAULT_IV_BYTES_SIZE));
byte[] b = new byte[DEFAULT_IV_BYTES_SIZE];
secureRandom.nextBytes(b);
return b;
}
/**
* Encrypt and encode message using 256-bit AES with key generated from password.
*
* @param password used to generated key,密钥
* @param plainText the thing you want to encrypt assumed String UTF-8,明文
* @return Base64 encoded CipherText
* @throws GeneralSecurityException if problems occur during encryption
*/
public static String encryptToBase64(final String password, byte[] ivBytes, String plainText)
throws GeneralSecurityException {
try {
final SecretKeySpec key = generateKey(password);
log("[encryptToBase64] plainText: " + plainText);
byte[] cipherText = encrypt(key, ivBytes, plainText.getBytes(DEFAULT_CHATSET));
//NO_WRAP is important as was getting \n at the end
String encoded = Base64.encodeToString(cipherText, Base64.NO_WRAP);
log("[encryptToBase64] encrypt and Base64.NO_WRAP:" + encoded);
return encoded;
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log(e.getMessage());
throw new GeneralSecurityException(e);
}
}
/**
* More flexible AES encrypt that doesn't encode
*
* @param key AES key typically 128, 192 or 256 bit
* @param iv Initiation Vector
* @param message in bytes (assumed it's already been decoded)
* @return Encrypted cipher text (not encoded)
* @throws GeneralSecurityException if something goes wrong during encryption
*/
public static byte[] encrypt(final SecretKeySpec key, final byte[] iv, final byte[] message)
throws GeneralSecurityException {
final Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(DEFAULT_CIPHER_TRANSFORMATION);
IvParameterSpec ivSpec = new IvParameterSpec(iv);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, ivSpec);
byte[] cipherTextBytes = cipher.doFinal(message);
log("[encrypt] cipherTextBytes:" + bytesToHex(cipherTextBytes));
return cipherTextBytes;
}
/**
* Decrypt and decode ciphertext using 256-bit AES with key generated from password
*
* @param password used to generated key
* @param base64EncodedCipherText the encrpyted message encoded with base64
* @return message in Plain text (String UTF-8)
* @throws GeneralSecurityException if there's an issue decrypting
*/
public static String decryptBase64(final String password, byte[] ivBytes, String base64EncodedCipherText)
throws GeneralSecurityException {
try {
final SecretKeySpec key = generateKey(password);
log("[decryptBase64] base64EncodedCipherText:" + base64EncodedCipherText);
byte[] decodedCipherTextBytes = Base64.decode(base64EncodedCipherText, Base64.NO_WRAP);
log("[decryptBase64] decodedCipherText:" + bytesToHex(decodedCipherTextBytes));
byte[] decryptedBytes = decrypt(key, ivBytes, decodedCipherTextBytes);
log("[decryptBase64] ecryptedBytes:" + bytesToHex(decryptedBytes));
String plainText = new String(decryptedBytes, DEFAULT_CHATSET);
log("[decryptBase64] plainText:" + plainText);
return plainText;
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log(e.getMessage());
throw new GeneralSecurityException(e);
}
}
/**
* More flexible AES decryptBase64 that doesn't encode
*
* @param key AES key typically 128, 192 or 256 bit
* @param iv Initiation Vector
* @param decodedCipherText in bytes (assumed it's already been decoded)
* @return Decrypted message cipher text (not encoded)
* @throws GeneralSecurityException if something goes wrong during encryption
*/
public static byte[] decrypt(final SecretKeySpec key, final byte[] iv, final byte[] decodedCipherText)
throws GeneralSecurityException {
final Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(DEFAULT_CIPHER_TRANSFORMATION);
IvParameterSpec ivSpec = new IvParameterSpec(iv);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key, ivSpec);
byte[] decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(decodedCipherText);
log("[decrypt] decryptedBytes:" + bytesToHex(decryptedBytes));
return decryptedBytes;
}
/**
* Converts byte array to hexidecimal useful for logging and fault finding
*/
private static String bytesToHex(byte[] bytes) {
final char[] hexArray = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8',
'9', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'};
char[] hexChars = new char[bytes.length * 2];
int v;
for (int j = 0; j < bytes.length; j++) {
v = bytes[j] & 0xFF;
hexChars[j * 2] = hexArray[v >>> 4];
hexChars[j * 2 + 1] = hexArray[v & 0x0F];
}
return new String(hexChars);
}
private static void log(String msg) {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public class AesTest {
String plaintext = "this is plaintext, hacket 和合法化、;;''(7&……%#%……@";
String key = "134fjk1dafkdajf1134fjk1dafkdajf*";
@Before
public void before() {
System.out.println("加密前明文:" + plaintext);
System.out.println("加密key:" + key);
}
@Test
public void testAesUtil() throws GeneralSecurityException {
byte[] iv = AESUtil.createIV();
String base64EncodedCipherText = AESUtil.encryptToBase64(key, iv, plaintext);
System.out.println("加密后base64密文:" + base64EncodedCipherText);
String plainText = AESUtil.decryptBase64(key, iv, base64EncodedCipherText);
System.out.println("明文:" + plainText);
}
}
结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
加密前明文:this is plaintext, hacket 和合法化、;;''(7&……%#%……@
加密key:134fjk1dafkdajf1134fjk1dafkdajf*
[generateKey] SHA-256 key:98E657E8E0D8D5F305B0E3767C3BB71D6CBB11C1A28A0E1DE515B3923891DF8F
[encryptToBase64] plainText: this is plaintext, hacket 和合法化、;;''(7&……%#%……@
[encrypt] cipherTextBytes:98BA594D95CB89224A7A2265449160C767E7192ABD85712AB990CF765A7DC21AF18D48B3C4894B73E76BDB1D807ED422734193AA6EE18496C1281FD541797C684A104ACA17BEBC5C5CBE657D040603EE
[encryptToBase64] encrypt and Base64.NO_WRAP:mLpZTZXLiSJKeiJlRJFgx2fnGSq9hXEquZDPdlp9whrxjUizxIlLc+dr2x2AftQic0GTqm7hhJbBKB/VQXl8aEoQSsoXvrxcXL5lfQQGA+4=
加密后base64密文:mLpZTZXLiSJKeiJlRJFgx2fnGSq9hXEquZDPdlp9whrxjUizxIlLc+dr2x2AftQic0GTqm7hhJbBKB/VQXl8aEoQSsoXvrxcXL5lfQQGA+4=
[generateKey] SHA-256 key:98E657E8E0D8D5F305B0E3767C3BB71D6CBB11C1A28A0E1DE515B3923891DF8F
[decryptBase64] base64EncodedCipherText:mLpZTZXLiSJKeiJlRJFgx2fnGSq9hXEquZDPdlp9whrxjUizxIlLc+dr2x2AftQic0GTqm7hhJbBKB/VQXl8aEoQSsoXvrxcXL5lfQQGA+4=
[decryptBase64] decodedCipherText:98BA594D95CB89224A7A2265449160C767E7192ABD85712AB990CF765A7DC21AF18D48B3C4894B73E76BDB1D807ED422734193AA6EE18496C1281FD541797C684A104ACA17BEBC5C5CBE657D040603EE
[decrypt] decryptedBytes:7468697320697320706C61696E746578742C206861636B657420E5928CE59088E6B395E58C96E380813B3B2727EFBC883726E280A6E280A6252325E280A6E280A640
[decryptBase64] ecryptedBytes:7468697320697320706C61696E746578742C206861636B657420E5928CE59088E6B395E58C96E380813B3B2727EFBC883726E280A6E280A6252325E280A6E280A640
[decryptBase64] plainText:this is plaintext, hacket 和合法化、;;''(7&……%#%……@
明文:this is plaintext, hacket 和合法化、;;''(7&……%#%……@
糗百 APP AES(推荐 4 星)
策略:
- SecretKey 采用默认的自己管理,需要保证 key 为 128bit、192bit 和 256bit 中的一个
- IV 采用随机生成 16bit
- 加密后的密文 byte 数组和 IV byte 数组合并,IV 在前面然后进行 Base64 编码发送给解密端
- 解密端先进行 Base64 解码,得到 IV byte 数组和密文 byte 数组
- 然后进行解密得到明文
- 不需要自己将 iv 手动告知后端,已经将 iv 封装在了密文中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
public class AESQiubai {
private static final int DEFAULT_IV_BYTES_SIZE = 16;
private static final String DEFAULT_CHATSET = "UTF-8";
private static final String HEX = "0123456789ABCDEF";
//AES 加密
private static final String AES = "Rijndael"; // AES/Rijndael
private static final String DEFAULT_CIPHER_TRANSFORMATION = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
/**
* 糗百App的加密,加密流程:
*
* 1. 随机创建一个IV
*
* 2. 自己生成一个密钥,自己需要保证为128bit、192bit、256bit(可优化,通过KeyGenerator/SHA)
*
* 3. 加密得到密文
*
* 4. 将iv byte数组和密文byte数组合并,iv在前面(前16位是iv,后面的是密文)
*
* 5. 在将这个合并的byte数组Base64传给后端
*
* @param key 加密密钥
* @param plainText 明文
* @return 返回一个经过加密,处理,Base64后的字符串
*/
public static String encrypyQiubai(String key, String plainText) {
try {
log("===============加密前==============");
byte[] encryptIV = createIV();
log("加密前iv bytes:" + toHex(encryptIV));
byte[] encryptToByteArray = encrypt(key, plainText, encryptIV);
log("加密后密文bytes:" + toHex(encryptToByteArray));
byte[] after = new byte[encryptIV.length + encryptToByteArray.length];
System.arraycopy(encryptIV, 0, after, 0, encryptIV.length);
System.arraycopy(encryptToByteArray, 0, after, encryptIV.length, encryptToByteArray.length);
log("加密后iv+密文合并的bytes:" + toHex(after));
String result = Base64.encodeToString(after, Base64.NO_WRAP);
log("加密后base64:" + result);
log("===============加密后==============");
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return plainText;
}
private static byte[] encrypt(String key, String plainText, byte[] iv) throws Exception {
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(DEFAULT_CHATSET), AES);
// SecretKeySpec skeySpec = generateKey(key);
// SecretKeySpec skeySpec = getSecretKeySpec(key);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(DEFAULT_CIPHER_TRANSFORMATION);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, skeySpec, new IvParameterSpec(iv));
byte[] encrypted = cipher.doFinal(plainText.getBytes(DEFAULT_CHATSET));
return encrypted;
}
public static String decryptQiubai(String key, String cipherBase64Text) {
try {
log("===============解密前==============");
byte[] cipherBase64TextDecode = Base64.decode(cipherBase64Text, Base64.NO_WRAP);
log("解密前得到的密文bytes:" + toHex(cipherBase64TextDecode));
// 解析得到iv
byte[] ivBytes = Arrays.copyOfRange(cipherBase64TextDecode, 0, DEFAULT_IV_BYTES_SIZE);
log("解密前得到的iv bytes:" + toHex(ivBytes));
// 得到密文
byte[] cipherDataBytes = Arrays.copyOfRange(cipherBase64TextDecode, DEFAULT_IV_BYTES_SIZE, cipherBase64TextDecode.length);
log("解密前得到的密文bytes:" + toHex(cipherDataBytes));
byte[] plainData = decrypt(key, cipherDataBytes, ivBytes);
String result = new String(plainData, DEFAULT_CHATSET);
log("解密后得到的明文:" + result);
log("===============解密后==============");
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "";
}
private static byte[] decrypt(String key, byte[] ciperText, byte[] iv) throws Exception {
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(DEFAULT_CHATSET), AES);
// SecretKeySpec skeySpec = generateKey(key);
// SecretKeySpec skeySpec = getSecretKeySpec(key);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(DEFAULT_CIPHER_TRANSFORMATION);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, skeySpec, new IvParameterSpec(iv));
byte[] decrypted = cipher.doFinal(ciperText);
return decrypted;
}
private static String toHex(String txt) {
return toHex(txt.getBytes());
}
private static String fromHex(String hex) {
return new String(toByte(hex));
}
private static byte[] toByte(String hexString) {
int len = hexString.length() / 2;
byte[] result = new byte[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
result[i] = Integer.valueOf(hexString.substring(2 * i, 2 * i + 2), 16).byteValue();
return result;
}
public static String toHex(byte[] buf) {
if (buf == null) {
return "";
}
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer(2 * buf.length);
for (int i = 0; i < buf.length; i++) {
appendHex(result, buf[i]);
}
return result.toString();
}
private static void appendHex(StringBuffer sb, byte b) {
sb.append(HEX.charAt((b >> 4) & 0x0f)).append(HEX.charAt(b & 0x0f));
}
private static void log(String msg) {
System.out.println(msg);
}
private static byte[] createIV() {
SecureRandom secureRandom = new SecureRandom();
secureRandom.setSeed(SecureRandom.getSeed(DEFAULT_IV_BYTES_SIZE));
byte[] b = new byte[DEFAULT_IV_BYTES_SIZE];
secureRandom.nextBytes(b);
return b;
}
}
测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public class AesTest {
String plaintext = "this is plaintext, hacket 和合法化、;;''(7&……%#%……@";
String key = "134fjk1dafkdajf1134fjk1dafkdajf*";
@Before
public void before() {
System.out.println("加密前明文:" + plaintext);
System.out.println("加密key:" + key);
}
@Test
public void testAesQbEntrypt() throws Exception {
String cipherBaseText = AESQiubai.encrypyQiubai(key, plaintext);
System.out.println("加密得到Base64后的密文:" + cipherBaseText);
String plainText = AESQiubai.decryptQiubai(key, cipherBaseText);
System.out.println("解密得到明文:" + plainText);
}
}
结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
加密前明文:this is plaintext, hacket 和合法化、;;''(7&……%#%……@
加密key:134fjk1dafkdajf1134fjk1dafkdajf*
===============加密前==============
加密前iv bytes:A79A65EE11EE55B1896FB4D13A0C4BAF
加密后密文bytes:413D77215B7E9DBE3DC457F6EA71D57194104678B37EA64B72BD766C68349CB654C4A07139E4BBB3A566F634BAFEE3E425F4543B1C224F2D38D668C12023C8B10A709231DAAA9289724847037934F5CA
加密后iv+密文合并的bytes:A79A65EE11EE55B1896FB4D13A0C4BAF413D77215B7E9DBE3DC457F6EA71D57194104678B37EA64B72BD766C68349CB654C4A07139E4BBB3A566F634BAFEE3E425F4543B1C224F2D38D668C12023C8B10A709231DAAA9289724847037934F5CA
加密后base64:p5pl7hHuVbGJb7TROgxLr0E9dyFbfp2+PcRX9upx1XGUEEZ4s36mS3K9dmxoNJy2VMSgcTnku7OlZvY0uv7j5CX0VDscIk8tONZowSAjyLEKcJIx2qqSiXJIRwN5NPXK
===============加密后==============
加密得到Base64后的密文:p5pl7hHuVbGJb7TROgxLr0E9dyFbfp2+PcRX9upx1XGUEEZ4s36mS3K9dmxoNJy2VMSgcTnku7OlZvY0uv7j5CX0VDscIk8tONZowSAjyLEKcJIx2qqSiXJIRwN5NPXK
===============解密前==============
解密前得到的密文bytes:A79A65EE11EE55B1896FB4D13A0C4BAF413D77215B7E9DBE3DC457F6EA71D57194104678B37EA64B72BD766C68349CB654C4A07139E4BBB3A566F634BAFEE3E425F4543B1C224F2D38D668C12023C8B10A709231DAAA9289724847037934F5CA
解密前得到的iv bytes:A79A65EE11EE55B1896FB4D13A0C4BAF
解密前得到的密文bytes:413D77215B7E9DBE3DC457F6EA71D57194104678B37EA64B72BD766C68349CB654C4A07139E4BBB3A566F634BAFEE3E425F4543B1C224F2D38D668C12023C8B10A709231DAAA9289724847037934F5CA
解密后得到的明文:this is plaintext, hacket 和合法化、;;''(7&……%#%……@
===============解密后==============
解密得到明文:this is plaintext, hacket 和合法化、;;''(7&……%#%……@
百度国际浏览器 AES
策略:
- SecretKey 采用 SHA-256 来生成 key
- 用的 IV 全部是 0 有安全隐患,为了兼容性?
- 加密后进行了 Base64 编码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
import android.util.Base64;
import android.util.Log;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.security.GeneralSecurityException;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
/**
* Encrypt and decrypt messages using AES 256 bit encryption that are compatible with AESCrypt-ObjC
* and AESCrypt Ruby.
* <p/>
* Created by scottab on 04/10/2014.
*/
public final class AESCrypt {
private static final String TAG = "AESCrypt";
//AESCrypt-ObjC uses CBC and PKCS5Padding
private static final String AES_MODE = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
private static final String CHARSET = "UTF-8";
//AESCrypt-ObjC uses SHA-256 (and so a 256-bit key)
private static final String HASH_ALGORITHM = "SHA-256";
//AESCrypt-ObjC uses blank IV (not the best security, but the aim here is compatibility)-ObjC uses blank IV (not the best security, but the aim here is compatibility)
private static final byte[] ivBytes = {0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00};
//togglable log option (please turn off in live!)
public static boolean DEBUG_LOG_ENABLED = false;
/**
* Generates SHA256 hash of the password which is used as key
*
* @param password used to generated key
* @return SHA256 of the password
*/
private static SecretKeySpec generateKey(final String password) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
final MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance(HASH_ALGORITHM);
byte[] bytes = password.getBytes("UTF-8");
digest.update(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
byte[] key = digest.digest();
log("SHA-256 key ", key);
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key, "AES");
return secretKeySpec;
}
/**
* Encrypt and encode message using 256-bit AES with key generated from password.
*
* @param password used to generated key
* @param message the thing you want to encrypt assumed String UTF-8
* @return Base64 encoded CipherText
* @throws GeneralSecurityException if problems occur during encryption
*/
public static String encrypt(final String password, String message)
throws GeneralSecurityException {
try {
final SecretKeySpec key = generateKey(password);
log("message", message);
byte[] cipherText = encrypt(key, ivBytes, message.getBytes(CHARSET));
//NO_WRAP is important as was getting \n at the end
String encoded = Base64.encodeToString(cipherText, Base64.NO_WRAP);
log("Base64.NO_WRAP", encoded);
return encoded;
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
if (DEBUG_LOG_ENABLED)
Log.e(TAG, "UnsupportedEncodingException ", e);
throw new GeneralSecurityException(e);
}
}
/**
* More flexible AES encrypt that doesn't encode
*
* @param key AES key typically 128, 192 or 256 bit
* @param iv Initiation Vector
* @param message in bytes (assumed it's already been decoded)
* @return Encrypted cipher text (not encoded)
* @throws GeneralSecurityException if something goes wrong during encryption
*/
public static byte[] encrypt(final SecretKeySpec key, final byte[] iv, final byte[] message)
throws GeneralSecurityException {
final Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(AES_MODE);
IvParameterSpec ivSpec = new IvParameterSpec(iv);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, ivSpec);
byte[] cipherText = cipher.doFinal(message);
log("cipherText", cipherText);
return cipherText;
}
/**
* Decrypt and decode ciphertext using 256-bit AES with key generated from password
*
* @param password used to generated key
* @param base64EncodedCipherText the encrpyted message encoded with base64
* @return message in Plain text (String UTF-8)
* @throws GeneralSecurityException if there's an issue decrypting
*/
public static String decrypt(final String password, String base64EncodedCipherText)
throws GeneralSecurityException {
try {
final SecretKeySpec key = generateKey(password);
log("base64EncodedCipherText", base64EncodedCipherText);
byte[] decodedCipherText = Base64.decode(base64EncodedCipherText, Base64.NO_WRAP);
log("decodedCipherText", decodedCipherText);
byte[] decryptedBytes = decrypt(key, ivBytes, decodedCipherText);
log("decryptedBytes", decryptedBytes);
String message = new String(decryptedBytes, CHARSET);
log("message", message);
return message;
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
if (DEBUG_LOG_ENABLED)
Log.e(TAG, "UnsupportedEncodingException ", e);
throw new GeneralSecurityException(e);
}
}
/**
* More flexible AES decrypt that doesn't encode
*
* @param key AES key typically 128, 192 or 256 bit
* @param iv Initiation Vector
* @param decodedCipherText in bytes (assumed it's already been decoded)
* @return Decrypted message cipher text (not encoded)
* @throws GeneralSecurityException if something goes wrong during encryption
*/
public static byte[] decrypt(final SecretKeySpec key, final byte[] iv, final byte[] decodedCipherText)
throws GeneralSecurityException {
final Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(AES_MODE);
IvParameterSpec ivSpec = new IvParameterSpec(iv);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key, ivSpec);
byte[] decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(decodedCipherText);
log("decryptedBytes", decryptedBytes);
return decryptedBytes;
}
private static void log(String what, byte[] bytes) {
if (DEBUG_LOG_ENABLED)
Log.d(TAG, what + "[" + bytes.length + "] [" + bytesToHex(bytes) + "]");
}
private static void log(String what, String value) {
if (DEBUG_LOG_ENABLED)
Log.d(TAG, what + "[" + value.length() + "] [" + value + "]");
}
/**
* Converts byte array to hexidecimal useful for logging and fault finding
*/
private static String bytesToHex(byte[] bytes) {
final char[] hexArray = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8',
'9', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'};
char[] hexChars = new char[bytes.length * 2];
int v;
for (int j = 0; j < bytes.length; j++) {
v = bytes[j] & 0xFF;
hexChars[j * 2] = hexArray[v >>> 4];
hexChars[j * 2 + 1] = hexArray[v & 0x0F];
}
return new String(hexChars);
}
private AESCrypt() {
}
}
非对称加密
非对称加密概念
也称公钥加密算法,对称加密算法带来的困扰:如何安全传递对称加密算法的密钥?
非对称加密由于加/解密钥不同(公钥加密,私钥解密),密钥管理简单,得到了很广泛的应用。RSA 是非对称加密系统最著名的公钥密码算法。但是由于 RSA 算法进行的都是大数计算,使得 RSA 最快的情况也比 AES 慢上倍,这是 RSA 最大的缺陷。但是其安全性较高,这也是大家比较喜欢的地方吧!
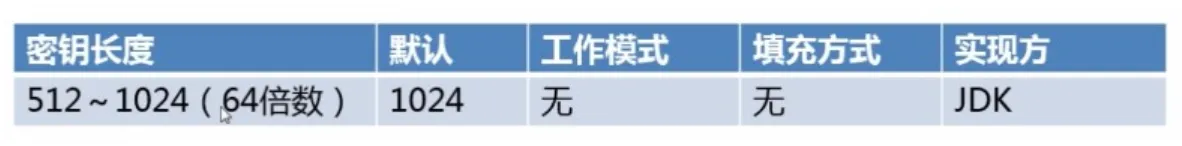
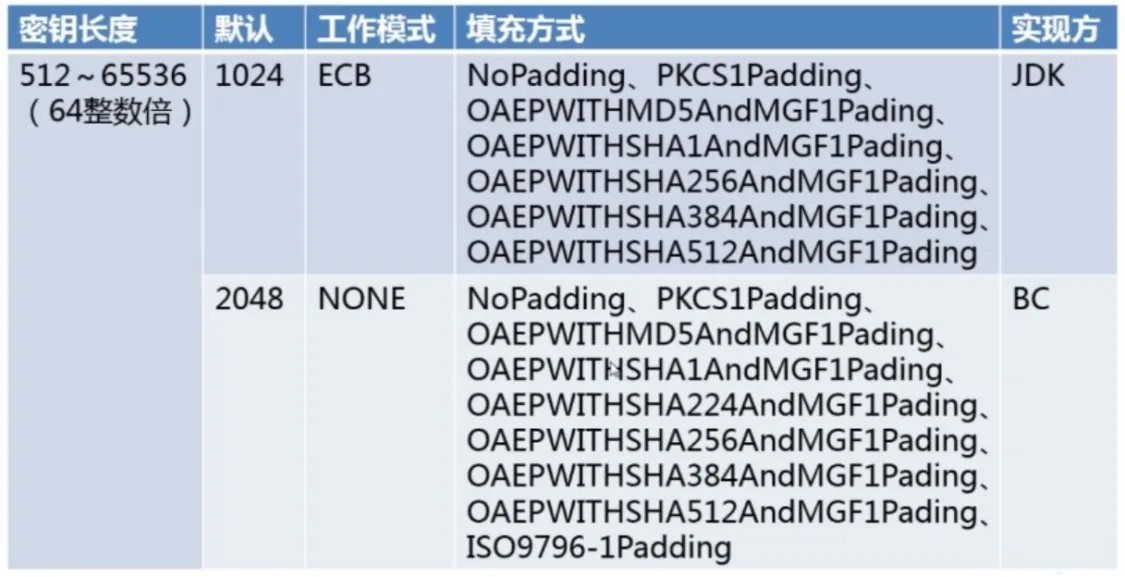
非对称加密分类
- DH(Diffie-Hellman) 密钥交换算法
- RSA 基于因子分解,应用最广
- ELGamal 基于离散对数
- ECC(Elliptical Curve Cryptography) 椭圆曲线加密
DH
非对称加密算法的起源:
RSA
可用于数据加密、数字签名
- 公钥加密,私钥解密
- 私钥加密,公钥解密
ELGamal
只提供公钥加密,私钥解密
Bouncy Castle
RSA 算法
RSA 算法来源
RSA 加密算法是一种非对称加密算法。在公开密钥加密和电子商业中 RSA 被广泛使用。RSA 是 1977 年由罗纳德·李维斯特(Ron Rivest)、阿迪·萨莫尔(Adi Shamir)和伦纳德·阿德曼(Leonard Adleman)一起提出的。当时他们三人都在麻省理工学院工作。RSA 就是他们三人姓氏开头字母拼在一起组成的RSA 加密算法是一种 非对称加密算法。在 公开密钥加密 和 电子商业 中 RSA 被广泛使用。RSA 是 1977 年由 罗纳德·李维斯特(Ron Rivest)、阿迪·萨莫尔(Adi Shamir)和 伦纳德·阿德曼(Leonard Adleman)一起提出的。当时他们三人都在 麻省理工学院 工作。RSA 就是他们三人姓氏开头字母拼在一起组成的
特点
- 相比较与 DES 只有一个密钥。RSA 有两把钥匙,公钥和私钥
- 支持数字签名,可以对传输过来的数据进行校验,确保数据在传输过程中不被修改
RSA 破解的难度
对极大整数做因数分解的难度决定了 RSA 算法的可靠性。
RSA 数论基础
倍数
①一个整数能够被另一个整数整除,这个整数就是另一整数的倍数。如 15 能够被 3 或 5 整除,因此 15 是 3 的倍数,也是 5 的倍数。 ②一个数除以另一数所得的商。如 a÷b=c,就是说,a 是 b 的倍数。例如:A÷B=C,就可以说 A 是 B 的 C 倍。 ③一个数的倍数有无数个,也就是说一个数的倍数的集合为无限集。 注意:不能把一个数单独叫做倍数,只能说谁是谁的倍数。
因素
假如: a*b=c(a、b、c 都是整数),那么我们称 a 和 b 就是 c 的因数。 需要注意的是,唯有被除数,除数,商皆为整数,余数为零时,此关系才成立。反过来说,我们称 c 为 a、b 的倍数。在研究因数和倍数时,不考虑 0。 列举因数:
- 6 的因数有:1 和 6,2 和 3。
- 9 的因数有:1 和 9,3。
- 10 的因数有:1 和 10,2 和 5。
- 15 的因数有:1 和 15,3 和 5。
- 12 的因数有:1 和 12,2 和 6,3 和 4。
- 25 的因数有:1 和 25,5。
- 36 的因数有:1 和 36,2 和 18,3 和 12,4 和 9,6
质数(素数)
质数(prime number)又称素数,有无限个。质数定义为在大于 1 的自然数中,除了 1 和它本身以外不再有其他因数,这样的数称为质数。
互质
在数论中,如果两个或两个以上的整数的最大公约数是 1,则称它们为互质。符号:⊥,又称互素。
- 任意两个质数构成互质关系,如 13 和 61
- 一个数是质数,另一个数只要不是前者的倍数,两者就构成互质关系,比如 3 和 10。另一个数只要不是前者的倍数,两者就构成互质关系,比如 3 和 10。
- 如果两个数之中,较大的那个数是质数,则两者构成互质关系,比如 97 和 57。如果两个数之中,较大的那个数是质数,则两者构成互质关系,比如 97 和 57。
- 1 和任意一个自然数都是互质关系,如 1 和 99
- p 是大于 1 的整数,则 p 和 p-1 构成互质关系,如 57 和 56
- p 是大于 1 的奇数,则 p 和 p-2 构成互质关系,如 17 和 15
欧拉函数
任意给定正整数 n,请问在小于等于 n 的正整数之中,有多少个与 n 构成互质关系?(比如,在 1 到 8 之中,有多少个数与 8 构成互质关系?)任意给定正整数 n,请问在小于等于 n 的正整数之中,有多少个与 n 构成互质关系?(比如,在 1 到 8 之中,有多少个数与 8 构成互质关系?)
计算这个值的方法就叫做欧拉函数计算这个值的方法就叫做 欧拉函数,以φ(n) 表示。在 1 到 8 之中,与 8 形成互质关系的是 1、3、5、7,所以 φ(n) = 4。以φ(n) 表示。在 1 到 8 之中,与 8 形成互质关系的是 1、3、5、7,所以 φ(n) = 4。
φ(n) 的计算方法并不复杂,但是为了得到最后那个公式,需要一步步讨论。φ(n) 的计算方法并不复杂,但是为了得到最后那个公式,需要一步步讨论。
- 第一种情况
如果 n=1,则 φ(1) = 1 。因为 1 与任何数(包括自身)都构成互质关系。 - 第二种情况
如果 n 是质数,则φ(n)=n-1。因为质数与小于它的每一个数,都构成互质关系。比如 5 与 1、2、3、4 都构成互质关系。 - 第三种情况
如果 n 是质数的某一个次方,即 n = p^k (p 为质数,k 为大于等于 1 的整数),比如 φ(8) = φ(2^3) =2^3 - 2^2 = 8 - 4 = 4。- 这是因为只有当一个数不包含质数 p,才可能与 n 互质。而包含质数 p 的数一共有 p(k-1) 个,即 1×p、2×p、3×p、…、p(k-1)×p,把它们去除,剩下的就是与 n 互质的数。
- 上面的式子还可以写成下面的形式:
- 可以看出,上面的第二种情况是 k=1 时的特例。
- 第四种情况
如果 n 可以分解成两个互质的整数之积
1
n = p1 x p2
则:
1
φ(n) = φ(p1p2) = φ(p1)φ(p2)
即积的欧拉函数等于各个因子的欧拉函数之积。比如,φ(56)=φ(8×7)=φ(8)×φ(7)=4×6=24。
RSA 应用
RSA 是目前最有影响力的公钥加密算法
加密:公钥加密、私钥解密,保证内容私密
认证:私钥加密、公钥解密,保证数据完整性,不能保证内容私密
公钥加密
公钥加密指的是客户端用服务端公钥加密,服务器用私钥解密
私钥签名
私钥签名指的 CA 机构的私钥签名
RSA 算法注意
RSA 加密内容过长导致抛异常 javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException: Data must not be longer than 117 bytes
RSA 非对称加密内容长度有限制,1024 位 key 的最多只能加密 127 位数据,否则就会报错 (javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException: Data must not be longer than 117 bytes) , RSA 是常用的非对称加密算法。最近使用时却出现了 “ 不正确的长度 “ 的异常,研究发现是由于待加密的数据超长所致。RSA 算法规定:待加密的字节数不能超过密钥的长度值除以 8 再减去 11(即:KeySize / 8 - 11),而加密后得到密文的字节数,正好是密钥的长度值除以 8(即:KeySize / 8)。
Decryption error
1
2
3
4
5
6
Exception in thread "main" javax.crypto.BadPaddingException: Decryption error
at sun.security.rsa.RSAPadding.unpadV15(RSAPadding.java:380)
at sun.security.rsa.RSAPadding.unpad(RSAPadding.java:291)
at com.sun.crypto.provider.RSACipher.doFinal(RSACipher.java:363)
at com.sun.crypto.provider.RSACipher.engineDoFinal(RSACipher.java:389)
at javax.crypto.Cipher.doFinal(Cipher.java:2165)
对称加密、非对称加密、摘要算法、消息摘要、数字签名、数字证书
1、对称加密
对称加密指的是加密和解密使用相同密钥的加密算法,也称单密钥加密。它的特点是算法公开、计算量少、加密速度快,对于同样大小的传输对象,对称加密效率通常为非对称加密的千倍左右,因此通常被广泛应用于很多加密协议的核心工作(HTTPS 在真正数据通信时就是用的对称加密算法)。对称加密算法的缺点是加解密使用同一把密钥,一旦一方密钥泄露,传输的数据就存在安全风险。
常见的对称加密算法有:
AES、DES、3DES、RC4、IDEA 等
2、非对称加密
非对称加密使用一对公钥和私钥来加密通信数据,也称为双密钥加密。公钥和私钥是成对出现的,通信数据使用公钥加密后,只能通过对应私钥来解密,同样使用私钥加密后也只能通过公钥来解密查看。公钥是对外公开的,外界通信方可以很容易获取到,而私钥是不公开的,只存在于己方。服务器使用私钥加密数据往外传输时,可以被持有公钥的客户端解密查看,但客户端使用公钥加密数据传输给服务端时,数据是严格安全的,只有服务器使用私钥才能解密查看。
非对称密钥数据通信是单向安全的,客户端使用服务端的公钥加密数据传向服务端是严格加密安全的。
非对称加密算法的主要用途:
- 单向传输加密数据
用于交换对称密钥 - 身份验证和数据校验
发送方使用私钥加密明文数据的 hash 值,并将明文、加密后的数据和公钥一起发送给接收方,接收方只需要通过公钥解码密文,然后用与发送方相同 hash 算法获取明文的 hash 值进行比较,一致则说明明文数据没有被篡改;一般用于数字签名
常见的非对称加密算法有:
RSA、DSA、Diffie-Hellman、ECC
3、摘要算法
摘要算法也称哈希算法、散列算法,可以将任意长度的数据转换成一个定长的、不可逆的数字。只要原文不同,计算的结果必然不同。摘要算法用于对比信息源是否一致,因此只要数据源发生变化,得到的摘要信息必然不同,通常用于签名校验。
常见的摘要算法有:
MD5、SHA-1、SHA-2、MAC、CRC 等
4、消息摘要/报文摘要 (MessageDigest)
CA,网站信息和公钥通过 hash 算法生成消息摘要
MessageDigest(报文摘要,简称 MD),单向哈希算法(例如 MD5、SHA 算法等),不可逆,找出具有同一报文摘要的两个不同报文是很困难的。如果报文一旦被修改,那么计算出的摘要就不同,通过这种方法可以检测到报文是否被修改。可以通过报文计算出摘要,但是难以从摘要中推算出原报文。并且任一长度的报文计算出的摘要是固定长度的。
5、数字签名
数字签名是非对称加密算法和摘要算法的一种应用,能否保证信息在传输过程中不被篡改,也能保证数据不能被伪造。使用时,发送方使用摘要算法获得发布内容的摘要,然后使用非对称加密算法的私钥对摘要进行加密(加密后的数据就是数字签名),然后将发布内容、数字签名和公钥一起发送给接收方即可。接收方接收到内容后,首先取出公钥解密数字签名,获得正文的摘要数据,然后使用相同的摘要算法计算摘要,将计算的摘要与解密的摘要进行比对,若一致,说明发布内容没有被篡改。
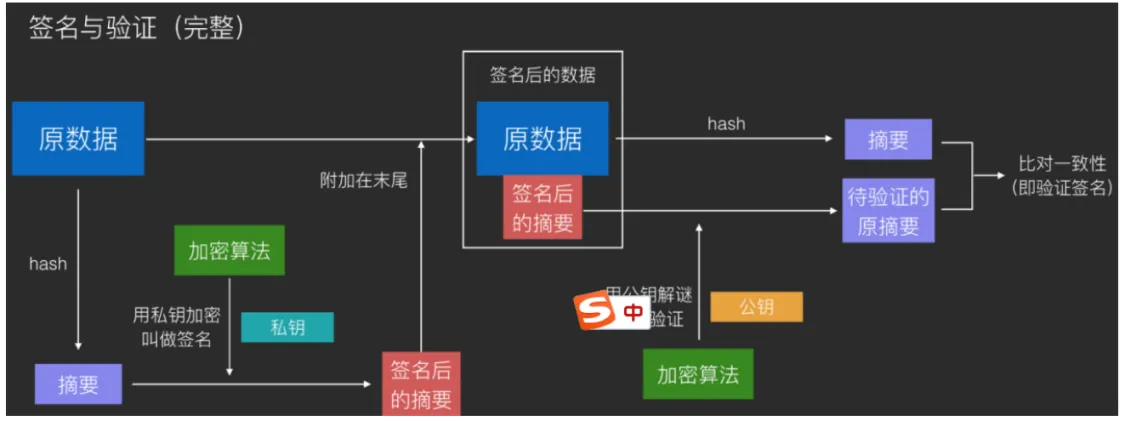
数字签名:消息摘要→RSA 私钥加密
单一的数字签名,存在安全风险,存在中间人攻击。
实际使用中,数字签名常常同数字证书一同出现。
签名:使用私钥加密
验证:使用公钥解密
功能:保证信息传输的完整性、身份认证、防止交易中抵赖发生
6、数字证书
数字证书是由权威的 CA 机构颁发的无法被伪造的证书,用于校验发送方实体身份的认证。
数字证书:数字证书中包含的明文内容 + 数字签名 +RSA 公钥
数字证书的内容:
要发布的明文内容、数字签名、CA 公钥
为什么 CA 制作的证书是无法被伪造的?
CA 制作的数字证书内包含 CA 对证书的数字签名,接收方可以使用 CA 公开的公钥解密数字证书,并使用相同的摘要算法验证当前数字证书是否合法。制作证书需要使用对应 CA 机构的私钥,只要 CA 的私钥不被泄露,CA 颁发的证书是无法被非法伪造的。
数字证书签名的基础就是非对称加密算法和数字签名,HTTPS 中就使用了数字证书来保证握手阶段服务端传输的公钥的可靠性。
认证过程:
- 首先接收方,收到发送方的数字证书、通过 CA 的公钥将数字签名解密得到 hash 签名;
- 然后用相同的摘要算法,计算数字证书中的明文内容,得到一串 hash 签名
- 比对 1 步骤解密出来的 hash 签名和 2 步骤计算出来的 hash 签名
- 如果一致,表示数据没有被篡改,否则可能被篡改
数字证书其实也用到了数字签名技术。只不过要签名的内容是消息发送方的公钥,以及一些其它信息。但与普通数字签名不同的是,数字证书中签名者不是随随便便一个普通的机构,而是要有一定公信力的机构。一般来说,这些有公信力机构的根证书已经在设备出厂前预先安装到了你的设备上了。所以,数字证书可以保证数字证书里的公钥确实是这个证书的所有者的,或者证书可以用来确认对方的身份。
数字证书解决的问题:主要是用来解决公钥的安全发放问题。
数字证书的格式普遍采用的是 X.509V3 国际标准,一个标准的 X.509 数字证书包含以下一些内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
1、证书的版本信息;
2、证书的序列号,每个证书都有一个唯一的证书序列号;
3、证书所使用的签名算法;
4、证书的发行机构名称,命名规则一般采用X.500格式;
5、证书的有效期,通用的证书一般采用UTC时间格式;
6、证书所有人的名称,命名规则一般采用X.500格式;
7、证书所有人的公开密钥;
8、证书发行者对证书的签名。
HTTPS 过程
- 数字证书:
- 签发者
- 证书用途
- 网站的公钥
- 网站的加密算法
- 网站的 HASH 算法
- 证书的到期时间
详情可见 [[HTTPS]]